Here
... (This was the most commonly given answer during a poll taken at a recent Harvard graduation). • No! Otherwise the seasons would not be opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres. ...
... (This was the most commonly given answer during a poll taken at a recent Harvard graduation). • No! Otherwise the seasons would not be opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres. ...
The Sky
... “planets” (non-stationary celestial objects) – Seven objects in the sky move relative to the stars: Sun, Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. English names for the days of the week are based on these. ...
... “planets” (non-stationary celestial objects) – Seven objects in the sky move relative to the stars: Sun, Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. English names for the days of the week are based on these. ...
3.2a Right Ascension and Declination
... Yours truly standing at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich with my right foot in the east and my left foot in the west! The PRIME MERIDIAN is the line between my feet – the reference line for LONGITUDE for the whole world. As there are 360˚ in a circle, the circle around the world could be reference ...
... Yours truly standing at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich with my right foot in the east and my left foot in the west! The PRIME MERIDIAN is the line between my feet – the reference line for LONGITUDE for the whole world. As there are 360˚ in a circle, the circle around the world could be reference ...
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself
... Earth determines which constellations remain below the horizon. They depend on time of year because Earth’s orbit changes the apparent location of the Sun among the stars. ...
... Earth determines which constellations remain below the horizon. They depend on time of year because Earth’s orbit changes the apparent location of the Sun among the stars. ...
An Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology
... Eve or the 30th June. Since the time definition was changed, 22 leap seconds have had to be added, about one every 18 months, but there were none between 1998 and 2005 showing the slowdown is not particularly regular. Leap seconds are somewhat of a nuisance for systems such as the Global Positioning ...
... Eve or the 30th June. Since the time definition was changed, 22 leap seconds have had to be added, about one every 18 months, but there were none between 1998 and 2005 showing the slowdown is not particularly regular. Leap seconds are somewhat of a nuisance for systems such as the Global Positioning ...
constellations are not real!
... There are about 21 zero and first magnitude stars. There are about 50 2nd magnitude stars including Polaris. The 3rd magnitude stars total about 150 There are some 600 4th magnitude stars 5th magnitude stars are about the faintest you can see on a good night. There are about 1500 of these stars, but ...
... There are about 21 zero and first magnitude stars. There are about 50 2nd magnitude stars including Polaris. The 3rd magnitude stars total about 150 There are some 600 4th magnitude stars 5th magnitude stars are about the faintest you can see on a good night. There are about 1500 of these stars, but ...
ASTR 105 Intro Astronomy: The Solar System
... Earth rotates west to east, so stars appear to circle from east to west [counterclockwise facing North clockwise facing South] Star Motion on http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion2/starpaths.html ...
... Earth rotates west to east, so stars appear to circle from east to west [counterclockwise facing North clockwise facing South] Star Motion on http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion2/starpaths.html ...
Celestial Motions - Stony Brook Astronomy
... The Local Sky • Zenith: The point directly overhead • Horizon: All points 90° away from zenith ...
... The Local Sky • Zenith: The point directly overhead • Horizon: All points 90° away from zenith ...
File - Mr. Gray`s Class
... similar to a globe of the sky. – It is an imaginary sphere where the sun, the moon, and all the other stars appear to be combined. ...
... similar to a globe of the sky. – It is an imaginary sphere where the sun, the moon, and all the other stars appear to be combined. ...
For stars
... the Stars (in Northern Hemisphere) • For stars (is similar for the Sun, Moon and planets) they first rise near the eastern horizon, move upward and toward the south, and then move down and set near the western horizon. ...
... the Stars (in Northern Hemisphere) • For stars (is similar for the Sun, Moon and planets) they first rise near the eastern horizon, move upward and toward the south, and then move down and set near the western horizon. ...
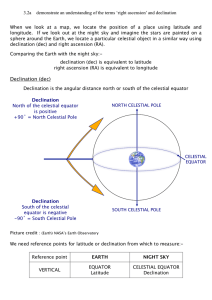
CELESTIAL COORDINATES
... From a latitude of 40°, an object with a declination of +40° will, at some point in time during the day or night, pass directly overhead through the zenith. In general Declination at zenith = Latitude of observer The 24 Ephemeris Stars in the SBO Catalog of Astronomical Objects have Object Numbers r ...
... From a latitude of 40°, an object with a declination of +40° will, at some point in time during the day or night, pass directly overhead through the zenith. In general Declination at zenith = Latitude of observer The 24 Ephemeris Stars in the SBO Catalog of Astronomical Objects have Object Numbers r ...
PRE-LAB
... invented sky charts that are comparable to maps. Maps have a coordinate system — you can find any place on EARTH by specifying its LONGITUDE and LATITUDE (the x and y axis). Below you can see what we mean by LONGITUDE and LATITUDE. The positions of the stars in the sky are described in the same mann ...
... invented sky charts that are comparable to maps. Maps have a coordinate system — you can find any place on EARTH by specifying its LONGITUDE and LATITUDE (the x and y axis). Below you can see what we mean by LONGITUDE and LATITUDE. The positions of the stars in the sky are described in the same mann ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... 1) During Spring Break you and your friends plan to travel south to Cancun, Mexico for a week of sun and fun. You arrive in Cancun on a clear night. You look up at the stars and notice that they appear different that the stars you see in Syracuse, NY. Which of the statements below is true regarding ...
... 1) During Spring Break you and your friends plan to travel south to Cancun, Mexico for a week of sun and fun. You arrive in Cancun on a clear night. You look up at the stars and notice that they appear different that the stars you see in Syracuse, NY. Which of the statements below is true regarding ...
S1_LectureOutlines
... – Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. – Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.5 day cycle of phases). – Tropical year (cycle of seasons) is 20 minutes shorter than sidereal years (time to orbit Sun). ...
... – Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. – Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.5 day cycle of phases). – Tropical year (cycle of seasons) is 20 minutes shorter than sidereal years (time to orbit Sun). ...
the astrolabe - IREM Aix
... Front of the astrolabe 1. Matrix or mother: a disc of brass or bronze 10 to 50 cm in diameter which accommodates the various parts of the instrument. 2. Tympanum: an engraved plate that is placed on the mother. Designed for a given latitude, certain astrolabes possess several of these. 3. Spider (or ...
... Front of the astrolabe 1. Matrix or mother: a disc of brass or bronze 10 to 50 cm in diameter which accommodates the various parts of the instrument. 2. Tympanum: an engraved plate that is placed on the mother. Designed for a given latitude, certain astrolabes possess several of these. 3. Spider (or ...
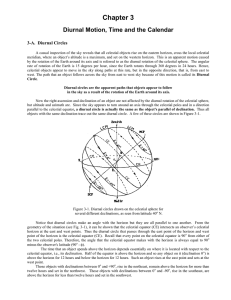
CHAPTER 3, Diurnal Motion - The College of New Jersey
... Notice that diurnal circles make an angle with the horizon but they are all parallel to one another. From the geometry of the situation (see Fig. 3-1), it can be shown that the celestial equator (CE) intersects an observer’s celestial horizon at the east and west points. Thus the diurnal circle that ...
... Notice that diurnal circles make an angle with the horizon but they are all parallel to one another. From the geometry of the situation (see Fig. 3-1), it can be shown that the celestial equator (CE) intersects an observer’s celestial horizon at the east and west points. Thus the diurnal circle that ...
Testing - Montgomery College
... – Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. – Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.53 day cycle of phases). – Tropical year (cycle of seasons) is 20 minutes shorter than sidereal years (time to orbit Sun). ...
... – Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. – Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.53 day cycle of phases). – Tropical year (cycle of seasons) is 20 minutes shorter than sidereal years (time to orbit Sun). ...
chapterS1time - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... – Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. – Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.5 day cycle of phases). – Tropical year (cycle of seasons) is 20 minutes shorter than sidereal years (time to orbit Sun). ...
... – Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. – Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.5 day cycle of phases). – Tropical year (cycle of seasons) is 20 minutes shorter than sidereal years (time to orbit Sun). ...
Chapter S1 How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary
... •! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods? –! Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. –! Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.5 day cycle of phases). –! Tropical year (cycle of season ...
... •! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods? –! Sidereal day (Earth’s rotation with respect to stars) is 4 minutes shorter than a solar day. –! Sidereal month (27.3 day orbit of moon) is shorter then synodic month (29.5 day cycle of phases). –! Tropical year (cycle of season ...
Chapter 2 CELESTIAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS
... the geographic sphere are specified by the coordinates called geographic longitude and latitude. The origin for this geographic coordinate system is the point where the Prime Meridian and the Geographic Equator intersect. This is a point located off the coast of west-central Africa. To specify a loc ...
... the geographic sphere are specified by the coordinates called geographic longitude and latitude. The origin for this geographic coordinate system is the point where the Prime Meridian and the Geographic Equator intersect. This is a point located off the coast of west-central Africa. To specify a loc ...
Week 2
... position on Earth determines which constellations remain below the horizon. • They depend on time of year because Earth’s orbit changes the apparent location of the Sun among the stars! ...
... position on Earth determines which constellations remain below the horizon. • They depend on time of year because Earth’s orbit changes the apparent location of the Sun among the stars! ...
Printer Friendly Version
... Pre Test on the Seasons (This is an example of instructions you will see on your test.) sheet. Write your form number and exam number after your name." Part 1 Multiple Choice 1. The two most important things which determine the amount of energy falling on an object in one day are: A. The changing st ...
... Pre Test on the Seasons (This is an example of instructions you will see on your test.) sheet. Write your form number and exam number after your name." Part 1 Multiple Choice 1. The two most important things which determine the amount of energy falling on an object in one day are: A. The changing st ...
Celestial Objects
... Precession 6 – The Earth behaves somewhat like a spinning top, causing the axis of rotation to trace out a circle. This slow conical motion of the Earth’s axis of rotation is called precession, and is due to the gravitational effects of the Sun and Moon on the Earth’s equatorial bulge. Precession sl ...
... Precession 6 – The Earth behaves somewhat like a spinning top, causing the axis of rotation to trace out a circle. This slow conical motion of the Earth’s axis of rotation is called precession, and is due to the gravitational effects of the Sun and Moon on the Earth’s equatorial bulge. Precession sl ...
Lesson 1 - The DK Foundation
... MC is an abbreviation of Medium Coeli: the midpoint of the Heavens with the IC (Imum Coeli) being its opposite end. The MC is a long way from being the point over our heads, unless one is born much nearer the Equator. The MC is the point of interception between the ecliptic, the path of the Sun and ...
... MC is an abbreviation of Medium Coeli: the midpoint of the Heavens with the IC (Imum Coeli) being its opposite end. The MC is a long way from being the point over our heads, unless one is born much nearer the Equator. The MC is the point of interception between the ecliptic, the path of the Sun and ...
SylTerNav\4Curr\emet
... 7.3.1 describe the concept of the earth's axial rotation causing change in the hour angle of bodies; 7.3.2 define Greenwhich Hour Angle (GHA), Local Hour Angle (LHA) and longitude and explain their relationships; 7.3.3 state the rate of change of GHA of the sun and Aries; 7.3.4 estimate the geograph ...
... 7.3.1 describe the concept of the earth's axial rotation causing change in the hour angle of bodies; 7.3.2 define Greenwhich Hour Angle (GHA), Local Hour Angle (LHA) and longitude and explain their relationships; 7.3.3 state the rate of change of GHA of the sun and Aries; 7.3.4 estimate the geograph ...
Armillary sphere

An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (in the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centred on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features such as the ecliptic. As such, it differs from a celestial globe, which is a smooth sphere whose principal purpose is to map the constellations.With the Earth as center, an armillary sphere is known as Ptolemaic. With the sun as center, it is known as Copernican.