Ch. 13,14 組織行為( Organizational Behavior)
... perception of a group to which he or she belongs. e.g. “已婚員工比未婚者更穩定”。911事件後,美國的 回教徒生活改變了。 Halo effect - a general impression of an individual based on a single characteristic. e.g. 以教學熱忱來對老師做整體評價。 ...
... perception of a group to which he or she belongs. e.g. “已婚員工比未婚者更穩定”。911事件後,美國的 回教徒生活改變了。 Halo effect - a general impression of an individual based on a single characteristic. e.g. 以教學熱忱來對老師做整體評價。 ...
understanding participants as consumers
... • Culture is the most basic cause of a person's wants and behavior – Learned from family, church, school, peers, and colleagues – Reflects basic values, perceptions, wants, and behaviors – Cultural shifts create opportunities for new products or may otherwise influence consumer behavior – Affects so ...
... • Culture is the most basic cause of a person's wants and behavior – Learned from family, church, school, peers, and colleagues – Reflects basic values, perceptions, wants, and behaviors – Cultural shifts create opportunities for new products or may otherwise influence consumer behavior – Affects so ...
class notes here
... personality. Describe the five personality traits that have proved to be most powerful in explaining individual behavior in organizations. Explain how emotions and emotional intelligence impact behavior. ...
... personality. Describe the five personality traits that have proved to be most powerful in explaining individual behavior in organizations. Explain how emotions and emotional intelligence impact behavior. ...
Social Psychology
... the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of one individual are influenced by the real, imagined, or inferred behavior or characteristics of other people ...
... the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of one individual are influenced by the real, imagined, or inferred behavior or characteristics of other people ...
Attitudes
... • attitude toward an individual based solely on the person’s group membership • behavioral component is discrimination • often not based on direct experience ...
... • attitude toward an individual based solely on the person’s group membership • behavioral component is discrimination • often not based on direct experience ...
Ch. 11 Personality Notes doc
... Personality is determined to a large extent by a person’s genes ...
... Personality is determined to a large extent by a person’s genes ...
LEADERSHIP, MOTIVATION, AND PROBLEM SOLVING
... Our motivation to perform depends upon the expectancy that we have concerning future outcomes and the value we place on these outcomes. ...
... Our motivation to perform depends upon the expectancy that we have concerning future outcomes and the value we place on these outcomes. ...
Albert Bandura - Personal Web Pages
... teacher is near or children who begin talking more at bedtime), 3. response facilitation (a function of the behavior of others - peer pressure), 4. environmental enhancement (children will fight more if they observe parents fighting). ...
... teacher is near or children who begin talking more at bedtime), 3. response facilitation (a function of the behavior of others - peer pressure), 4. environmental enhancement (children will fight more if they observe parents fighting). ...
Social-Cognitive Theory
... social, cognitive, or enviornmental. • The relationship between these three factors provides even more insight into the complex concept that is morality. • Identification between the observer and the model and if the observer also has a good deal of self-efficacy. • Self-efficacy beliefs function as ...
... social, cognitive, or enviornmental. • The relationship between these three factors provides even more insight into the complex concept that is morality. • Identification between the observer and the model and if the observer also has a good deal of self-efficacy. • Self-efficacy beliefs function as ...
Social influence Lecture
... in this case, the message is a direct order, generally from a person in authority, such as a police officer, principal, or parent, who can back up the command with some sort of force if necessary. Obedience embodies social influence in its most direct and powerful form. Why do people willingly obey ...
... in this case, the message is a direct order, generally from a person in authority, such as a police officer, principal, or parent, who can back up the command with some sort of force if necessary. Obedience embodies social influence in its most direct and powerful form. Why do people willingly obey ...
Clothing Communication
... An individual’s unique combination of mental, emotional, and social qualities expressed through your attitudes, emotions and behaviours Emotions: People dress in respect to their emotions, often clothing will communicate how a person is feeling Self-Concept: A positive self-concept will often reflec ...
... An individual’s unique combination of mental, emotional, and social qualities expressed through your attitudes, emotions and behaviours Emotions: People dress in respect to their emotions, often clothing will communicate how a person is feeling Self-Concept: A positive self-concept will often reflec ...
M O D U L E 1 0
... 18 an accidental pairing of a reinforcer and a behavior causes that behavior to occur again. 19 a program or rule that determines how and when a response will be rewarded. 20 if the removal of an aversive stimulus increases the chances of a response occurring again, it is called a __________ reinfor ...
... 18 an accidental pairing of a reinforcer and a behavior causes that behavior to occur again. 19 a program or rule that determines how and when a response will be rewarded. 20 if the removal of an aversive stimulus increases the chances of a response occurring again, it is called a __________ reinfor ...
Personality Disorders - MrsVeseysTAEMentalDisorders
... skills. It can be difficult to treat a person with paranoia as they may be irritable, emotionally guarded, hostile, and unwilling; therefore, progress is slow. Therapy attempts to break the cycle of suspicion and isolation by using relaxation and anxiety management and by aiding the person to change ...
... skills. It can be difficult to treat a person with paranoia as they may be irritable, emotionally guarded, hostile, and unwilling; therefore, progress is slow. Therapy attempts to break the cycle of suspicion and isolation by using relaxation and anxiety management and by aiding the person to change ...
PSY101_Chap14_04-30 - Human Resourcefulness Consulting
... assisting the experimenter – Naïve subject is a person who has agreed to participate in an experiment but is not aware that deception is being used to conceal its real purpose ...
... assisting the experimenter – Naïve subject is a person who has agreed to participate in an experiment but is not aware that deception is being used to conceal its real purpose ...
Introduction to Medical Ethics
... permission granted voluntarily by a person who is of sound mind after the procedure and all risks involved have been explained in terms the person can understand ...
... permission granted voluntarily by a person who is of sound mind after the procedure and all risks involved have been explained in terms the person can understand ...
CHAPTER 15 Social Psychology
... • Bias in attributions – Fundamental attribution error – Self-serving bias ...
... • Bias in attributions – Fundamental attribution error – Self-serving bias ...
Sport Psychology: History
... Dominance is also a characteristic of this personality trait because they like to be in control and have influence over others. ...
... Dominance is also a characteristic of this personality trait because they like to be in control and have influence over others. ...
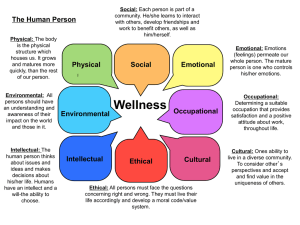
human person
... Social: Each person is part of a community. He/she learns to interact with others, develop friendships and work to benefit others, as well as him/herself. ...
... Social: Each person is part of a community. He/she learns to interact with others, develop friendships and work to benefit others, as well as him/herself. ...
Theory of Reasoned Action and Theory of Planned Behavior
... What ISN’T in the Model Other factors such as the modifying factors in the HBM (demographics, etc.) are not directly addressed. They can have an indirect effect on the other components, but are not specifically incorporated into the model. ...
... What ISN’T in the Model Other factors such as the modifying factors in the HBM (demographics, etc.) are not directly addressed. They can have an indirect effect on the other components, but are not specifically incorporated into the model. ...
Handouts Ch 10
... rigid, and inflexible in one's opinions and subsequent behavior. Fundamental attribution errorThe tendency to explain other's actions in terms of internal causes and our own behavior in terms of circumstances, environmental influences, and opportunities. Locus of ControlThe generalized beliefs tha ...
... rigid, and inflexible in one's opinions and subsequent behavior. Fundamental attribution errorThe tendency to explain other's actions in terms of internal causes and our own behavior in terms of circumstances, environmental influences, and opportunities. Locus of ControlThe generalized beliefs tha ...
CHAPTER THREE
... • We are only able to understand today in terms of, and because of, our past experiences. • Yet, we also know that 'Today' is unlike 'Yesterday'. • We inherit Yesterday's patterns and need them to interpret what our senses are experiencing in the ...
... • We are only able to understand today in terms of, and because of, our past experiences. • Yet, we also know that 'Today' is unlike 'Yesterday'. • We inherit Yesterday's patterns and need them to interpret what our senses are experiencing in the ...
Structuralism and Functionalism
... Sigmund Freud’s philosophy. Man processes early childhood experiences as a reference for behaviors ...
... Sigmund Freud’s philosophy. Man processes early childhood experiences as a reference for behaviors ...