- Clil in Action
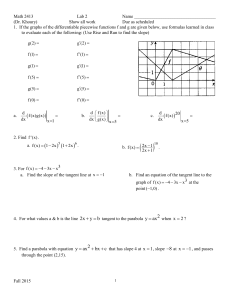
... 1) Write an article or prepare an interview. 2) Prepare the article or the debate, outlining the main points of the argument, on the basis of what has been studied. 3) If the written activity is the modality chosen by the teacher, the student should provide a written article, indicating the target o ...
... 1) Write an article or prepare an interview. 2) Prepare the article or the debate, outlining the main points of the argument, on the basis of what has been studied. 3) If the written activity is the modality chosen by the teacher, the student should provide a written article, indicating the target o ...
The Division Theorem • Theorem Let n be a fixed integer ≥ 2. For
... • Suppose every student has a 10-digit student id number, but there are only 35,000 student records you wish to store in a fixed amount of array space, say in an array with 50,000 lines. • If you in fact had 1010 lines in the array, you could use the student id number itself as an index into it. But ...
... • Suppose every student has a 10-digit student id number, but there are only 35,000 student records you wish to store in a fixed amount of array space, say in an array with 50,000 lines. • If you in fact had 1010 lines in the array, you could use the student id number itself as an index into it. But ...
The Inverse Trigonometric Functions - Beck-Shop
... trigonometric functions and their graphs, and the associated derivatives and integrals. In Section 1F these functions are used to establish some formulae for the general solutions of trigonometric equations. ...
... trigonometric functions and their graphs, and the associated derivatives and integrals. In Section 1F these functions are used to establish some formulae for the general solutions of trigonometric equations. ...
§1. Basic definitions Let IR be the set of all real numbers, while IR
... xn we denote an element of X corresponding to n. This defines a set of numbered elements {x1 , x2 , . . . , xn , . . .} (or, for brevity, {xn }) called a sequence defined on X. If X = IR then {xn } is called a sequence of numbers. If X is a set of functions: xn = xn (t), then {xn (t)} is a sequence ...
... xn we denote an element of X corresponding to n. This defines a set of numbered elements {x1 , x2 , . . . , xn , . . .} (or, for brevity, {xn }) called a sequence defined on X. If X = IR then {xn } is called a sequence of numbers. If X is a set of functions: xn = xn (t), then {xn (t)} is a sequence ...
Fundamental theorem of calculus
The fundamental theorem of calculus is a theorem that links the concept of the derivative of a function with the concept of the function's integral.The first part of the theorem, sometimes called the first fundamental theorem of calculus, is that the definite integration of a function is related to its antiderivative, and can be reversed by differentiation. This part of the theorem is also important because it guarantees the existence of antiderivatives for continuous functions.The second part of the theorem, sometimes called the second fundamental theorem of calculus, is that the definite integral of a function can be computed by using any one of its infinitely-many antiderivatives. This part of the theorem has key practical applications because it markedly simplifies the computation of definite integrals.