* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell structure and Bioenergetics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
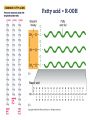
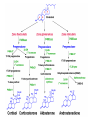
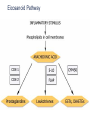
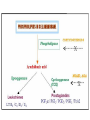
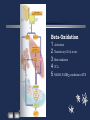
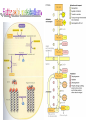
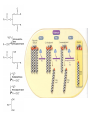
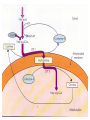
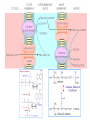
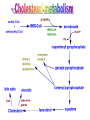
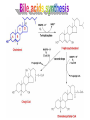
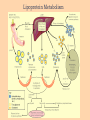
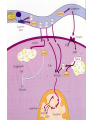
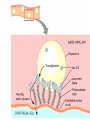
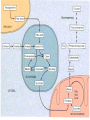
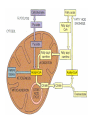
Basic and Metabolism of Lipid Donrawee Leelarungrayub (BSc, PT), (Ph.D. Biochem) Department of Physical Therapy Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Outline 1. Basic structure of Lipid 2. Basic of Lipid Metabolism; Oxidation and Synthesis 3. Regulation of Lipid Metabolism 4. Ketone Metabolism 5. Relationship between Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Kinds and sources of Lipids • Simples lipids; Nester of lipid and alcohol • Fats • Waxes • Complex lipid • Phospholipids: glycerophospholipids, sphingophospholipids • Glycolipids = FA + sphogosine + CHO • Lipoproteins: sulfolipids, aminolipids • Derived lipids; Fatty acids, Steroids, Hydrocarbons Fatty acid and Structure Fatty acid = R-OOH Common Fatty acid in Humans Palmitic acid Stearic acid Palmitoleic acid Olieic acid Linoleic acid Linolenic acid Arachidonic acid C = 16 C = 18 C = 16 C = 18 C = 18 C = 18 C = 20 Short and Long chain of Fatty acid Short chain (2-4 carbons) and medium chain (6-12 carbons) - coconut oil, palm kernel oil = directly absorbed in small intestine, transport to the liver through the portal vein - diffuse freely without carnitine esterification into the mitochondria Long chain ( > 14 carbons) - found in triglycerol (fat) and structural lipids - require the carnitine shuttle to move form cytosol into the mitochondria Unsaturated fatty acid Double bonds in most naturally occurring fatty acid = cis Trans fatty acid = margarine and other hydrogenated vegetable oils = risk factor to atherosclerosis Oxidation of unsaturation fatty acid in membrane lipids = membrane damage => hemolytic anemia (Vit E deficiency) Phospholipid Diacylgycerol with a phosphate group on the third glycerol carbon – Major component of cellular membrane Phospholipase cleave specific bonds in phospholipid – Phospholipase A1 and A2 – Phospholipase C – Phospholipase D Lung surfactant : abundant phhospholipids, phosphatidylcholine = Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), hyaline membrane disease Sphingolipids Derivatives of ceramids, esterification of a fatty acid with amino group of sphingosine Localized mainly in the white matter of the central nervous system Sphingomyelins => nerve cells and blood cells, signal transduction Cerebrosides : galactose or glucose => myelin sheath Gangliosides : oligosaccharide (sialic acid) => myelin sheath Steroids Lipid containing a ring system with a hydroxyl or ketone groups Cholesterol : cellular membrane, modulates membrane fluidity Precursor for synthesis of steroid hormones, skin-derived vitamin D, and bile acids – Cholesterol: 27 Carbons – Bile acids: 24 carbons – Androgens: 19 carbons – Progesterone and adrenocortical steroids ; 21 carbons – Estrogens: 18 carbons Eicosanoids Eicosanoids function as short-range, short-term signaling molecules – Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2 Prostaglandins – Formed by the action of cyclooxygenase on arachidonic acid – Prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) is the precursor for prostandins and thromboxanes Prostaglandins Promote acute inflammations Stimulate or inhibit smooth muscle contraction, depending on type and tissue Promote vasodilation (arterioles) or vasocontriction (cerebral vessels) Pain in acute inflammation Production of fever Eicosanoid Pathway Thromboxane A2 (TXA2) Produced in platelets by the action of thromboxane synthase on PGH2 Strongly promotes arteriole contraction and platelet aggregation Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSIAD) acetylate and inhibit cyclooxygenase, leading to reduced synthesis of prostaglandins Triglycerides - neutral fat - glycerol + 3 ROOH 1. Highly concentrated energy reserve 2. Formed by esterification of fatty acids with glycerol 3. Excess fatty acids in diet and fatty acids synthezied and stored in adipose cellls Beta-Oxidation 1. Activation 2. Transfer acyl CoA to mt. 3. Beta-oxidation 4. TCA 5. NADH, FADH2 oxidation in ETS Beta-Oxidation 1. Glucose ------- Acetyl CoA GLUT4 2. Regulation Short term regulation – ACC , Glucogon Long term regulation – Insulin + ACC -- Hormone sentitive lipase (HSL) -- Carnitine acyltransferase I (CPTI) Lipoprotein Metabolism Ketone bodies Metabolism Ketone synthesis --- liver mitochondria Blood - ketone bodies Ketone body utilization – muscle kidney and brain TCA Metabolic regulation; lipolysis and lypogenesis Fed state: lipoprotein lipase Fasting state; cAMP --- FA and glycerol Exercise; adrenaline --- cAMP Sources; – – – – – acetyl CoA malonyl CoA NADPH PPP Malate -- pyruvate