Tuberculin Skin Testing Resource
... If asymptomatic and CXR normal, discuss options for LTBI treatment with client. Refer to Quick Reference – Assessment and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection. Annual CXR not recommended for TB screening unless becomes symptomatic or ...
... If asymptomatic and CXR normal, discuss options for LTBI treatment with client. Refer to Quick Reference – Assessment and Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection. Annual CXR not recommended for TB screening unless becomes symptomatic or ...
Tompkins-Flu-032017
... • Target the HA eliciting neutralizing serum antibody responses • Most have “contaminating” antigens, including NA, but these are not quantitated or considered in immunogenicity or efficacy Live-attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) • Elicits mucosal and serum antibody, as well as cellular immune resp ...
... • Target the HA eliciting neutralizing serum antibody responses • Most have “contaminating” antigens, including NA, but these are not quantitated or considered in immunogenicity or efficacy Live-attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) • Elicits mucosal and serum antibody, as well as cellular immune resp ...
The Model of Prion Replication
... scrapie in sheep, and bovine spongiform encephalopathies in cows. These diseases are characterized by long incubation periods, lack of immune response, and invisibility to detection as viruses. In 1982 Stanley Prusiner postulated that these diseases are caused not by viruses, but by abnormally shape ...
... scrapie in sheep, and bovine spongiform encephalopathies in cows. These diseases are characterized by long incubation periods, lack of immune response, and invisibility to detection as viruses. In 1982 Stanley Prusiner postulated that these diseases are caused not by viruses, but by abnormally shape ...
INFECTON CONTROL: PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES
... 28. When a disease spreads from one person to another by contact, it is: a. central c. contagious b. disinfect d. coughing 29. A submicroscopic structure capable of infecting plants and animals including bacteria is a: a. motility c. contagious b. mitosis d. virus 30. A virus can live and reproduce ...
... 28. When a disease spreads from one person to another by contact, it is: a. central c. contagious b. disinfect d. coughing 29. A submicroscopic structure capable of infecting plants and animals including bacteria is a: a. motility c. contagious b. mitosis d. virus 30. A virus can live and reproduce ...
Cognitive Decline
... – Tau-opathy (another protein misfolding disorder), specific isoform often causes PSP – Many have mutations in Chr 3 or 17q21 (MAPT) – associated with variable isoforms of tau – Same mutation can cause PSP in 1 family member, corticobasal syndrome in another, and progressive nonfluent aphasia or bvF ...
... – Tau-opathy (another protein misfolding disorder), specific isoform often causes PSP – Many have mutations in Chr 3 or 17q21 (MAPT) – associated with variable isoforms of tau – Same mutation can cause PSP in 1 family member, corticobasal syndrome in another, and progressive nonfluent aphasia or bvF ...
Toxoplasma - Worms and Germs
... Oocysts are only shed by cats. Unsporulated oocysts in fresh feces are not infective; they need appropriate oxygen, humidity and temperature to sporulate. Sporulated oocysts are the most environmentally resistant life stage of the parasite. Ingestion of as few as ten oocysts may infect an intermedia ...
... Oocysts are only shed by cats. Unsporulated oocysts in fresh feces are not infective; they need appropriate oxygen, humidity and temperature to sporulate. Sporulated oocysts are the most environmentally resistant life stage of the parasite. Ingestion of as few as ten oocysts may infect an intermedia ...
Mumps - ARPHS
... Mumps is a disease caused by the mumps virus. It usually spreads by close face-to-face interaction with an infected person. In the past, mumps infection was common in childhood but is now uncommon in Auckland due to immunisation. Immunisation is our main protection against the disease. ...
... Mumps is a disease caused by the mumps virus. It usually spreads by close face-to-face interaction with an infected person. In the past, mumps infection was common in childhood but is now uncommon in Auckland due to immunisation. Immunisation is our main protection against the disease. ...
Evaluation Guidelines of MN Patients Suspected of Having Ebola Virus Disease (PDF: 88KB/2 pages)
... For patients with a high-risk exposure but without a fever or fever is less than 38.6° C or 101.5° F, testing is recommended only if there are other compatible clinical symptoms present and blood work findings are abnormal (i.e., thrombocytopenia <150,000 cells/μL and/or elevated transaminases) or ...
... For patients with a high-risk exposure but without a fever or fever is less than 38.6° C or 101.5° F, testing is recommended only if there are other compatible clinical symptoms present and blood work findings are abnormal (i.e., thrombocytopenia <150,000 cells/μL and/or elevated transaminases) or ...
The Hepatitis B Virus Life Circle: Achievements and
... Formation of cccDNA in the establishment of HBV infection • cccDNA is synthesized de novo from incoming virus….(this pathway is not blocked by RTinhibitors) • ….or after reimport of newly formed mature (!) rcDNA-containing nucleocapsids (“amplification”) •cccDNA formation depends on the activity of ...
... Formation of cccDNA in the establishment of HBV infection • cccDNA is synthesized de novo from incoming virus….(this pathway is not blocked by RTinhibitors) • ….or after reimport of newly formed mature (!) rcDNA-containing nucleocapsids (“amplification”) •cccDNA formation depends on the activity of ...
Bloodborne Pathogen Training - Comprehensive Sub Solutions
... When hand washing facilities are available in the classroom, the exposed employee shall wash his/her hands and any other exposed skin area with soap and running water, If a hand washing facility is not available the employee shall use an antiseptic cleaner with paper towels, or towelettes, which ...
... When hand washing facilities are available in the classroom, the exposed employee shall wash his/her hands and any other exposed skin area with soap and running water, If a hand washing facility is not available the employee shall use an antiseptic cleaner with paper towels, or towelettes, which ...
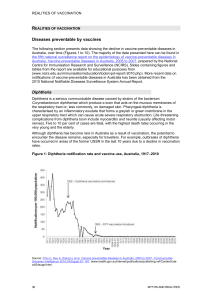
Realities of vaccination - Immunise Australia Program
... throat, and stuffy or runny nose. The virus can cause a mild or severe illness depending on the type of influenza virus and general health of the affected person. People of all ages can become severely ill with influenza and complications following influenza can be fatal, particularly in the elderly ...
... throat, and stuffy or runny nose. The virus can cause a mild or severe illness depending on the type of influenza virus and general health of the affected person. People of all ages can become severely ill with influenza and complications following influenza can be fatal, particularly in the elderly ...
Mycobacterium bovis J.M. Grange , C. Daborn O. Cosivi
... Thus, the incidence of pulmonary, relative to nonpulmonary, tuberculosis of bovine origin is higher in rural than in urban regions [4]. Reactivation of disease due to M. tuberculosis, after a period of dormancy, usually occurs in the lung where it often leads to open, smear-positive, infectious dise ...
... Thus, the incidence of pulmonary, relative to nonpulmonary, tuberculosis of bovine origin is higher in rural than in urban regions [4]. Reactivation of disease due to M. tuberculosis, after a period of dormancy, usually occurs in the lung where it often leads to open, smear-positive, infectious dise ...
Purchase of non-funded meningococcal vaccines
... likely to cause disease. • In 2012 almost two-thirds (60%) of meningococcal disease was caused by group B and one-third (33%) ...
... likely to cause disease. • In 2012 almost two-thirds (60%) of meningococcal disease was caused by group B and one-third (33%) ...
dvmzoo0602_036-39 Bart.r
... most well-known form of bartonellosis, it represents only one of five distinct clinical syndromes associated with Bartonella spp. infection. (The other forms have been previously listed.) The number of reported cases of CSD reported each year varies between resources, ranging from 6,000 to 22,000 ne ...
... most well-known form of bartonellosis, it represents only one of five distinct clinical syndromes associated with Bartonella spp. infection. (The other forms have been previously listed.) The number of reported cases of CSD reported each year varies between resources, ranging from 6,000 to 22,000 ne ...
Symptoms
... non-infected person, or by infected body fluids coming into contact with mucous membranes or damaged tissues. ...
... non-infected person, or by infected body fluids coming into contact with mucous membranes or damaged tissues. ...
Keratinocytes derived from chicken embryonic
... differences with the parental vBAC20 in former studies addressing the dissemination of both viruses in primary CESCs [22] and clusters of C capsids were observed in cytoplasm of infected K-cESCs, indicating that deenvelopment and/or C capsid nuclear egress took place in K-cESCs. MDV has been reporte ...
... differences with the parental vBAC20 in former studies addressing the dissemination of both viruses in primary CESCs [22] and clusters of C capsids were observed in cytoplasm of infected K-cESCs, indicating that deenvelopment and/or C capsid nuclear egress took place in K-cESCs. MDV has been reporte ...
Fact Sheet: Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus
... response to the inactivated virus. Protects the individual, but the virus may still replicate in the gut and could spread to infect others. ...
... response to the inactivated virus. Protects the individual, but the virus may still replicate in the gut and could spread to infect others. ...
Partnerships bring infection prevention practices to nurses
... the association has been doing. ANA and the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC) have launched the ANA/APIC Resource Center, a centralized, web-based information site on topics ranging from hand washing to PPE. Available since June, the website represents an 18m ...
... the association has been doing. ANA and the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC) have launched the ANA/APIC Resource Center, a centralized, web-based information site on topics ranging from hand washing to PPE. Available since June, the website represents an 18m ...
Ear Infection - For Medical Professionals
... Trigeminal neuralgia Initially may present with otalgia With time, will usually progress to classic symptoms (episodic, severe, lancinating facial pain) Treatment: carbamazepine, gabapentin (Neurology) balloon compression of trigeminal ganglion ...
... Trigeminal neuralgia Initially may present with otalgia With time, will usually progress to classic symptoms (episodic, severe, lancinating facial pain) Treatment: carbamazepine, gabapentin (Neurology) balloon compression of trigeminal ganglion ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.