* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
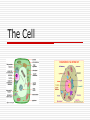
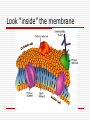
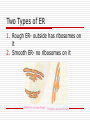
The Cell Cell Theory All things are made up of at least one cell Cells carry on life processes (RENT…) Come from “old” cells Exceptions? Where did the 1st one come from? Viruses aren’t cells Cells fall into 2 categories 1. Prokaryotic- NO membranes around organelles (nucleus, ect.) ex. Bacteria 2. Eukaryotic- have membranes ex. Animals, plants Cell Structures Organelle- a structure inside of a cell that is specialized to do a certain job Organelles include: 1.Cell wall Found in plants only Made of cellulose (poly) Gives plants shape and structure 2. Cell Membrane (plasma) Separates cell parts from the outside environment Controls what enters and exits (Selectively Permeable) Maintains homeostasis Look “inside” the membrane 3. Nucleus Control center of the cell Surrounded by own membrane Contains genetic information (DNA) 4. Cytoplasm Watery material inside of the cell Chemical reactions take place here 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum(ER) Channels that connect different parts inside of the cell Transport things Two Types of ER 1. Rough ER- outside has ribosomes on it 2. Smooth ER- no ribosomes on it 6. Ribosome Proteins are made here Found in two places 1. cytoplasm 2. rough ER 7. Golgi Body Process, package, and store materials Looks like stack of pancakes 8. Lysosome Produce digestive enzymes Break down food (intracellular) 9. Vacuole Digestion takes place Combines “fuses” with lysosomes Sometimes pumps out extra water (contractile) 11. Centrioles Only found in animal cells 2 pair- 90 degree angles Help cell divide 12.Mitochondria Power house Site of cellular respiration (energy) Contains folds called cristae Lots of mitochondria= lots of energy 13. Chloroplast Contain chlorophyll (green pigment) Site of photosynthesis Cell Boundaries Cell Membrane Made of lipid bilayer(2) with proteins and carbs stuck in it Sometimes called a fluid mosaic model (moves like water) Large proteins pump things through membrane Pass Through Membrane Diffusion Things move from high to low concentration Stops when things equal out (equilibrium) Does not need energy Osmosis Special type of diffusion with water Effects of Osmosis 1. Isotonic- same inside and out (equilibrium) 2. Hypertonic- more water inside than out (less solute inside) 3. Hypotonic- less water inside than out (more solute inside) Active Transport Things move from low to high (opposite of diffusion) REQUIRES energy Organization of Life (organelles) Cells tissues organs systems organism PRACTICE FINDING THE CELL PARTS A Typical Animal Cell