S11 PHY114 Problem Set 3
... star where located at the center of the star. Newton knew this fact, but he proved it by a much more complicated method: Gauss found this simpler proof many decades later. (d) The gravitational field of a non-spherical star is not the same as that of a point mass at its center. The argument above bre ...
... star where located at the center of the star. Newton knew this fact, but he proved it by a much more complicated method: Gauss found this simpler proof many decades later. (d) The gravitational field of a non-spherical star is not the same as that of a point mass at its center. The argument above bre ...
Modeling the Photophoretic Force and Brownian Motion of a Single
... The initial simulations of tracking the trajectories of aggregates due to the photophoretic forces were incorrect due to the fact that the Brownian motion model was incorrect. Closer observations for modeling Brownian motion was taken. The model was changed from an aggregate to a single sphere and t ...
... The initial simulations of tracking the trajectories of aggregates due to the photophoretic forces were incorrect due to the fact that the Brownian motion model was incorrect. Closer observations for modeling Brownian motion was taken. The model was changed from an aggregate to a single sphere and t ...
the constellations of the zodiac
... The Babylonian calendar assigned each month to a sign, beginning with the position of the Sun at vernal equinox (March 21) which, at the time, was in the Aries constellation. For this reason the first constellation of the zodiac is still called “Aries” even after the vernal equinox has moved away fr ...
... The Babylonian calendar assigned each month to a sign, beginning with the position of the Sun at vernal equinox (March 21) which, at the time, was in the Aries constellation. For this reason the first constellation of the zodiac is still called “Aries” even after the vernal equinox has moved away fr ...
File - metc instructors collab site
... Defines 'rational horizon', 'zenith' and 'nadir' Defines 'vertical circle' and 'prime vertical circle' Defines 'elevated pole' and 'depressed pole' Proves that the altitude of the elevated pole is equal to the observer's latitude Defines the observer's upper and lower celestial meridian Identifies t ...
... Defines 'rational horizon', 'zenith' and 'nadir' Defines 'vertical circle' and 'prime vertical circle' Defines 'elevated pole' and 'depressed pole' Proves that the altitude of the elevated pole is equal to the observer's latitude Defines the observer's upper and lower celestial meridian Identifies t ...
History
... Late GREEK Astronomy Hipparchus (160-127 B.C.) – First to observe the precession of the poles and explained them with eccentric circles as planetary orbits; thus… – Agreed with Aristarchus’ heliocentric view. – To avoid criticism, he explained the precession from a geocentric view using epicycles a ...
... Late GREEK Astronomy Hipparchus (160-127 B.C.) – First to observe the precession of the poles and explained them with eccentric circles as planetary orbits; thus… – Agreed with Aristarchus’ heliocentric view. – To avoid criticism, he explained the precession from a geocentric view using epicycles a ...
Word - Stefan`s Florilegium
... In our current system of reckoning, the time of sunrise and sunset varies throughout the year, being 6 AM and 6 PM respectively only at the two equinoxes. The ancients Greeks, on the other hand, considered the day and night as being quite distinct and divided the day into 12 equal parts and the nigh ...
... In our current system of reckoning, the time of sunrise and sunset varies throughout the year, being 6 AM and 6 PM respectively only at the two equinoxes. The ancients Greeks, on the other hand, considered the day and night as being quite distinct and divided the day into 12 equal parts and the nigh ...
CONSTELLATIONS
... Locate and identify the following constellations. The myth of Andromeda claims that her mother, Queen Cassiopeia, was so proud of her daughter's beauty that she boasted it surpassed even that of the nymphs of the sea. Such arrogance offended the gods, who released floods in retribution and threatene ...
... Locate and identify the following constellations. The myth of Andromeda claims that her mother, Queen Cassiopeia, was so proud of her daughter's beauty that she boasted it surpassed even that of the nymphs of the sea. Such arrogance offended the gods, who released floods in retribution and threatene ...
ADAS Simple Guide to Telescope Instrumentation and Operation
... showing angle of latitude, declination and ...
... showing angle of latitude, declination and ...
talk - AVN training site
... measured in degrees. All objects above the horizon have positive altitudes and the horizon can be defined as a set of all points for which the altitude is 0°. Azimuth => angular distance measured eastward from the north point along the horizon from 0° to 360° up to the point where the vertical circ ...
... measured in degrees. All objects above the horizon have positive altitudes and the horizon can be defined as a set of all points for which the altitude is 0°. Azimuth => angular distance measured eastward from the north point along the horizon from 0° to 360° up to the point where the vertical circ ...
Latitude and Longitude - Harvard University Laboratory for
... A star at the zenith will have declination equal to your latitude. If you can get a good north-south axis, it is possible to measure latitude. Eg. Use a long stick with a rule at the end and a plumb-bob to keep the stick vertical This was used by the Polynesians to measure latitude – They would typi ...
... A star at the zenith will have declination equal to your latitude. If you can get a good north-south axis, it is possible to measure latitude. Eg. Use a long stick with a rule at the end and a plumb-bob to keep the stick vertical This was used by the Polynesians to measure latitude – They would typi ...
Chapter 3
... Any circle on the surface of the earth whose plane passes through the center of the earth is called a great circle. Thus, a great circle is a circle with the greatest possible diameter on the surface of the earth. Any circle on the surface of the earth whose plane does not pass through the earth's c ...
... Any circle on the surface of the earth whose plane passes through the center of the earth is called a great circle. Thus, a great circle is a circle with the greatest possible diameter on the surface of the earth. Any circle on the surface of the earth whose plane does not pass through the earth's c ...
Chapter 2
... depend on the time or place where observations are made, they can be used to arrange the stars in order in catalogues. Catalogues are used by astronomers to find a particular star to observe. The fact that right ascension and declination don’t vary with time or place is an advantage in this case. It ...
... depend on the time or place where observations are made, they can be used to arrange the stars in order in catalogues. Catalogues are used by astronomers to find a particular star to observe. The fact that right ascension and declination don’t vary with time or place is an advantage in this case. It ...
Using Star Charts
... the north to an angle of 44o. Imagine yourself at the centre of the cylinder looking up at it. A horizontal plane through your position marks the horizon where it cuts the chart. During the night the chart rotates around its axis, causing some stars to rise and some to set. If the positions of the p ...
... the north to an angle of 44o. Imagine yourself at the centre of the cylinder looking up at it. A horizontal plane through your position marks the horizon where it cuts the chart. During the night the chart rotates around its axis, causing some stars to rise and some to set. If the positions of the p ...
Celestial Navigation
... 'Beam me up, Scotty', and Captain Kirk of SS Enterprise is vaporized, transported through space, only to materialize on another planet; adventures well known to generations of Star Trek fans. As it happens, centuries before Star Trek ever came into being, when it was a mere twinkle in the galaxy i ...
... 'Beam me up, Scotty', and Captain Kirk of SS Enterprise is vaporized, transported through space, only to materialize on another planet; adventures well known to generations of Star Trek fans. As it happens, centuries before Star Trek ever came into being, when it was a mere twinkle in the galaxy i ...
Science Argumentative Writing Prompt Problem: Scientists have
... It is not known with certainty how planets are formed. The most popular theory is that they are formed during the collapse of a nebula into a thin disk of gas and dust. A proto-star (proto = early) forms at the core, surrounded by a rotating proto-planetary disk. Through a process called accretion ( ...
... It is not known with certainty how planets are formed. The most popular theory is that they are formed during the collapse of a nebula into a thin disk of gas and dust. A proto-star (proto = early) forms at the core, surrounded by a rotating proto-planetary disk. Through a process called accretion ( ...
Volume XXVI - Royal Asiatic Society
... sea and sailed up the Tai-tong river, “guided or at least influenced by the reigning constellation,” With him came five thousand followers including scholars, astrologers, calendar makers, musicians, artisans and workmen skilled in “a hundred useful trades,” Stone markers used in his system of land ...
... sea and sailed up the Tai-tong river, “guided or at least influenced by the reigning constellation,” With him came five thousand followers including scholars, astrologers, calendar makers, musicians, artisans and workmen skilled in “a hundred useful trades,” Stone markers used in his system of land ...
Coordinates and Time - University of Florida Astronomy
... Now why on the last slide did I write (J2000.0) after the RA and Dec? What that notation means is that these are the coordinates at which you would find the galactic center on the first day of 2000. This is unfortunately necessary because the equatorial coordinates of objects change with time. ...
... Now why on the last slide did I write (J2000.0) after the RA and Dec? What that notation means is that these are the coordinates at which you would find the galactic center on the first day of 2000. This is unfortunately necessary because the equatorial coordinates of objects change with time. ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
slides - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... – Altitude: vertical angular elevation above the horizon – Azimuth: direction from North to the object: angle measured along the horizon towards the east along the horizon. ...
... – Altitude: vertical angular elevation above the horizon – Azimuth: direction from North to the object: angle measured along the horizon towards the east along the horizon. ...
Lecture 8 - Kepler and Brahe
... that this is a voluntary choice based on his attitude. He refused to add epicycles. But now, of course, he had no model of the motions of the planets. Kepler realized that to get the most out of Tycho’s data, he first needed to determine the Earth’s orbit, since all planetary observations are made f ...
... that this is a voluntary choice based on his attitude. He refused to add epicycles. But now, of course, he had no model of the motions of the planets. Kepler realized that to get the most out of Tycho’s data, he first needed to determine the Earth’s orbit, since all planetary observations are made f ...
Lecture 1 - Simon P Driver
... along the eclip/c# (1 deg per 78 years). NB: nowdays Sun in Pisces during Vernal Equinox ...
... along the eclip/c# (1 deg per 78 years). NB: nowdays Sun in Pisces during Vernal Equinox ...
History of Astronomy
... The solstices (about June 21 and December 21) are when the Sun rises at the most extreme north and south points The equinoxes (equal day and night and about March 21 and September 23) are when the Sun rises directly east Ancients marked position of Sun rising and setting to determine the seaso ...
... The solstices (about June 21 and December 21) are when the Sun rises at the most extreme north and south points The equinoxes (equal day and night and about March 21 and September 23) are when the Sun rises directly east Ancients marked position of Sun rising and setting to determine the seaso ...
PHYS_3380_082615_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - in some regions, not much differentiation between the seasons. - different constellations visible at different times of the year - can use them to tell what month it is. For example, Scorpius is only visible in the northern hemisphere's evening sky in the summer. - many of the myths associated wit ...
... - in some regions, not much differentiation between the seasons. - different constellations visible at different times of the year - can use them to tell what month it is. For example, Scorpius is only visible in the northern hemisphere's evening sky in the summer. - many of the myths associated wit ...
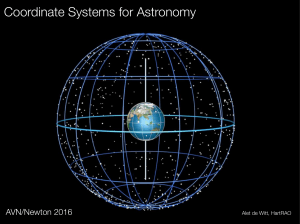
Armillary sphere

An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (in the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centred on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features such as the ecliptic. As such, it differs from a celestial globe, which is a smooth sphere whose principal purpose is to map the constellations.With the Earth as center, an armillary sphere is known as Ptolemaic. With the sun as center, it is known as Copernican.