* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 02 Hypothyroidism
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
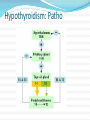
Nursing 870 Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism is a common endocrine disorder resulting from deficiency of thyroid hormone Usually a primary process, thyroid gland is unable to produce sufficient amounts of thyroid hormone Can be secondary, the thyroid gland is normal, but it receives insufficient stimulation because of low secretion of thyrotropin (ie, thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH]) from the pituitary gland May be iatrogenic, drug induced May be congenital Hypothyroidism: Causes Lack of iodine: most common in the world Autoimmune: most common in the US Hashimoto’s thyroiditis Thyroid Screening No universal recommendation The American Thyroid Association Screening at age 35 years and every 5 years More frequent if at high risk Pregnant women Women older than 60 years Patients with type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune disease Patients with a history of neck irradiation Thyroid Screening The American College: screening women older than 50, with 1 or more clinical features of disease The American Academy of Family Physicians: screening asymptomatic patients older than 60 years The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists: recommends TSH measurements in all women of childbearing age before pregnancy or during the first trimester The US Preventive Task Force concludes that the evidence is insufficient to recommend for or against routine screening for thyroid disease in adults PollEv: A TSH of 40 is consistent with Hyper Or Hypo – thyroidism? Hypothyroidism: Patho Hypothyroidism: Patho Early in the disease process, compensatory mechanisms maintain T3 levels Decreased production of T4 causes an increase in the secretion of TSH by the pituitary gland TSH stimulates hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the thyroid gland and 5’-deiodinase activity, thereby increasing T3 production. Hypothyroidism: Patho CV Decreased contractility Cardiac enlargement Pericardial effusion Decreased pulse, Decreased cardiac output GI tract changes Achlorhydria Prolonged intestinal transit time Gastric stasis GYN Delayed puberty Anovulation Menstrual irregularities, Infertility are common. TSH screening should be a routine part of any investigation into menstrual irregularities or infertility. Hypothyroidism: Patho Can cause Increased levels of total cholesterol Increased LDL Decreased HDL because of a change in metabolic clearance. In addition Increase in insulin resistance. Hypothyroidism: Etiology Primary hypothyroidism Chronic lymphocytic (autoimmune) thyroiditis Postpartum thyroiditis Subacute (granulomatous) thyroiditis Drug-induced hypothyroidism Iatrogenic hypothyroidism Genetic Iodine deficiency or excess Hypothyroidism: Etiology Central hypothyroidism (secondary or tertiary) Results when the hypothalamic-pituitary axis is damaged Pituitary adenoma Tumors impinging on the hypothalamus Lymphocytic hypophysitis Sheehan syndrome History of brain or pituitary irradiation Drugs (eg, dopamine, prednisone, or opioids) Congenital nongoiterous hypothyroidism type 4 TRH resistance TRH deficiency Hypothyroidism: Epidemiology The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 1999-2002) of 4392 individuals reflecting the US population reported hypothyroidism (defined as TSH levels exceeding 4.5 mIU/L) in 3.7% of the population The WHO data from 130 countries found inadequate iodine nutrition in 30.6% of the population. Hypothyroidism: Epidemiology Age Frequency of hypothyroidism, goiters, and thyroid nodules increases with age Most prevalent in elderly populations, with 2-20% of older age groups having some form of hypothyroidism The Framingham study found hypothyroidism (TSH > 10 mIU/L) in 5.9% of women and 2.4% of men older than 60 years Hypothyroidism: Epidemiology Gender More common in females (2-8 times higher) Race Higher in whites (5.1%) and Mexican Americans than in African Americans (1.7%) African Americans tend to have lower median TSH values. PollEv: Name a symptom of hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism: Symptoms Fatigue, loss of energy, lethargy Weight gain Decreased appetite Cold intolerance Dry skin Hair loss Sleepiness Muscle pain, joint pain, weakness in the extremities Depression Emotional lability, mental impairment Forgetfulness, impaired memory, inability to concentrate Constipation Menstrual disturbances, impaired fertility Decreased perspiration Paresthesias, nerve entrapment syndromes Blurred vision Decreased hearing Fullness in the throat, hoarseness Myxedema Coma A severe form of hypothyroidism that results in An altered mental status Hypothermia Bradycardia Hypercarbia Hyponatremia Cardiomegaly, pericardial effusion, cardiogenic shock, and ascites may be present Hypothyroidism: PE Weight gain Slowed speech and movements Dry skin Jaundice Pallor Coarse, brittle, straw-like hair Loss of scalp hair, axillary hair, pubic hair, or a combination Dull facial expression Coarse facial features Periorbital puffiness Macroglossia Goiter (simple or nodular) Hypothyroidism: PE Hoarseness Decreased systolic blood pressure and increased diastolic blood pressure Bradycardia Pericardial effusion Abdominal distention, ascites (uncommon) Hypothermia (only in severe hypothyroid states) Nonpitting edema (myxedema) Pitting edema of lower extremities Hyporeflexia with delayed relaxation, ataxia, or both Hypothyroidism: Differential Anemia Autoimmune thyroid disease Goiter Myxedema Subacute Thyroid lymphoma Iodine deficiency Addison’s disease Anovulation Sleep apnea Hypothyroidism: Differential Cardiac tamponade Chronic fatigue syndrome Constipation Depression Dysmenorrhea Many other considerations related to symptoms Hypothyroidism: Diagnostics TSH Normal accepted as 0.40-4.2 mIU/L Generally the most sensitive screening tool for primary hypothyroidism Less expensive than other tests Rapid turn around time T4 Generally obtained if TSH is above normal More expensive than TSH Takes longer for results Hypothyroidism: Diagnostics Primary hypothyroidism Elevated TSH levels and decreased T4 If elevated TSH levels (usually 4.5-10.0 mIU/L) but normal T4, considered to have mild or subclinical hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism: Diagnostics Assays for anti–thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) and antithyroglobulin (anti-Tg) antibodies May be helpful in determining the etiology of hypothyroidism or in predicting future hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism Overt hypothyroidism Diagnosis when TSH >10 with a subnormal free T4 Subclinical hypothyroidism TSH above normal limit, with a normal free T4 Only if no severe illness and if normal hypothalamic, pituitary axis Hypothyroidism: Diagnostics CBC: may show anemia Electrolytes: may show dilutional hyponatremia Lipid levels may be elevated Creatinine may be elevated (reversible) Liver function and creatinine kinase elevations have been found Hypothyroidism: Diagnostics US: used to detect nodules and infiltrative disease Fine needle aspiration: Procedure of choice for evaluating suspicious nodules 5-15% of solitary nodules are cancerous Hypothyroidism: Treatment Treat any underlying disorder Thyroid replacement (levothyroxine) For most cases of mild to moderate hypothyroidism, a starting levothyroxine dosage of 50-75 µg/day For elderly or if known ischemic heart disease Start at 1/4th to ½ of the expected dosage Adjust in small increments after no less than 4-6 weeks Clinical benefits begin in 3-5 days and level off after 4- 6 weeks After dosage stabilization, monitored q 6 months or annually Hypothyroidism: Treatment If central (ie, pituitary or hypothalamic) hypothyroidism Use T4 levels, not TSH levels to guide treatment In most cases, the free T4 level should be kept in the upper third of the reference range Hypothyroidism: Treatment Monitor the patients clinical status Look for evidence of overtreatment If symptoms continue after normalization of TSH Investigate other possible causes Sub-clinical Hypothyroidism Controversy re treatment Treatment has been shown to reduce total cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, to decrease arterial stiffness and systolic blood pressure. In patients with concomitant subclinical hypothyroidism and iron deficiency anemia, iron supplementation may be ineffective if levothyroxine not given Sub-clinical Hypothyroidism Treat for TSH > 10 mIU/L Treat for TSH 5-10 mIU/L in conjunction with goiter or positive anti-TPO antibodies (Guidelines from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists) References Garber, J., Cobin, R., Gharib, H., Hennessey, J., Klein, I., et al. (2012). Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: Cosponsored by the American Association of Endocrinologist and the American Thyroid Association. Endocrine Practice, 18, 6, 9881028, Available at: https://www.aace.com/files/final-file-hypo-guidelines.pdf