* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sound Transduction 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
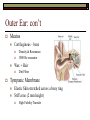
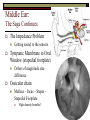
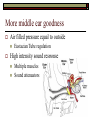
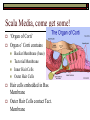
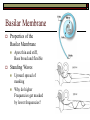
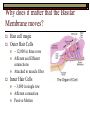
Sound Transduction 1 Or, if the a tree falls in a forest and no one is around does it still reflect light? What is Resonance? Resonance Characteristic frequency response Density & Tuning Sharpness Hi dense = Lo Sharpness Size/Cavity Breaking Glass Demo The Outer Ear: All about resonance Pinna Flange ~1 – 7000 Hz resonance Why such high frequencies? ~3 - 4000 Hz resonance Concha Immobile cartilage side of head Thoughts? Directionality Finger in folds demo Spectral Filter (e.g., Rayker et al., 2004) Resonance Frequencies ~1000 – 7000 Hz Notch Filter ~ 700, 3500, 7000, 14000 Hz Outer Ear: con’t Meatus Cartilaginous – bone Wax + Hair Density & Resonance 3000 Hz resonator Dirt Filter Tympanic Membrane Elastic Skin stretched across a bony ring Stiff cone (2 mm height) High Fidelity Transfer Middle Ear: The Saga Continues The Impedance Problem Tympanic Membrane to Oval Window (stapedial footplate) Getting sound to the sensors Orders of magnitude size difference Ossicular chain Malleus – Incus – Stapes – Stapedial Footplate High density benefits! More middle ear goodness Air filled pressure equal to outside Eustacian Tube regulation High intensity sound response Multiple muscles Sound attenuators Quick Interruption! TLA 1: Hearing Under Water (HUW) Why is this important? Ingredients: Stick your ear, or a friend’s ear under water Make sound in air and under water and listen with: Sound source (Clicker?) Still water (bath, sink, pool) Out of water ear Under water ear Questions: Which produces the loudest sound? Is it difficult to determine directionality? Into the Inner Ear Major subdivisions of the Bony Labyrinth Vestibular & Auditory Auditory-side = Cochlea Cochlea Cavity within bone, Fluid-filled caverns Curls like a snail Life in the Cochlea Three major subdivisions Scala Vestibuli: Largest cavity, filled with perilymph (e.g., Ricci & Fettiplace, 1998) Scala Media: Smallest cavity, filled with endolymph (e.g., Ricci & Fettiplace, 1998) Positively charged Sodium Ions (Na+) More positively charged Potassium & Calcium Ions (K+, Ca++) Where the action is!!! Scala Tympani: Mid size cavity, filled with perilymph Connected to Scala Vestibuli Scala Media, come get some! ‘Organ of Corti’ Organ o’ Corti contains Basilar Membrane (base) Tectorial Membrane Inner Hair Cells Outer Hair Cells Hair cells embedded in Bas. Membrane Outer Hair Cells contact Tect. Membrane Basilar Membrane Properties of the Basilar Membrane Apex thin and stiff, Base broad and flexible Standing Waves Upward spread of masking Why do higher Frequencies get masked by lower frequencies? Why does it matter that the Basilar Membrane moves? Hair cell magic Outer Hair Cells ~ 12,000 in three rows Afferent and Efferent connections Attached to muscle fiber Inner Hair Cells ~ 3,000 in single row Afferent connection Passive Motion Actual Transduction! Wave along Basilar Membrane Causes inner hair cell shearing Shearing opens channel Endolymph in Scala Media attracts perilymph in Scala Tympani Charges up Hair cell to cause neural firing What are the outer hair cells doing? Outer Hair cells motile & embedded in Tectorial Membrane Theory 1. Stiffen to attenuate sound along the basilar membrane, shear to add energy to the basilar membrane Theory 2. Stiffen to raise the Tectorial membrane away from the inner hair cells, shear to lower the Tectorial membrane and obstruct the inner hair cells The big picture Outer/Middle ear filter and intensify sound Inner ear detects sound Inner Hair Cell movement along the basilar membrane Converts Mechanical energy to Electrical energy (nerve impulse) Outer hair cells help modulate movement along the basilar membrane Questions?