* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the endosymbiotic theory?
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
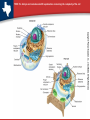
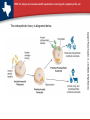
TEKS 7G: Analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. Endosymbiotic Theory Notes TEKS 7G: Analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. Is the living cell simple or complex? • Cells vary in complexity. • Most eukaryotic cells are highly specialized and contain an intricate array of organelles and internal compartments. • Many prokaryotic cells lack internal membranes and organelles except for ribosomes. • However, even prokaryotic cells are complex in their own way. TEKS 7G: Analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. plant and animal cells contain a variety of organelles. Some structures are specific to either plant cells or animal cells only. TEKS 7G: Analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. How did cellular complexity come about? • The fossil record provides few clues about the history of life at the cellular level. • Microscopic fossils generally lack internal detail of cellular structure. • However, careful studies of living cells have helped to answer questions about the origins of cellular complexity. TEKS 7G: Analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. What is the endosymbiotic theory? • The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells formed from symbiotic relationships among prokaryotes. • The theory proposes that mitochondria evolved from free-living aerobic bacteria that began to live inside anaerobic prokaryotes. • Chloroplasts evolved from free-living photosynthetic bacteria paired with the earliest (contd.) eukaryotes. TEKS 7G: Analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. The endosymbiotic theory is diagramed below. TEKS 7G: Analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. What evidence supports the endosymbiotic theory? • Mitochondria and chloroplasts are similar in size to bacteria, have their own genomes, contain ribosomes similar to those of prokaryotes, and are formed by division of preexisting mitochondria and chloroplasts. • The membrane systems of chloroplasts resemble those of photosynthetic prokaryotes. • Some cells today contain endosymbiotic bacteria and algae. TEKS 7G: Analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. Do we fully understand the cell? • No, but evidence suggests that complex cellular structures and pathways were produced by the process of evolution. • However, there are many uncertainties in our current understanding of cellular complexity.