Mannich Reaction - SUST Repository
... suitably activated saturated derivatives ,and NH substrates may be amine ,amides,hetrocycles,etc.Out of OH substrate alcohol are mainly able to give stable Mannich products5.C-,N-,O- and SMannich bases are known. C- Mannich bases such as : R-(C=O)-C-CH2N ,Z-C (Z= carboxy ,Nitro,N-hetroaryl,etc),Z=C ...
... suitably activated saturated derivatives ,and NH substrates may be amine ,amides,hetrocycles,etc.Out of OH substrate alcohol are mainly able to give stable Mannich products5.C-,N-,O- and SMannich bases are known. C- Mannich bases such as : R-(C=O)-C-CH2N ,Z-C (Z= carboxy ,Nitro,N-hetroaryl,etc),Z=C ...
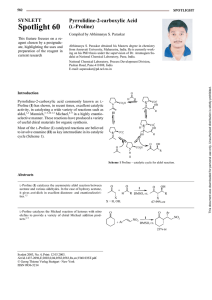
Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid (l
... from Amravati University, Maharastra, India. He is currently working on his PhD thesis under the supervision of Dr. Arumugum Sudalai at National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India. ...
... from Amravati University, Maharastra, India. He is currently working on his PhD thesis under the supervision of Dr. Arumugum Sudalai at National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India. ...
proline catalyzed direct asymmetric aldol and mannich reactions
... Following these initial studies of the Mannich reaction, Barbas and coworkers further explored the scope of this reaction. They found that a cross-Mannich reaction with aldehyde donors affords the syn diastereomers (Table 2, 30-32). The enantioselectivity is independent of existing stereocenters, an ...
... Following these initial studies of the Mannich reaction, Barbas and coworkers further explored the scope of this reaction. They found that a cross-Mannich reaction with aldehyde donors affords the syn diastereomers (Table 2, 30-32). The enantioselectivity is independent of existing stereocenters, an ...
Chapter 1--Title
... The Claisen Rearrangement Allyl phenyl ethers undergo a rearrangement upon heating that yields an allyl phenol The process is intramolecular; the allyl group migrates to the aromatic ring as the ether functional group becomes a ketone ...
... The Claisen Rearrangement Allyl phenyl ethers undergo a rearrangement upon heating that yields an allyl phenol The process is intramolecular; the allyl group migrates to the aromatic ring as the ether functional group becomes a ketone ...
Slides
... amines to form enamines l Cyclic amines are often used l The reaction is catalyzed by acid l Removal of water drives enamine formation to completion ...
... amines to form enamines l Cyclic amines are often used l The reaction is catalyzed by acid l Removal of water drives enamine formation to completion ...
Carbocation Rearrangements
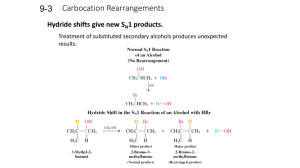
... Rearrangement of an initial secondary carbocation to the more stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride shift results in a rearranged product. ...
... Rearrangement of an initial secondary carbocation to the more stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride shift results in a rearranged product. ...
Step 1
... however, rather confusingly two ways of using this suffix. The exam board tend to use the common version where the name stem ends in -yl propylamine. ...
... however, rather confusingly two ways of using this suffix. The exam board tend to use the common version where the name stem ends in -yl propylamine. ...
The Grignard Reagent
... The Grignard Reaction • Grignard reagents react with carbonyl compounds to form alcohols. The type of alcohol produced depends on the type of carbonyl reacted. • In this experiment you will generate a tertiary alcohol from the reaction of a Grignard reagent with an ester. This process consists of t ...
... The Grignard Reaction • Grignard reagents react with carbonyl compounds to form alcohols. The type of alcohol produced depends on the type of carbonyl reacted. • In this experiment you will generate a tertiary alcohol from the reaction of a Grignard reagent with an ester. This process consists of t ...
Chapter 14 Selenium reagents
... Hydrogenolysis of carbon-selenium bonds is achievable using catalytic methods, dissolving metals, triaryltin hydrides and ‘nickel boride’. 1,2,3-Selenadiazole undergo elimination, giving alkynes, either on heating or treatment with organolithium reagents. Highly reactive cycloalkynes are prepara ...
... Hydrogenolysis of carbon-selenium bonds is achievable using catalytic methods, dissolving metals, triaryltin hydrides and ‘nickel boride’. 1,2,3-Selenadiazole undergo elimination, giving alkynes, either on heating or treatment with organolithium reagents. Highly reactive cycloalkynes are prepara ...
HL ISSN: 2231 – 3087(print) / 2230 – 9632 (Online)
... (decompose). This phosphonium salt formed was either reacted with aldehyde functional group or not can be confirmed by carrying out suitable test of aldehyde functionality of phosphonium salt. It can be shown by positive neutral FeCl3 test (phenolic OH group) and 2,4-DNP test (aldehydic carbonyl gro ...
... (decompose). This phosphonium salt formed was either reacted with aldehyde functional group or not can be confirmed by carrying out suitable test of aldehyde functionality of phosphonium salt. It can be shown by positive neutral FeCl3 test (phenolic OH group) and 2,4-DNP test (aldehydic carbonyl gro ...
Group B_reaction of alkenes
... groups, with its pair of electrons shifts to the adjacent +vely charged C to form a stable tertiary carbocation. • 1,2-methyl shift •Major product- is the most stable carbocation. ...
... groups, with its pair of electrons shifts to the adjacent +vely charged C to form a stable tertiary carbocation. • 1,2-methyl shift •Major product- is the most stable carbocation. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. Predict the product and explain the mechanism of the followi ...
... 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. Predict the product and explain the mechanism of the followi ...
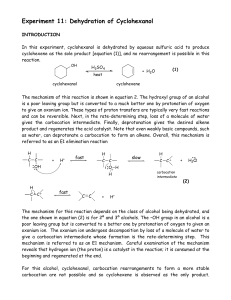
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
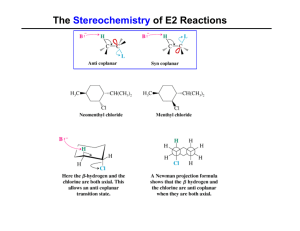
The Stereochemistry of E2 Reactions
... Dehydration of Alcohols: E1 Mechanism Rate Limiting Step ...
... Dehydration of Alcohols: E1 Mechanism Rate Limiting Step ...
Organic Chemistry
... synthesis of chiral products from achiral starting materials and under achiral reaction conditions of necessity gives enantiomers as a racemic mixture. • Nature achieves the synthesis of single enantiomers by using enzymes, which create a chiral environment in which reaction takes place. • Enzymes s ...
... synthesis of chiral products from achiral starting materials and under achiral reaction conditions of necessity gives enantiomers as a racemic mixture. • Nature achieves the synthesis of single enantiomers by using enzymes, which create a chiral environment in which reaction takes place. • Enzymes s ...
Stereoselective Construction of a β
... site was affected by the base employed in the acyclic system.6 The results of the diastereoselective Wittig rearrangement of cyclic furfuryl ethers 8 are shown in Table 1. Treatment of (E)-8 with excess alkyllithium or LDA in THF afforded isopropenyl alcohol anti-9 as a predominant stereoisomer in m ...
... site was affected by the base employed in the acyclic system.6 The results of the diastereoselective Wittig rearrangement of cyclic furfuryl ethers 8 are shown in Table 1. Treatment of (E)-8 with excess alkyllithium or LDA in THF afforded isopropenyl alcohol anti-9 as a predominant stereoisomer in m ...
Grignard Reaction - This is Synthesis
... The formation of organometallic Grignard reagents from halides and elemental magnesium is a rather tricky and often slow starting process. Prevention of moisture and air is crucial. Therefore standard reaction conditions in open vessels require special precautions to activate the magnesium and to ke ...
... The formation of organometallic Grignard reagents from halides and elemental magnesium is a rather tricky and often slow starting process. Prevention of moisture and air is crucial. Therefore standard reaction conditions in open vessels require special precautions to activate the magnesium and to ke ...
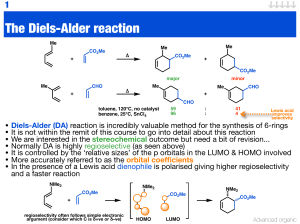
The Diels-Alder reaction
... • Diels-Alder (DA) reaction is incredibly valuable method for the synthesis of 6-rings • It is not within the remit of this course to go into detail about this reaction • We are interested in the stereochemical outcome but need a bit of revision... • Normally DA is highly regioselective (as seen abo ...
... • Diels-Alder (DA) reaction is incredibly valuable method for the synthesis of 6-rings • It is not within the remit of this course to go into detail about this reaction • We are interested in the stereochemical outcome but need a bit of revision... • Normally DA is highly regioselective (as seen abo ...
PowerPoint **
... Why alkenyl halides such as CH3CBr=ChCH3 don’t undergo substitution upon treatment with a strong base(-NH2)? Ans: ring strain. ...
... Why alkenyl halides such as CH3CBr=ChCH3 don’t undergo substitution upon treatment with a strong base(-NH2)? Ans: ring strain. ...
Asymmetric Organocatalysis
... One of these approaches consists in activating the acceptors – mostly α,β-unsaturated aldehydes (R4 = H) and ketones (R4 = alkyl) – by reversible conversion to a chiral iminium ion. As shown in Scheme 4.2a, reversible condensation of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound with a chiral secondary ami ...
... One of these approaches consists in activating the acceptors – mostly α,β-unsaturated aldehydes (R4 = H) and ketones (R4 = alkyl) – by reversible conversion to a chiral iminium ion. As shown in Scheme 4.2a, reversible condensation of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound with a chiral secondary ami ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 5. Explain the change in the geometry of excited state molecule in a photochemical process and the variation in its physical property. 6. What is Norrish type I and II cleavage reactions? Give suitable examples. 7. What are the important guidelines to be followed while choosing alternate synthetic r ...
... 5. Explain the change in the geometry of excited state molecule in a photochemical process and the variation in its physical property. 6. What is Norrish type I and II cleavage reactions? Give suitable examples. 7. What are the important guidelines to be followed while choosing alternate synthetic r ...
CHAPTER 9 Further Reactions of Alcohols and the Chemistry of
... Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl sulfonates creates a good leaving group for subsequent displacement by an anionic nucleophile ...
... Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl sulfonates creates a good leaving group for subsequent displacement by an anionic nucleophile ...