* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hap11 - WordPress.com
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
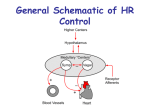
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
The Vascular System Lecture 11 1 Regulation of Stroke Volume SV = end diastolic volume (EDV) minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction 2 Factors Affecting Stroke Volume Preload – amount ventricles are stretched by contained blood Contractility – cardiac cell contractile force due to factors other than EDV Afterload – back pressure exerted by blood in the large arteries leaving the heart 3 Frank-Starling Law of the Heart Preload, or degree of stretch, of cardiac muscle cells before they contract is the critical factor controlling stroke volume Slow heartbeat and exercise increase venous return to the heart, increasing SV Blood loss and extremely rapid heartbeat decrease SV 4 Extrinsic Factors Influencing Stroke Volume Contractility is the increase in contractile strength, independent of stretch and EDV Increase in contractility comes from: Increased sympathetic stimuli Certain hormones Ca2+ and some drugs 5 Extrinsic Factors Influencing Stroke Volume Agents/factors that decrease contractility include: Acidosis Increased extracellular K+ Calcium channel blockers Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 6 Contractility and Norepinephrine Sympathetic stimulation releases norepinephrine and initiates a cyclic AMP secondmessenger system 7 Figure 18.22 Regulation of Heart Rate Positive chronotropic factors increase heart rate Caffeine Negative chronotropic factors decrease heart rate Sedatives Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 8 Regulation of Heart Rate: Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic nervous system (SNS) stimulation is activated by stress, anxiety, excitement, or exercise Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) stimulation is mediated by acetylcholine and opposes the SNS PNS dominates the autonomic stimulation, slowing heart rate and causing vagal tone If the Vagus Nerve was cut, the heart would lose its tone. Thus, increasing the heart rate by 25 beats per minute. 9 Atrial (Bainbridge) Reflex Atrial (Bainbridge) reflex – a sympathetic reflex initiated by increased blood in the atria Causes stimulation of the SA node Stimulates baroreceptors in the atria, causing increased SNS stimulation 10 Chemical Regulation of the Heart The hormones epinephrine and thyroxine increase heart rate Intra- and extracellular ion concentrations must be maintained for normal heart function 11 Factors Involved in Regulation of Cardiac Output Figure 18.23 12 Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Congestive heart failure (CHF) is caused by: Coronary atherosclerosis Persistent high blood pressure Multiple myocardial infarcts Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) – main pumping chambers of the heart are dilated and contract poorly 13 Developmental Aspects of the Heart Figure 18.24 14 Developmental Aspects of the Heart Fetal heart structures that bypass pulmonary circulation Foramen ovale connects the two atria Ductus arteriosus connects pulmonary trunk and the aorta 15 Examples of Congenital Heart Defects Figure 18.25 16 Age-Related Changes Affecting the Heart Sclerosis and thickening of valve flaps Decline in cardiac reserve Fibrosis of cardiac muscle Atherosclerosis 17 Congestive Heart Failure Causes of CHF coronary artery disease, hypertension, MI, valve disorders, congenital defects Left side heart failure less effective pump so more blood remains in ventricle heart is overstretched & even more blood remains blood backs up into lungs as pulmonary edema suffocation & lack of oxygen to the tissues Right side failure fluid builds up in tissues as peripheral edema Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 18 Coronary Artery Disease Heart muscle receiving insufficient blood supply narrowing of vessels--atherosclerosis, artery spasm or clot atherosclerosis--smooth muscle & fatty deposits in walls of arteries Treatment drugs, bypass graft, angioplasty, stent 19 Clinical Problems MI = myocardial infarction death of area of heart muscle from lack of O2 replaced with scar tissue results depend on size & location of damage Blood clot use clot dissolving drugs streptokinase & heparin balloon angioplasty Angina pectoris heart pain from ischemia (lack of blood flow and oxygen ) of cardiac muscle 20 By-pass Graft 21 Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 22 Arteries and Veins Anotomy Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 23 Exchange b/w blood of capillary and tissue fluid 24 Systemic circulation 25 Systemic veins 26 Head and Neck veins and arteries 27 Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 28 29 30 31 32 Fetal Circulation 33 Hormones that affect blood pressure Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 34 The Renin-Angiotensin mechanism 35 Nervous mechanism that regulate blood pressure Chapter 18, Cardiovascular System 36