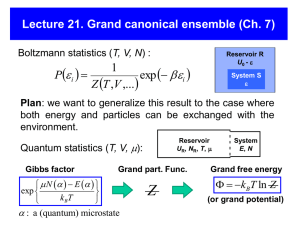
Fine Structure 35.1 Relativistic Hamiltonian
... There are relativistic and electromagnetic effects we have missed in our treatment of the pure Coulombic, classical approach. These are relatively easy to put back in perturbatively. Fine structure consists of two separate physical effects: one relativistic correction, one associated with spin-orbit ...
... There are relativistic and electromagnetic effects we have missed in our treatment of the pure Coulombic, classical approach. These are relatively easy to put back in perturbatively. Fine structure consists of two separate physical effects: one relativistic correction, one associated with spin-orbit ...
4 OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
... quantity and, therefore, must have a direction. In this case, since the motion is linear or one dimensional, it is sufficient to specify the direction as simply being positive or negative. The choice of whether above or below the rest position is positive is arbitrary but, once decided, this must be ...
... quantity and, therefore, must have a direction. In this case, since the motion is linear or one dimensional, it is sufficient to specify the direction as simply being positive or negative. The choice of whether above or below the rest position is positive is arbitrary but, once decided, this must be ...
Identical Quantum Particles and Weak Discernibility - Philsci
... Saunders has recently claimed that “identical quantum particles” with an anti-symmetric state (fermions) are weakly discernible objects, just like irreflexively related ordinary objects in situations with perfect symmetry (Black’s spheres, for example). Weakly discernible objects have all their qual ...
... Saunders has recently claimed that “identical quantum particles” with an anti-symmetric state (fermions) are weakly discernible objects, just like irreflexively related ordinary objects in situations with perfect symmetry (Black’s spheres, for example). Weakly discernible objects have all their qual ...
CfE Advanced Higher Physics Unit 2: Quanta and Waves
... Towards the end of the 19th century, physical phenomena were described in terms of "classical" theory, as either particles or waves. However, some new discoveries (such as the photoelectric effect) could not be explained using classical theory. As we have seen, such phenomena required a theory that ...
... Towards the end of the 19th century, physical phenomena were described in terms of "classical" theory, as either particles or waves. However, some new discoveries (such as the photoelectric effect) could not be explained using classical theory. As we have seen, such phenomena required a theory that ...
Low-energy spectrum and finite temperature properties of quantum
... are R = N rs /π and ω0 = CF ~2 π 2 /(32mrs2 ). The Heisenberg coupling energy of the model Hamiltonian can be fitted to the splitting of the lowest band (vibrational ground state) at a given angular momentum. For example, for six electrons J can be determined from the energy difference of the lowest ...
... are R = N rs /π and ω0 = CF ~2 π 2 /(32mrs2 ). The Heisenberg coupling energy of the model Hamiltonian can be fitted to the splitting of the lowest band (vibrational ground state) at a given angular momentum. For example, for six electrons J can be determined from the energy difference of the lowest ...
CfE Advanced Higher Physics Unit 2: Quanta and
... Towards the end of the 19th century, physical phenomena were described in terms of "classical" theory, as either particles or waves. However, some new discoveries (such as the photoelectric effect) could not be explained using classical theory. As we have seen, such phenomena required a theory that ...
... Towards the end of the 19th century, physical phenomena were described in terms of "classical" theory, as either particles or waves. However, some new discoveries (such as the photoelectric effect) could not be explained using classical theory. As we have seen, such phenomena required a theory that ...
Document
... 5. Long decoherence times How many gate operations could be carried out within a fixed decoherence time? “ For the atoms of ultracold gases in optical lattices, Feshbach resonances can be used to increase the collisional interactions and thereby speed up gate operations. However, the ‘unitarity lim ...
... 5. Long decoherence times How many gate operations could be carried out within a fixed decoherence time? “ For the atoms of ultracold gases in optical lattices, Feshbach resonances can be used to increase the collisional interactions and thereby speed up gate operations. However, the ‘unitarity lim ...
5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model
... Not just any frequency of light will cause the photoelectric effect. • Red light will not cause potassium to eject electrons, no matter how intense the light. • Yet a very weak yellow light shining on potassium begins the effect. ...
... Not just any frequency of light will cause the photoelectric effect. • Red light will not cause potassium to eject electrons, no matter how intense the light. • Yet a very weak yellow light shining on potassium begins the effect. ...
The Early Universe in Loop Quantum Cosmology
... scale is a priori free (set by the Barbero–Immirzi parameter [5, 6]; in this paper we set the value equal to one for simplicity) but fixed to be close to the Planck scale by black hole entropy calculations [7, 8, 9, 10]. Thus, it is not of relevance on directly accessible scales and will only become ...
... scale is a priori free (set by the Barbero–Immirzi parameter [5, 6]; in this paper we set the value equal to one for simplicity) but fixed to be close to the Planck scale by black hole entropy calculations [7, 8, 9, 10]. Thus, it is not of relevance on directly accessible scales and will only become ...
(Total Four Semesters, 100 marks in each Paper followed by
... Four vector potential, electromagnetic field tensor, Lorentz invariance, Lorentz force, covariant form of Maxwell’s equations, four vector current, continuity equation, Gauge invariance of Maxwell equation, electromagnetic energy- momentum tensor, Motion of charge particle in electromagnetic field, ...
... Four vector potential, electromagnetic field tensor, Lorentz invariance, Lorentz force, covariant form of Maxwell’s equations, four vector current, continuity equation, Gauge invariance of Maxwell equation, electromagnetic energy- momentum tensor, Motion of charge particle in electromagnetic field, ...
Photons
... the atoms were rearranged into regular planes so that constructive interference could occur. When the sample was again exposed to an electron beam they observed maxima and minima at different scattering angles. This discovery led to the invention of the electron microscope. a. Explain the origin of ...
... the atoms were rearranged into regular planes so that constructive interference could occur. When the sample was again exposed to an electron beam they observed maxima and minima at different scattering angles. This discovery led to the invention of the electron microscope. a. Explain the origin of ...
Polarizability and Collective Excitations in Semiconductor Quantum
... al. Solid State Comm. 119, 323 (2001)) give a ratio between the two modes which is about 2. However, we have indications that the ratio grows with the number of electrons, and it is difficult to establish from the present calculations which is the asymptotic value . Moreover for such a large number ...
... al. Solid State Comm. 119, 323 (2001)) give a ratio between the two modes which is about 2. However, we have indications that the ratio grows with the number of electrons, and it is difficult to establish from the present calculations which is the asymptotic value . Moreover for such a large number ...
Quantum-electrodynamical approach to the Casimir force
... PACS 03.70+k theory of quantized fields Abstract We derive the Casimir force expression from Maxwell’s stress tensor by means of original quantum-electro-dynamical cavity modes. In contrast with similar calculations, our method is straightforward and does not rely on intricate mathematical extrapola ...
... PACS 03.70+k theory of quantized fields Abstract We derive the Casimir force expression from Maxwell’s stress tensor by means of original quantum-electro-dynamical cavity modes. In contrast with similar calculations, our method is straightforward and does not rely on intricate mathematical extrapola ...
Quantum State Control via Trap-induced Shape Resonance in
... large positive scattering lengths, where the bound state would be close to dissociation. This can be achieved in tight traps, where the scattering length is on the order of z0 and the energy gap approaches a significant fraction of ~ω (see Fig. 3). For example, in an optical lattice of 133 Cs atoms ...
... large positive scattering lengths, where the bound state would be close to dissociation. This can be achieved in tight traps, where the scattering length is on the order of z0 and the energy gap approaches a significant fraction of ~ω (see Fig. 3). For example, in an optical lattice of 133 Cs atoms ...
Quantum Teleportation
... information, also called "Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) correlation" or "entanglement". In the 1960s John Bell showed that a pair of entangled particles, which were once in contact but later move too far apart to interact directly, can exhibit individually random behavior that is too strongly correl ...
... information, also called "Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) correlation" or "entanglement". In the 1960s John Bell showed that a pair of entangled particles, which were once in contact but later move too far apart to interact directly, can exhibit individually random behavior that is too strongly correl ...