* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces and Motion PP
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
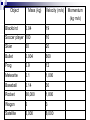
Forces and Motion Describing Motion An object is in motion when its distance from a reference point is changing Variables involved? Speed and Velocity Speed = distance ÷ time Average speed = total distance total time Velocity is speed in a certain direction Graphing Speed Acceleration The rate at which velocity changes Increasing speed Decreasing speed Changing direction Acceleration = Change in velocity Change in time Explaining Motion – Newton’s Laws Galileo → Isaac Newton Force A push or pull; ex. Tug of War A transfer of energy Net Force = the sum of all forces on an object Vector diagram – magnitude and direction 1 Newton = the force required to accelerate a 1 kg mass at 1 m/sec2 Newton’s First Law (aka The Law of Inertia) An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force – resistance to change; an object’s tendency to keep doing what it’s doing What does mass have to do with inertia? Inertia Types of Forces Types of Forces Friction Force that occurs when the surfaces of matter move past each other Always opposes motion Produces heat Amount of friction depends on……. Amount of force pushing objects together How rough/smooth the surfaces are Friction Forces Sliding Rolling Fluid Static Friction: Helpful or Harmful? Ways to increase friction Ways to decrease friction Friction animation Gravity or The Law of Universal Gravitation Force of attraction between objects Affected by the mass of the objects and the distance between them Weight = measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object Falling objects ? Terminal velocity Freefall Orbit Projectile Motion Newton’s 2nd Law The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied How is acceleration changed by force? How is acceleration changed by mass? Force = Mass X Acceleration Newton = kg x m/sec2 What is the net force on a 1000 kg elevator accelerating at 2m/sec2? What is the net force required to accelerate a 55 kg shopping cart at 15 m/sec2? Newton’s 3rd Law aka The Action/Reaction Law For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of equal strength in the opposite direction All forces act in pairs The forces are applied to two different objects Momentum A measure of an object’s “inertia of motion” Momentum = Mass x velocity kg·m/sec Law of Conservation of Momentum: the total momentum of objects that interact does not change, unless acted on by an outside force (eg. Friction) Collision Animations Object Blackbird Mass (kg) Velocity (m/s) 0.04 19 Soccer player 100 10 Skier 60 20 Bullet 0.004 600 Frog 0.9 12 Meteorite 0.1 1,000 Baseball 0.14 30 Rocket 36,000 1,800 Wagon 2 3 Satellite 3,000 8,000 Momentum (kg·m/s)