Know your molecules organizer
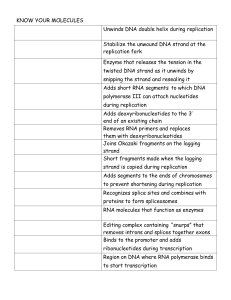
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
Protein Synthesis Notes: Transcription and Translation
... 3. The RNA bases attach to the complementary DNA template, and ________ is made! 4. The RNA polymerase recognizes a „stop‟ part on the DNA molecule and _____________________ the new _________________ molecule. The mRNA leaves the ___________________ and travels to the ______________________. o Trans ...
... 3. The RNA bases attach to the complementary DNA template, and ________ is made! 4. The RNA polymerase recognizes a „stop‟ part on the DNA molecule and _____________________ the new _________________ molecule. The mRNA leaves the ___________________ and travels to the ______________________. o Trans ...
File
... 17. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the gro ...
... 17. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the gro ...
DNA - TeacherWeb
... Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the protein. 3. Cells use only the genes that directs the making of proteins needed by that cell. ...
... Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the protein. 3. Cells use only the genes that directs the making of proteins needed by that cell. ...
Write True if the statement is true
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
Genetic Information
... will only bond with their complementary base like a lock and a key o adenine + thymine o guanine + cytosine if you know one strand you can figure out the other strand o CGTTAACGTA o GCAATTGCAT DNA Replication o Occurs during interphase, right before cell enters prophase (mitosis and mitosis I) ...
... will only bond with their complementary base like a lock and a key o adenine + thymine o guanine + cytosine if you know one strand you can figure out the other strand o CGTTAACGTA o GCAATTGCAT DNA Replication o Occurs during interphase, right before cell enters prophase (mitosis and mitosis I) ...
Earth`s Early History 10-2
... Identify some of the hypotheses about early Earth and the origin of life. Discuss the hypothesis that explains the origin of ...
... Identify some of the hypotheses about early Earth and the origin of life. Discuss the hypothesis that explains the origin of ...
Presentation title: Introduction to RNA
... The central dogma of genetics is that the genome, comprised of DNA, encodes many thousands of genes that can be transcribed into RNA. Following this, the RNA may be translated into amino acids giving a functional protein. While the genome of an individual will be identical for each cell througho ...
... The central dogma of genetics is that the genome, comprised of DNA, encodes many thousands of genes that can be transcribed into RNA. Following this, the RNA may be translated into amino acids giving a functional protein. While the genome of an individual will be identical for each cell througho ...
Reviewing Key Concepts Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Section Review 12-3
... 5. Each tRNA molecule contains three unpaired bases, called the , which ensure that amino acids are added in the correct sequence. ...
... 5. Each tRNA molecule contains three unpaired bases, called the , which ensure that amino acids are added in the correct sequence. ...
Protein Synthesis Questions
... 13. If an mRNA had the following code, what string of amino acids would be formed? Use Figure 12-17 to help you. ...
... 13. If an mRNA had the following code, what string of amino acids would be formed? Use Figure 12-17 to help you. ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... LS-C5. Illustrate the relationship of the structure and function of DNA to protein synthesis and the characteristics of an organism. ...
... LS-C5. Illustrate the relationship of the structure and function of DNA to protein synthesis and the characteristics of an organism. ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
Worksheet 6 - Iowa State University
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
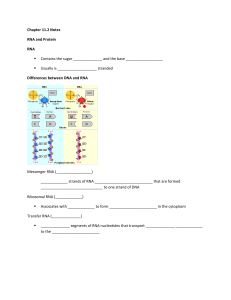
Chapter 11.2 Notes RNA and Protein RNA Contains the sugar and
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
DNA -> RNA -> Proteins
... Transcription • This process is called transcription, because the DNA transcribes “copies” itself • It takes advantage of base pairing ...
... Transcription • This process is called transcription, because the DNA transcribes “copies” itself • It takes advantage of base pairing ...
Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria.
... Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria. 1. Define the three main types of RNA. 2. What are the nucleotides that are used to synthesize RNA? 3. What is the direction of RNA polymerization? 4. What is meant by the statement “RNA polymerization is thermodynamically assisted by PPi hydroly ...
... Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria. 1. Define the three main types of RNA. 2. What are the nucleotides that are used to synthesize RNA? 3. What is the direction of RNA polymerization? 4. What is meant by the statement “RNA polymerization is thermodynamically assisted by PPi hydroly ...
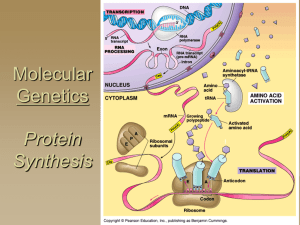
Molecular Genetics
... encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
... encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
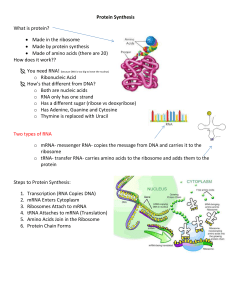
Protein Synthesis - Madison County Schools
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
Three Types of RNA and Their Functions
... Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA is more often found in nature as a single-strand composition. There are three main types of RNA, mRNA, tRNA and rRNA, and they play active roles within p ...
... Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA is more often found in nature as a single-strand composition. There are three main types of RNA, mRNA, tRNA and rRNA, and they play active roles within p ...
CS4030: Tutorial 1- Biological Issues (from Bioinformatics ch 1)
... 1. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) differs from ribonucleic acid (RNA) in two ways: (1) RNA uses the nitrogenous base uracil in place of DNA’s thymine, and (2) the hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the 2’ carbon of the deoxyribose sugar of RNA is replaced with just a hydrogen (H) in DNA. Sketch the chemic ...
... 1. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) differs from ribonucleic acid (RNA) in two ways: (1) RNA uses the nitrogenous base uracil in place of DNA’s thymine, and (2) the hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the 2’ carbon of the deoxyribose sugar of RNA is replaced with just a hydrogen (H) in DNA. Sketch the chemic ...
File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes f ...
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes f ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.