* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A-level
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
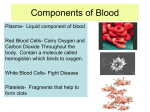
A-level Transport in Mammals The need for a transport system in multicellular organisms As animal grew in size and complexity, specific tissues and organs are developed. The system is needed to transport materials such as food, oxygen to various organ. The waste such as carbon dioxide will be removed. The Composition of Blood Blood - cell particles 45% – plasma 55% Plasma - water 92% – plasma proteins 7% » » » » Fibrinogen Prothrombin Serum Globulins Albumins Cell particles erythrocytes leucocytes platelets Transport functions of blood Oxygen is transported from lungs to tissues Carbon dioxide is transported from tissues to lungs Organic digestive products and mineral salts will be transported to various tissue Excretory products such as urea will be tranported from liver to kidney Hormones such as insulin will be transported from pancreas to liver. Heat is transported from liver and muscle to all parts of the body to keep warm. The role of haemoglobin in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide Haemoglobin is a protein composed of four polypeptide chains, two alpha and two beta Each chain will attached the atoms of iron The centre of the haemoglobin molecule is HAEM which combines reversibly which oxygen to form Oxy-haemoglobin. Oxygen-dissociation curve The % of saturation of blood with oxygen is plotted against the oxygen tension. S-shaped curve Haemoglobin absorbs oxygen rapidly at first and progressively more slowly when the pigment exposed to a gradual increase in oxygen tension. Partial pressure of oxygen in the lungs is usually less than in the atmosphere because air in the lungs includes the residual air from which some oxygen has already been removed. The curve facilitates unloading Small drop in oxygen tension will bring a large comparatively large fall in the % saturation of blood and haemoglobin responds by giving up more oxygen It takes up oxygen in the lungs and releasing it in the tissue. Bohr effect Increasing the carbon dioxide tension has the effect of shifting the oxygen dissoication curve to the right Heamoglobin must exposed to high oxygen tension to become fully saturated Comparison of oxygen dissociation curves for fetal and maternal haemoglobin of humans The curve of fetal haemoglobin is to the left of the mother's because fetus obtain oxygen through the placenta. Thus, it must have a higher affinity for oxygen than themother's haemoglobin Myoglobin The myoglobin molecule is common is skeletal muscle tissues of mammals and is responsible for the colour of 'red muscle' It displays a greater affinity for oxygen and its oxygen dissociation curve is displaced to the left of haemoglobin. It acts as a storage of oxygen in resting muscle They release oxygen when supplies of oxyhaemoglobin have been exhausted such as severe muscular exercies. Carriage of carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide is transported as hydrogencarbonate ions Carbon dioxide combines with water to forem carbonic acid which dissociates into hydrogen and carbonate ions The structure and function of blood vessels Artery – thick walll – more elastic tissue – the diameter of lumen is smaller – no valves – high pressure – carries oxygenated blood except the pulmonary artery Vein – thinner wall – less elastic tissue – the diameter of lumen is larger – valves present – low pressure – carries deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein Capillary – thinest wall – no elastic tissue – the largest diameter of the lumen – no valves – carreis oxygenated and deoxygenated blood – pressure lower than arteries but highter than veins The diagram of the heart The Structure of the heart The heart has 4 chambers (or spaces): Atria - receive blood Ventricles - pump blood away to organs The heart is divided in left and right sides. The right atrium receives blood from the entire body except from lungs. The right ventricle pumps this blood to the lungs The left atrium receives blood from the lungs. The left ventricle pumps the blood to the all the organs in the body. The cardiac rhythm All vertebrate hearts are myogenic which the heart beat is initiated wihtin the heart muscle itself rather than by a nerve impulse form outside. SA (Sinoatrial) Node Called "pacemaker" because it keeps the heartbeat regular. Determine the basic rate of heart beat Found in the upper dorsal wall of the right atrium. Initiates the heartbeat by sending excitation impulse every 0.85 seconds to cause the atria to contract. AV (Atrioventricular) Node Found at the base of the right atrium near the septum. When receives stimulation from SA node, AV node signals ventricles to contract by way of Purkinje fibers. Bundles of His and Purkinje Fibres Receive the signal from the purkinje fibres, ventricles contract simultaneously Blood will be squeezed out towards to the pulmonary arteries and aorta Cardio-vascular Centres Present in the medulla oblongata of the brain Cardio-acceleratory centre is linked by the sympathetic system to the SA node, cardic output can be increased by stimulated this nerves Cardio-inhibitory centre is linked by the parasympathetic fibres within the vagus nerve, to the SA node, AV node and bundle of His. They decrease the cardiac output. Sympathetic nerves have more stimulation -------------> faster heart beat Vagus nerve have more stimulation -------------> slower heart beat Nervous and hormonal control of the heart beat I. Carbon dioxide – 1.Carbon dioxide in blood is high • pH of blood is low • It will stimulates the chemo-receptors in the carotid body and aortic arch • They send nerve impulse along the afferent nerve to the Cardio-acceleratory center • Nerve impulses are sent along the sympathetic nerves to the SA node to increase the rate of heart beat • Increase the rate for delivering carbon dioxide to the lungs for removal 2. Carbon dioxide in blood is low – Fall in carbon dioxide – pH of blood will rise – It will stimulates carotid body to reducing the heart beat through cardio-inhibitory centre. II. Oxygen Oxygen tension in blood is low when the body is active. It will stimulate the chemo-receptors in the carotid bodies. The nerve impulse produced will be transmitted to the cardio-acceleratory centre Heart beat will be increased III. Hormones Thyroxine and adrenalin increase the heart beat Acetylcholine decrease heart beat The diagram of lymph vessel Lymph The tissue fluid drained into lymph capillaries is known as lymph. Lymph system is closely associated with cardiovascular system. Takes up excess tissue fluid and returns it to bloodstream. Absorbs fats in intestinal villi and transports them to bloodstream. Helps defend body against disease by producing lymphocytes and anti-bodies to destroy the bacteria. Lymphatic Vessels Transport One Way Most body regions richly supplied with lymphatic capillaries. Structure of larger lymph vessels similar to veins including presence of valves. Movement of lymph depends upon skeletal muscle contraction, similar to veins. Lymph capillaries take up unabsorbed tissue fluid. Once within lymph vessels, fluid is termed lymph. Lymphatic capillaries join to form two ducts: Right lymphatic duct serves right arm, right side of head and neck, and right thoracic area. Larger thoracic duct serves left arm and thoracic area, abdomen and lower body. Both ducts drain into the subclavian veins in the thorax.