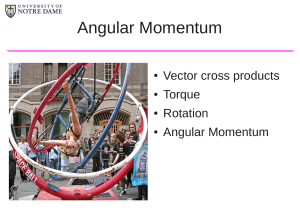
Angular Momentum
... ⃗ =Σ ⃗τ ext dt dt The angular acceleration of an object is the result of a net torque applied to it So if we apply a torque to the disk in the picture in the direction that it's rotating (F is parallel to v), the angular acceleration tends to increase the angular velocity and the angular momentum. I ...
... ⃗ =Σ ⃗τ ext dt dt The angular acceleration of an object is the result of a net torque applied to it So if we apply a torque to the disk in the picture in the direction that it's rotating (F is parallel to v), the angular acceleration tends to increase the angular velocity and the angular momentum. I ...
Electrostatic-directed deposition of nanoparticles on a field
... bias voltage. Apparently, by about −0.5 V selectivity exceeded 99%. This corroborated with the fact that as the reverse bias was increased the negative electric field generated on the p-type regions was also increased to sufficiently repel the incoming negatively charged nanoparticles, and resulted ...
... bias voltage. Apparently, by about −0.5 V selectivity exceeded 99%. This corroborated with the fact that as the reverse bias was increased the negative electric field generated on the p-type regions was also increased to sufficiently repel the incoming negatively charged nanoparticles, and resulted ...
1. The figure below represents the planet Jupiter. The centre of the
... Jupiter has a radius of 7.14 × 107 m and the gravitational field strength at its surface is 24.9 N kg–1. (i) ...
... Jupiter has a radius of 7.14 × 107 m and the gravitational field strength at its surface is 24.9 N kg–1. (i) ...
15.hamilton11e_ppt_18(1)
... The object will move only if the force is of sufficient magnitude to overcome the object’s inertia. The pattern and range of joint movements depends on the purpose of the motion. Force exerted by the body will be transferred to an external object in proportion to the effectiveness of the counterforc ...
... The object will move only if the force is of sufficient magnitude to overcome the object’s inertia. The pattern and range of joint movements depends on the purpose of the motion. Force exerted by the body will be transferred to an external object in proportion to the effectiveness of the counterforc ...
Math 8.02 Document Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... In 8.01, you learned of force fields wherein a force vector F(x,y,z) could be assigned to every point in space. [In Electromagnetism, we also have vector fields, such as the electric field vector E(x,y,z)] You will learn about it early in 8.02. A typical integration with which you may be familiar is ...
... In 8.01, you learned of force fields wherein a force vector F(x,y,z) could be assigned to every point in space. [In Electromagnetism, we also have vector fields, such as the electric field vector E(x,y,z)] You will learn about it early in 8.02. A typical integration with which you may be familiar is ...
vector. - cloudfront.net
... Given that A + B = C, and 1) they are perpendicular to each other 2) they are parallel and in the same direction that lAl 2 + lBl 2 = lCl 2, how are vectors A and B 3) they are parallel but in the opposite oriented with respect to direction each other? 4) they are at 45° to each other 5) they can be ...
... Given that A + B = C, and 1) they are perpendicular to each other 2) they are parallel and in the same direction that lAl 2 + lBl 2 = lCl 2, how are vectors A and B 3) they are parallel but in the opposite oriented with respect to direction each other? 4) they are at 45° to each other 5) they can be ...
Mathematical Fundamentals
... influence of electric field. Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) is an assertion of the conservative property of charges under the implicit assumption that there is no accumulation of charge at the junction. Electromagnetic theory deals directly with the electric and magnetic field vectors where as circui ...
... influence of electric field. Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) is an assertion of the conservative property of charges under the implicit assumption that there is no accumulation of charge at the junction. Electromagnetic theory deals directly with the electric and magnetic field vectors where as circui ...
Science
... 9. Students shall distinguish between simple harmonic motion and waves. 10. Students shall compare and contrast the law of reflection and the law of refraction. Electricity and Magnetism 11. Students shall understand the relationship between electric forces and electric fields. 12. Students shall un ...
... 9. Students shall distinguish between simple harmonic motion and waves. 10. Students shall compare and contrast the law of reflection and the law of refraction. Electricity and Magnetism 11. Students shall understand the relationship between electric forces and electric fields. 12. Students shall un ...
Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... the arrows (same direction as force on positive charge). When electric field lines are drawn, the following rules must be followed: (1) lines begin at positive charge (or infinity) and terminate on a negative charge (or infinity), (2) the number of lines drawn leaving a positive charge or approachin ...
... the arrows (same direction as force on positive charge). When electric field lines are drawn, the following rules must be followed: (1) lines begin at positive charge (or infinity) and terminate on a negative charge (or infinity), (2) the number of lines drawn leaving a positive charge or approachin ...