Children`s infectious diseases - the NSW Multicultural Health
... About 10 to 12 days until first symptoms, and 14 days until the rash develops. Symptoms Fever, tiredness, runny nose, cough and sore red eyes for a few days followed by a red blotchy rash that starts on the face and spreads down the body and lasts 4 to 7 days. Do I need to keep my child home? Yes, f ...
... About 10 to 12 days until first symptoms, and 14 days until the rash develops. Symptoms Fever, tiredness, runny nose, cough and sore red eyes for a few days followed by a red blotchy rash that starts on the face and spreads down the body and lasts 4 to 7 days. Do I need to keep my child home? Yes, f ...
-click here for handouts (full page)
... heart or vomiting of greenish material, stiffness of the spine, and in infants, convulsions. In cases which were fatal, loss of consciousness occurred. The course of the disease is very rapid, termination by death or by cure. In most of the patients who died in 24 hours or a little after, the bo ...
... heart or vomiting of greenish material, stiffness of the spine, and in infants, convulsions. In cases which were fatal, loss of consciousness occurred. The course of the disease is very rapid, termination by death or by cure. In most of the patients who died in 24 hours or a little after, the bo ...
Identification of infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) through agar
... caused by infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV). Infected bursae were collected from filed outbreaks of IBD at Lahore, Pakistan. A 10% W/V suspension was made in the phosphate buffer saline and centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 20 min. The presence of IBDV in the supernatants of suspect homogenates was c ...
... caused by infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV). Infected bursae were collected from filed outbreaks of IBD at Lahore, Pakistan. A 10% W/V suspension was made in the phosphate buffer saline and centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 20 min. The presence of IBDV in the supernatants of suspect homogenates was c ...
presentation ( format)
... Isolate student until first five days antibiotics completed or until 21 days after onset of Control measures symptoms Isolate symptomatic contacts Candidates for Prophylaxis indicated for household and post-exposure other close contacts measures Monitor for 21 days after last contact Post-exposure m ...
... Isolate student until first five days antibiotics completed or until 21 days after onset of Control measures symptoms Isolate symptomatic contacts Candidates for Prophylaxis indicated for household and post-exposure other close contacts measures Monitor for 21 days after last contact Post-exposure m ...
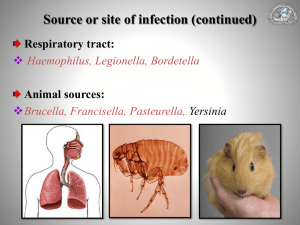
Gram-Negative Rods
... Pontiac fever is a mild flulike form of Legionella infection that does not result in pneumonia. ...
... Pontiac fever is a mild flulike form of Legionella infection that does not result in pneumonia. ...
Dane County Friends of Ferals Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)
... Cats at greatest risk of infection are those that may be exposed to infected cats, either via prolonged close contact or through bite wounds. Such cats include: • Cats living with infected cats or with cats of unknown infection status • Cats allowed outdoors unsupervised, where they may be bitten by ...
... Cats at greatest risk of infection are those that may be exposed to infected cats, either via prolonged close contact or through bite wounds. Such cats include: • Cats living with infected cats or with cats of unknown infection status • Cats allowed outdoors unsupervised, where they may be bitten by ...
Respiratory Illness Fact sheets
... as possible to limit the spread of illness to other children. It is also advisable for them to stay away from people who are likely to suffer more serious illness, should as the very young, the elderly and those with chronic health problems. ...
... as possible to limit the spread of illness to other children. It is also advisable for them to stay away from people who are likely to suffer more serious illness, should as the very young, the elderly and those with chronic health problems. ...
Symposium: Nutrition and Infection, Prologue and Progress Since
... The cycle of malnutrition–infection–more nutritional deterioration–more infection was a powerful pathway. The evidence suggested that simply intervening in this cycle by improving nutritional intake in the presence of repeated exposure to infection (as occurs in malnourished children in developing c ...
... The cycle of malnutrition–infection–more nutritional deterioration–more infection was a powerful pathway. The evidence suggested that simply intervening in this cycle by improving nutritional intake in the presence of repeated exposure to infection (as occurs in malnourished children in developing c ...
vaccines - Sutherlin Veterinary Hospital
... transferred to them in the first milk or colostrum. Maternal immunity is only temporary. It declines steadily over the first few weeks of life and is largely gone by twelve weeks. The rate of decline is variable depending on many factors. ...
... transferred to them in the first milk or colostrum. Maternal immunity is only temporary. It declines steadily over the first few weeks of life and is largely gone by twelve weeks. The rate of decline is variable depending on many factors. ...
Corynebacterium kutscheri | Charles River Research Animal
... C. kutscheri is susceptible to most common disinfectants used in animal facilities. Any chemical or mechanical sterilant will also serve to remove C. kutscheri from the environment. C. kutscheri has been isolated from seawater, and can survive up to 8 days at 4˚C in PBS. Environmental reservoirs or ...
... C. kutscheri is susceptible to most common disinfectants used in animal facilities. Any chemical or mechanical sterilant will also serve to remove C. kutscheri from the environment. C. kutscheri has been isolated from seawater, and can survive up to 8 days at 4˚C in PBS. Environmental reservoirs or ...
Chikungunya Virus
... the Caribbean islands first in St. Martin in the French Antilles followed by autochthonous cases reported in December on Martinque. By late February 2014, over 2,000 laboratoryconfirmed cases attributable to both travel within the Caribbean and autochthonous cases in St. Martin, Guadeloupe, St. Bart ...
... the Caribbean islands first in St. Martin in the French Antilles followed by autochthonous cases reported in December on Martinque. By late February 2014, over 2,000 laboratoryconfirmed cases attributable to both travel within the Caribbean and autochthonous cases in St. Martin, Guadeloupe, St. Bart ...
Immunisation update
... Previous vaccine 23PPV (Pneumovax23) not effective in infants Given at 6 weeks, 5 and 15 months Children at high risk still have PCV7 + 23PPV ...
... Previous vaccine 23PPV (Pneumovax23) not effective in infants Given at 6 weeks, 5 and 15 months Children at high risk still have PCV7 + 23PPV ...
Oral ulcers Mutaz Ali Hassan Faculty of Dentistry University of
... The term immunemediated sub-epithelial blistering diseases (IMSEBD) has therefore been used. Immunological differences may account for the significant differences in their clinical presentation and responses to therapy, but unfortunately data on this are few. Diagnosis The diagnosis and management o ...
... The term immunemediated sub-epithelial blistering diseases (IMSEBD) has therefore been used. Immunological differences may account for the significant differences in their clinical presentation and responses to therapy, but unfortunately data on this are few. Diagnosis The diagnosis and management o ...
Common Sexually Transmitted Diseases
... Syphilis: Clinical Presentation Primary / Infectious / Early Syphilis Stage: Primary Phase Primary chancre Begins as papule and erodes into painless ulcer with a hard edge and clean base Usually in the genital area Appears 9-90 days after exposure Can be solitary or multiple (eg. kissing ...
... Syphilis: Clinical Presentation Primary / Infectious / Early Syphilis Stage: Primary Phase Primary chancre Begins as papule and erodes into painless ulcer with a hard edge and clean base Usually in the genital area Appears 9-90 days after exposure Can be solitary or multiple (eg. kissing ...
Infectious disease
... Abstract: Leishmaniasis is a disease that ranges in severity from skin lesions to serious disfigurement and fatal systemic infection. Resistance to infection is associated with a T-helper-1 immune response that activates macrophages to kill the intracellular parasite in a nitric oxide-dependent mann ...
... Abstract: Leishmaniasis is a disease that ranges in severity from skin lesions to serious disfigurement and fatal systemic infection. Resistance to infection is associated with a T-helper-1 immune response that activates macrophages to kill the intracellular parasite in a nitric oxide-dependent mann ...
Document
... • Presents as a hot, tender area of confluent erythema of the skin • Can cause systemic infection with fever, headache and vomiting. • Erysipelas is more superficial and has a more well demarcated border ...
... • Presents as a hot, tender area of confluent erythema of the skin • Can cause systemic infection with fever, headache and vomiting. • Erysipelas is more superficial and has a more well demarcated border ...
New Generation Vaccines, 3rd Edition
... narrative details included in the figure legends. A fairly broad range of HIV-related conditions are represented in this volume, though diseases that are not common in Europe and the United States are absent (e.g., cutaneous leshmaniasis and lymphogranuloma venereum). Additional weaknesses are noted ...
... narrative details included in the figure legends. A fairly broad range of HIV-related conditions are represented in this volume, though diseases that are not common in Europe and the United States are absent (e.g., cutaneous leshmaniasis and lymphogranuloma venereum). Additional weaknesses are noted ...
Glomerular Diseases
... Prognosis of MCD • Mostly patients are children < 16yrs. • Respond to corticosteroids. • Remissions may be there, but overall prognosis is excellent. ...
... Prognosis of MCD • Mostly patients are children < 16yrs. • Respond to corticosteroids. • Remissions may be there, but overall prognosis is excellent. ...
MEMO Strep Throat:
... contact through coughing or sneezing. Exposure to a person who has untreated strep throat may pose a risk for acquiring this infection. A person may be a carrier of the strep bacteria without having symptoms. Period of communicability: A person can develop symptoms of strep throat from 1 to 6 days a ...
... contact through coughing or sneezing. Exposure to a person who has untreated strep throat may pose a risk for acquiring this infection. A person may be a carrier of the strep bacteria without having symptoms. Period of communicability: A person can develop symptoms of strep throat from 1 to 6 days a ...
Antifungal Drugs
... Liver: severe hepatotoxic reactions, until the development of hepatitis. Endocrine system: impaired production of testosterone and corticosteroids, accompanied by gynecomastia, oligospermia, impotence, female menstrual cycle. ...
... Liver: severe hepatotoxic reactions, until the development of hepatitis. Endocrine system: impaired production of testosterone and corticosteroids, accompanied by gynecomastia, oligospermia, impotence, female menstrual cycle. ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.