Lect.05 - Infectious Diseases in Children. Immunization
... potentially lethal diseases. It is important to be aware of the findings and progression associated with these diseases in order to expediate evaluation, treatment, prevention and followup. Remember – contagious illness poses a particular threat to students who have compromised immune ...
... potentially lethal diseases. It is important to be aware of the findings and progression associated with these diseases in order to expediate evaluation, treatment, prevention and followup. Remember – contagious illness poses a particular threat to students who have compromised immune ...
SMAS_442.1 Medicines_QA_NSAIDs_chickenpox
... A prospective multicentre case-control study identified cases who were children (18 years or under) hospitalised with primary varicella complicated by invasive group A streptococcal (GAS) infection or necrotising soft tissue infection (16). Controls were children with uncomplicated primary varicella ...
... A prospective multicentre case-control study identified cases who were children (18 years or under) hospitalised with primary varicella complicated by invasive group A streptococcal (GAS) infection or necrotising soft tissue infection (16). Controls were children with uncomplicated primary varicella ...
new world issues disease wip
... particular, HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis; the mitigation of the effects of non-communicable diseases; sexual and reproductive health, development, and ageing; nutrition, food security and healthy eating; substance abuse; and drive the development of reporting, publications, and networking. ...
... particular, HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis; the mitigation of the effects of non-communicable diseases; sexual and reproductive health, development, and ageing; nutrition, food security and healthy eating; substance abuse; and drive the development of reporting, publications, and networking. ...
(TB) at Cornell - Cornell Health
... TB disease can become infected with TB bacteria, but in most cases their immune system prevents that infection from causing TB disease. This condition is called latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). LTBI means the person has the TB bacteria in their body, but has yet to develop obvious symptoms (sym ...
... TB disease can become infected with TB bacteria, but in most cases their immune system prevents that infection from causing TB disease. This condition is called latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). LTBI means the person has the TB bacteria in their body, but has yet to develop obvious symptoms (sym ...
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
... OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to, hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes ...
... OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to, hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes ...
Life At Sea: Sores, Scabs, and Scurvy Diseases The following are
... symptoms - Lack of energy, sleepiness, vulnerability to colds and flu. Can be fatal. Syphilis - infectious disease caused by bacteria transmitted by sexual contact. symptoms - sores appear on infected area, after six weeks a rash appears. Fever, sores, and headaches continue until 12 weeks. The last ...
... symptoms - Lack of energy, sleepiness, vulnerability to colds and flu. Can be fatal. Syphilis - infectious disease caused by bacteria transmitted by sexual contact. symptoms - sores appear on infected area, after six weeks a rash appears. Fever, sores, and headaches continue until 12 weeks. The last ...
Lymes Disease
... As the rash increases in size, it clears in the middle and develops a red ring around the outside. This rash: May expand to a very large size, Is usually not painful or itchy, and Often appears on the thighs, groin, trunk, armpit, or back. rash has been reported in about 60 to 80 percent of adults a ...
... As the rash increases in size, it clears in the middle and develops a red ring around the outside. This rash: May expand to a very large size, Is usually not painful or itchy, and Often appears on the thighs, groin, trunk, armpit, or back. rash has been reported in about 60 to 80 percent of adults a ...
Hepatitis C and the link to liver disease
... the Hepatitis C virus has been identified as the leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. Approximately 5-10% of infected individuals will develop cirrhosis over a 20-30 year period of time. The virus cannot easily be transmitted. Contaminated blood products and intravenous drug use are the ...
... the Hepatitis C virus has been identified as the leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. Approximately 5-10% of infected individuals will develop cirrhosis over a 20-30 year period of time. The virus cannot easily be transmitted. Contaminated blood products and intravenous drug use are the ...
Immune system08
... specialized cells and organs that protect an organism from outside biological influences • Defends against pathogens and disease ...
... specialized cells and organs that protect an organism from outside biological influences • Defends against pathogens and disease ...
Strep
... Streptococcal disease has been reported in your child’s classroom. Identification: Streptococcal disease (group A-Beta Hemolytic) often called "strep" cause a wide variety of infections. The most common is sore throat or skin infections (impetigo). Other diseases such as scarlet fever, middle ear in ...
... Streptococcal disease has been reported in your child’s classroom. Identification: Streptococcal disease (group A-Beta Hemolytic) often called "strep" cause a wide variety of infections. The most common is sore throat or skin infections (impetigo). Other diseases such as scarlet fever, middle ear in ...
Fifth Disease
... Fifth disease, or erythema infectiosum, is a mild childhood illness caused by the human parvovirus B19. Its symptoms include a facial rash or "slapped cheek" appearance and a lacelike rash on the trunk and extremities. The rash may appear and reappear over several weeks. Temporary arthritic pain or ...
... Fifth disease, or erythema infectiosum, is a mild childhood illness caused by the human parvovirus B19. Its symptoms include a facial rash or "slapped cheek" appearance and a lacelike rash on the trunk and extremities. The rash may appear and reappear over several weeks. Temporary arthritic pain or ...
File - Mr. B. Hanson
... genital warts • Caused by a virus • 20 million people have the disease • 1 million new cases each year • #1 cause of cervical cancer in women • There are many different types. 30 are sexually transmitted. ...
... genital warts • Caused by a virus • 20 million people have the disease • 1 million new cases each year • #1 cause of cervical cancer in women • There are many different types. 30 are sexually transmitted. ...
Common skin infections
... - There is no treatment for measles. A vaccine has been available since 1963, and has had a dramatic effect on the incidence of measles in the developed world; unfortunately, the vaccine does not produce strong immunity in all individuals, and compliance remains a problem ...
... - There is no treatment for measles. A vaccine has been available since 1963, and has had a dramatic effect on the incidence of measles in the developed world; unfortunately, the vaccine does not produce strong immunity in all individuals, and compliance remains a problem ...
DNA-viruses
... before or during birth • hand transmission by mother to infant • Infection of mouth, skin, eyes, CNS • Preventative screening of pregnant women – delivery by C-section if outbreak at the time of birth ...
... before or during birth • hand transmission by mother to infant • Infection of mouth, skin, eyes, CNS • Preventative screening of pregnant women – delivery by C-section if outbreak at the time of birth ...
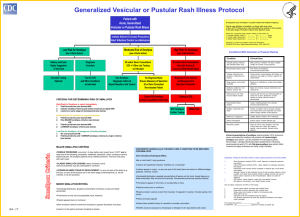
Generalized Vesicular or Pustular Rash Illness Protocol
... Centrifugal distribution: greatest concentration of lesions on face and distal extremities First lesions on the oral mucosa/palate, face, forearms Patient appears toxic or moribund Slow evolution: lesions evolve from macules to papulespustules over days ...
... Centrifugal distribution: greatest concentration of lesions on face and distal extremities First lesions on the oral mucosa/palate, face, forearms Patient appears toxic or moribund Slow evolution: lesions evolve from macules to papulespustules over days ...
Immunizations - Pediatric Nursing
... human parvovirus B19 that causes flu-like symptoms and a rash. It is called fifth disease because it was fifth on a list of common childhood illnesses that are accompanied by a rash, including measles, rubella (or German measles), scarlet fever (or scarlatina), and scarlatinella, a variant of scarle ...
... human parvovirus B19 that causes flu-like symptoms and a rash. It is called fifth disease because it was fifth on a list of common childhood illnesses that are accompanied by a rash, including measles, rubella (or German measles), scarlet fever (or scarlatina), and scarlatinella, a variant of scarle ...
Newcastle Disease
... disease in adults. In young, fully susceptible birds, serious respiratory disease problems can be seen, often resulting in mortality, following infection with the more pathogenic LaSota strains complicated by infections with one or more of a range of other microorganisms. Vaccination or infection of ...
... disease in adults. In young, fully susceptible birds, serious respiratory disease problems can be seen, often resulting in mortality, following infection with the more pathogenic LaSota strains complicated by infections with one or more of a range of other microorganisms. Vaccination or infection of ...
immunization1
... Prior to vaccines was the most common cause of childhood bacterial meningitis(brain damage, deafness, death) ...
... Prior to vaccines was the most common cause of childhood bacterial meningitis(brain damage, deafness, death) ...
Bacteria and You Web Quest Part 1 Choose any two articles from
... Diphtheria : upper respiratory tract illness having sore throat, low-grade fever and an adherent layer on the tonsils, nasal cavity, pharynx. Epidemic Typhus : caused by louse-borne bacteria. Impetigo : superficial skin infection common in the age group of 2 to 6. Legionellosis : pneumonia or mild r ...
... Diphtheria : upper respiratory tract illness having sore throat, low-grade fever and an adherent layer on the tonsils, nasal cavity, pharynx. Epidemic Typhus : caused by louse-borne bacteria. Impetigo : superficial skin infection common in the age group of 2 to 6. Legionellosis : pneumonia or mild r ...
History,Epidemiology,Reason for increase incidence,Transmission
... • People with latent infections are treated to prevent them from progressing to active TB disease later in life. However, treatment using Rifampicin and Pyrazinamide is not risk-free. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notified healthcare professionals of revised recommendations ag ...
... • People with latent infections are treated to prevent them from progressing to active TB disease later in life. However, treatment using Rifampicin and Pyrazinamide is not risk-free. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notified healthcare professionals of revised recommendations ag ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.