* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Urinary System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
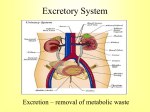
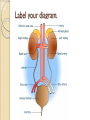
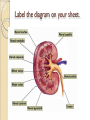
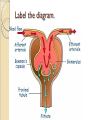
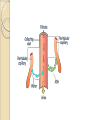
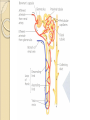
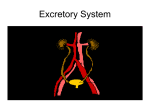
Urinary System Urinary System Functions • • • • • Remove salts and nitrogenous waste Maintain water and electrolyte concentration Regulate pH and volume of fluids Help control RBC production by secreting erythropoieten Made of – Kidneys-filtering units – Ureters-transport urine from kidney to bladder – Bladder-holds urine – Urethra-gets it out of the body Label your diagram. Kidney Function Remove metabolic waste from blood, dilute it with water and electrolytes to form urine Secrete erythropoeiten-control RBC production Activation of vitamin D Maintain blood volume and pressure Retroperitoneally located-behind parietal peritoneum; left slightly higher than right Kidney Structure Renal sinus-hollow chamber in the kidney Renal pelvis-funnel shaped sac ◦ Divided into major and minor calyces Small renal papillae project into minor calyces 2 major portions of the kidney ◦ Medulla-houses tubes leading to papillae ◦ Cortex-has functional unit of kidneys called nephrons Label the diagram on your sheet. Renal blood flow Renal arteries branch off the abdominal aorta ◦ These branch into smaller arterioles Afferent arteriole-leads to the nephron Renal vein leaves the kidney and attaches to the inferior vena cava Nephron-1 million nephrons per kidney • 2 parts – Renal corpuscle-filtering portion of the kidney • Glomerulus-ball of capillaries – Blood is filtered here – Capillaries have tiny openings called fenestrae to increase permeability • Glomerulus capsule (Bowman’s capsule) -surrounds the glomerulus – Receives the fluid the glomerulus filters – Renal tubule-tube that leaves the glomerulus capsule Label the diagram. Nephron blood supply • • • Afferent arterioles-lead into the capillaries of the glomerulus Efferent arterioles (smaller)-blood flows into these after filtration in the glomerulus Peritubular capillaries-efferent arterioles branch into these – Surround the renal tubule – Reabsorption and secretion here • Blood enters the venous system Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Cells that come in contact with the glomerulus • 3 parts • – Juxtaglomerular cells-smooth muscle cells • Contain renin (discuss later) – Tubule – Macula densa-densely packed epithelial cells • Come in contract with afferent and efferent arterioles – Help to determine blood pressure • Caused by stretch of cells in this area • http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/AP2204/AP2204.swf










![Urinary System_student handout[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008293858_1-b77b303d5bfb3ec35a6e80f57f440bef-150x150.png)