* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What You Need to Know To Administer an Injection
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Anthrax vaccine adsorbed wikipedia , lookup
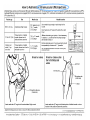
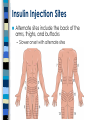
Injection Administration Techniques Rachel Nowak, PharmD Clinical Instructor, UWSOP Bartell Drugs Clinical Coordinator January 29, 2010 Objectives Describe proper techniques for administering injectable drugs Describe precautions to take when administering injectable products Appreciate pharmacist role in administering injectable medications Vaccines 101 Immunity Passive Immunity – Antibody produced by one human or other animal is transferred to another – Temporary protection • Example: Immunity an infant receives from its mother Active Immunity – Immune system is stimulated to produce cellular and humoral immunity – Lasting protection • Example: Survive infection from the disease causing organism Basic MOA of Vaccines Vaccinations produce active immunity. Immune response and immunologic memory produced is similar to that caused by natural infection. Comes without the risks of the actual disease and associated complications. Classifications of Vaccines Live attenuated – Attenuated or weakened form of diseasecausing bacterium or virus – Must replicate to be effective • Uncontrolled replication of the vaccine virus can cause severe reactions - only occurs in patients with immunodeficiency – Immune response is cellular & humoral – Circulating antibodies interfere – Usually produce immunity after one dose Classifications of Vaccines Inactivated – Inactivated form of bacterium or virus – Can’t replicate • Can’t cause disease, even in immunodeficient patients – Immune response primarily humoral – Less affected by circulating antibody than live vaccines – Always requires more than one dose – Antibody titer decline over time Immunization Procedures Screening Standard Questions – Do you have any drug/food allergies? – Do you have any chronic diseases? – What medications do you take? Basic Vaccine Screening Questions Are you sick today? Are you allergic to latex? Do you have any allergies to any vaccine or vaccine components? – Ex: Eggs, gelatin Have you ever had a serious reaction after receiving a vaccine? Have you had Guillian-Barre Syndrome in the past? Is it possible that you could be pregnant? Breastfeeding? Additional Vaccine Screening Questions Do you have cancer, leukemia, AIDs, or any other immune system problem? Do you take cortisone, prednisone, other steroids, anticancer drugs, or have you had radiation treatments? In the past year, have you received a transfusion of blood or blood products or been given immune globulin or an antiviral medication? Have you received any vaccinations in the past 4 weeks? Consent Answer any questions patient may have Patient needs to understand benefits and risks of getting immunized and consent to vaccine administration. – If it is a child under 18, then parent or guardian consent should be obtained Vaccine Information Statements (VIS) Patient education sheets developed by the CDC – Helps to explain the risks and benefits of receiving a particular vaccine Federal law requires that VISs be used for most vaccines when vaccinating patients – Should be given before vaccine administered Parts of a Syringe Preparing Syringe Choose correct SYRINGE size – If <0.5ml need low-dose syringe (1mL, 3mL) – Finely graduated syringe will ensure accurate amount – Fluzone (influenza) is 0.5mL dose – Pneumovax (pneumonia) is 0.5mL dose Maximum volumes – Deltoid – No more than 0.5-1mL – Large muscle (gluteus medius) • Adult – no more than 4mL • Child – no more than 1-2mL Needle Lengths and Gauges Preparing Needle Choose correct needle LENGTH and GAUGE Minimize tissue injury and SQ leakage Allow easy passage (23 vs. 25 gauge) Needle length depends on injection site – Adults 5/8” vs. 1” vs. 1.5” – Children 5/8” vs. 1” – If less SQ fat, use smaller needle Get Organized Get all supplies ready in advance – ex: Band-Aid, alcohol pad, cotton ball, VIS Double Check – Correct vaccine, dose, & expiration date – Go over screening/consent form with patient Record – Vaccine name, manufacturer, lot number, expiration date – Location of administration (L/R deltoid) – Provider administering the vaccine – Vaccine Information Sheet publication date Administer the Vaccine Cleanse area with alcohol swab – Allow alcohol to dry Target – C technique and shoot (IM) – Bunch skin (SQ) Inject – DO NOT Aspirate – Dart-like motion with steady pressure – Inject at: • 90° angle for IM • 45° angle for SQ Final Steps Do not recap needle Dispose of needle properly Apply pressure to injection site with cotton ball (if necessary) Apply adhesive bandage Provide patient with immunization record & Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) Record all necessary information Have patient remain under surveillance for ~15 minutes Routes of Administration Intramuscular (IM) Injections Subcutaneous (SQ) Injections Self-Injection Teaching: Insulin Advise patients to wash hands Have patient confirm type of insulin on bottle label Roll vial or pen in palms, if appropriate Show patients in counseling where to read dose on syringe and appropriate amount to draw – Ensure using best syringe for dose Inject at 90° angle for SQ insulin Injecting into the subcutaneous fat of the belly most common – Site should be approximately 2 inches from belly button Rotate sites – avoid formation of fatty deposits or scarring Insulin Injection Sites Alternate sites include the back of the arms, thighs, and buttocks – Slower onset with alternate sites Self-Injection Teaching: Insulin Go over insulin storage – Generally insulin not in use should not be stored in fridge – Extreme temperatures and excess agitation should be avoided Discard dates – Important to go over how long insulin can be stored at room temperature Insulin inspection Mixing of Insulins Proper disposal of sharps Self-Injection Teaching Pen devices/ insulin cartridges: – Deliver insulin subcutaneously through a needle. – All a little different and might require extra teaching time – In specific patient populations these devices have been demonstrated to improve: • accuracy of administration • adherence – Requires needle to be left embedded in skin for at least 5 seconds after plunger depressed Managing Adverse Reactions Vasovagal Syncope (Fainting) Be aware of patient behavior Have patient sit before administration Lay patient down if necessary Check airway, breathing and vital signs Anaphylaxis Rare but potentially fatal Occurs within 15 minutes Call 911 Lay patient down, check airway, breathing, vital signs Be prepared and ready to administer epinephrine (Epipen) Delayed Adverse Reactions Child – fever, fussy, crying, injection site Adult – injection site discomfort Symptomatic relief – Fluids – Pain medications • No aspirin for children • Acetaminophen (Tylenol) • Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) Reporting Adverse Reactions Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) Required for: - Rare, serious or unexpected events Emergency Plan and Training Access to Emergency Medical Services (EMS) – phone on hand Be prepared for adverse reactions – CPR trained staff – Necessary medications on hand – Have patient remain under surveillance after administration Universal Precautions Controlling Infection Transmission Be Prepared Control infection transmission – Use universal precautions – Proper cleaning and disposal of waste Anticipate adverse effects Assure patient safety – Know your equipment – Establish quality procedures – Practice good technique Protect Yourself: Use Universal Precautions Infection control guidelines designed to protect workers from exposure to diseases spread by blood and certain body fluids Assume all patients to be infectious for blood-borne diseases Universal Precautions Apply To: Blood semen vaginal secretions synovial fluid cerebrospinal fluid pleural fluid peritoneal fluid pericardial fluid amniotic fluid Universal precautions should be applied to all body fluids when it is difficult to identify the specific body fluid or when body fluids are visibly contaminated with blood. Universal Precautions DO NOT necessarily apply to: feces nasal secretions sputum sweat tears urine vomit saliva (except in the dental setting) But, you must still be mindful of transmitting infectious material. They may not carry blood-borne illness, but they do carry viruses and bacteria. Universal Precautions Wear gloves if likely to touch body substances or mucous membranes – Latex or non-latex – Monitor for allergies Wear eye protection if likely to be splashed Wear lab coat or gown if likely to be soiled Universal Precautions Place needles in special containers (Sharps Container) Place soiled articles in plastic bag for disposal Place soiled linen in laundry bag Pharmacists Role Pharmacist Role Dispensing versus administration Makes sense for: – Vaccinations – Teaching patients to self-inject • Insulin and glucagon • Increasing availability of self-injection products – Allergic reactions, migraine, MS, infertility Proper training required Why are immunizations so important? Profession: – Establishes the role of the pharmacist Patients: – Pharmacists are easily accessible Population: – Preventing disease For More Information APhA: Pharmacy-Based Immunization Delivery Certificate Program – www.pharmacist.com Center for Disease Control – Vaccines – http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System – http://vaers.hhs.gov