Lesson 5: The Parallel Plate System
... 6. An electron with a velocity of 5.0 x 106 m/s is injected into a parallel plate apparatus through a hole in the positive plate. It moves across the vacuum between the plates, colliding with the negative plate at 1.0 x 106 m/s. What is the potential difference between the plates? (68 V) 7. Assuming ...
... 6. An electron with a velocity of 5.0 x 106 m/s is injected into a parallel plate apparatus through a hole in the positive plate. It moves across the vacuum between the plates, colliding with the negative plate at 1.0 x 106 m/s. What is the potential difference between the plates? (68 V) 7. Assuming ...
Physics 121 Lecture Summary
... The concept summary notes were originally created following the section numbers, outline, and symbols of a different textbook than we are using this quarter (Fall 2010). The notes are good and can be utilized right away. Just be careful of the section numbers listed until they are updated. As the qu ...
... The concept summary notes were originally created following the section numbers, outline, and symbols of a different textbook than we are using this quarter (Fall 2010). The notes are good and can be utilized right away. Just be careful of the section numbers listed until they are updated. As the qu ...
Magnetic Field powerpoint lecture
... – The magnetic force associated with a steady magnetic field does no work when a particle is displaced • This is because the force is perpendicular to the displacement ...
... – The magnetic force associated with a steady magnetic field does no work when a particle is displaced • This is because the force is perpendicular to the displacement ...
Force and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Motion draws our attention. Motion itself can be beautiful, causing us to marvel at the forces needed to achieve spectacular motion, such as that of a dolphin jumping out of the water, or a pole vaulter, or the flight of a bird, or the orbit of a satellite. The study of motion is kinematics, but kin ...
... Motion draws our attention. Motion itself can be beautiful, causing us to marvel at the forces needed to achieve spectacular motion, such as that of a dolphin jumping out of the water, or a pole vaulter, or the flight of a bird, or the orbit of a satellite. The study of motion is kinematics, but kin ...
CCC Hoh Fuk Tong College
... (c) The time interval for the pulse to travel from A to B can be found from the corresponding traces registered by the search coils. The experiment is repeated with slinky spring stretched to different lengths and the corresponding time intervals found are tabulated below. (i) Complete the table by ...
... (c) The time interval for the pulse to travel from A to B can be found from the corresponding traces registered by the search coils. The experiment is repeated with slinky spring stretched to different lengths and the corresponding time intervals found are tabulated below. (i) Complete the table by ...
Paper
... As the pinning force in a PPP is directed perpendicular to the washboard channels of the PPP [1], the vortices generally tend to move along these channels. Such a guided motion of vortices in the presence of the Hall effect produces anisotropic transport behaviour for which even (+) and odd (–) with ...
... As the pinning force in a PPP is directed perpendicular to the washboard channels of the PPP [1], the vortices generally tend to move along these channels. Such a guided motion of vortices in the presence of the Hall effect produces anisotropic transport behaviour for which even (+) and odd (–) with ...
printer-friendly version
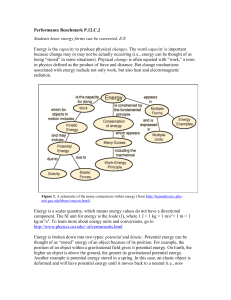
... 1. Students incorrectly believe that energy can be made, used, and lost. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy is not created or destroyed only transferred from potential to kinetic (or vice versa). Students should understand that just because they cannot see energy transfer (into and ...
... 1. Students incorrectly believe that energy can be made, used, and lost. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy is not created or destroyed only transferred from potential to kinetic (or vice versa). Students should understand that just because they cannot see energy transfer (into and ...
Part 1 Set 1 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... We found that space was three dimensional, so we developed the idea of vectors and found out how to work with them (add them in rectangular form). We then considered relations between space and time – motion with velocity and acceleration. We next looked at how to cause or predict motion using force ...
... We found that space was three dimensional, so we developed the idea of vectors and found out how to work with them (add them in rectangular form). We then considered relations between space and time – motion with velocity and acceleration. We next looked at how to cause or predict motion using force ...
Lecture 8
... • Friction is relatively easy, it just has two values, depending on whether the object is moving or at rest. • Friction does not depend on the velocity of the object! • Some forces, however, do depend on the velocity of the object. ...
... • Friction is relatively easy, it just has two values, depending on whether the object is moving or at rest. • Friction does not depend on the velocity of the object! • Some forces, however, do depend on the velocity of the object. ...
Document
... If WEXT >0, work is done by the external agent on the charges. If WEXT <0, work is done on the external agent by the field. Potential energy depends not only on the “source” but also on the “test” particle. Thus it will be more convenient if we can define a potential function which is function of “s ...
... If WEXT >0, work is done by the external agent on the charges. If WEXT <0, work is done on the external agent by the field. Potential energy depends not only on the “source” but also on the “test” particle. Thus it will be more convenient if we can define a potential function which is function of “s ...
Introduction to Capacitance Part A What property of objects is best
... , the the energy dissipated in the resistor. ...
... , the the energy dissipated in the resistor. ...
Monte Carlo Simulation of Electron Transport in
... where the proportionality constant Ξd is called the deformation potential. ∇ phonons, therefore the deformation potential applies only to longitudinal phonons. The scattering rate for the acoustic phonon scattering is given by [6]: ...
... where the proportionality constant Ξd is called the deformation potential. ∇ phonons, therefore the deformation potential applies only to longitudinal phonons. The scattering rate for the acoustic phonon scattering is given by [6]: ...