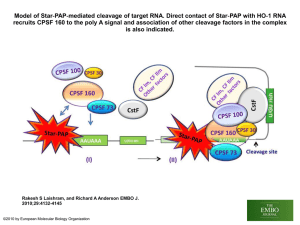
Chapter 10 Lesson 1
... 5. Transcription in Eukaryotes...pg. 252-253 a. Introns – do not code for a.acids b. Exons – code for a.acids (expressed) c. Why introns…? 1. no current function 2. ancient genes that have lost function 3. remnants of viruses d. Process called mRNA processing pg. 253 ...
... 5. Transcription in Eukaryotes...pg. 252-253 a. Introns – do not code for a.acids b. Exons – code for a.acids (expressed) c. Why introns…? 1. no current function 2. ancient genes that have lost function 3. remnants of viruses d. Process called mRNA processing pg. 253 ...
doc 3.4.2 protein synthesis checklist
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Initiation at the promoter site by RNA polymerase opens up the DNA molecule Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
... Initiation at the promoter site by RNA polymerase opens up the DNA molecule Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
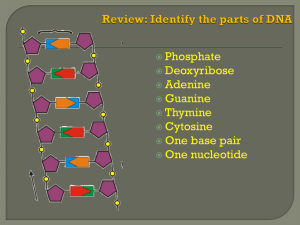
DNA and RNA
... only bind with Thymine and Guanine will only bond with Cytosine based on the number of hydrogen bonds each can form. A and T each form 2 while C and G each form ...
... only bind with Thymine and Guanine will only bond with Cytosine based on the number of hydrogen bonds each can form. A and T each form 2 while C and G each form ...
Protein Synth Notes GO New
... Example Problem 1. Write out the complementary DNA bases for the DNA strand: DNA #1: A A C G T G C A T T G A C G G DNA #2: __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ B. RNA molecule: 1. sugar: 2. nitrogen bases & pairings: 3. # of strands: 4. location: starts in Types of RNA ...
... Example Problem 1. Write out the complementary DNA bases for the DNA strand: DNA #1: A A C G T G C A T T G A C G G DNA #2: __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ B. RNA molecule: 1. sugar: 2. nitrogen bases & pairings: 3. # of strands: 4. location: starts in Types of RNA ...
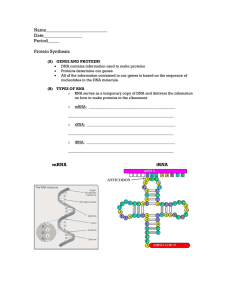
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... The nucleotide sequence transcribed from DNA to a strand of mRNA is a genetic message that has ALL the information needed to build a protein. ...
... The nucleotide sequence transcribed from DNA to a strand of mRNA is a genetic message that has ALL the information needed to build a protein. ...
Genomics wordsearch
... nucleotides in a DNA/RNA molecule which codes for an amino acid Cytosine – A nucleotide component of DNA/RNA ...
... nucleotides in a DNA/RNA molecule which codes for an amino acid Cytosine – A nucleotide component of DNA/RNA ...
“bDNA for gene expression in plant and animal tissue”
... “bDNA for gene expression in plant and animal tissue” December 2nd, 2014 at 12:00-1:00pm Genomics bldg. Room 1102A Speaker: Harry Vacek, Quantigene Specialist Please RSVP to james.van@ebioscience.com food will be provided for RSVPs Measure up to 80 genes or 4 RNA targets in 1 sample Imagine if you c ...
... “bDNA for gene expression in plant and animal tissue” December 2nd, 2014 at 12:00-1:00pm Genomics bldg. Room 1102A Speaker: Harry Vacek, Quantigene Specialist Please RSVP to james.van@ebioscience.com food will be provided for RSVPs Measure up to 80 genes or 4 RNA targets in 1 sample Imagine if you c ...
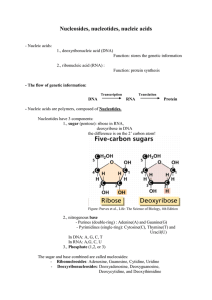
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... strands are connected by hydrogenbonds between the bases (complementary basepairing): ...
... strands are connected by hydrogenbonds between the bases (complementary basepairing): ...
Cloze passage 4
... Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 scientist who put ...
... Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 scientist who put ...
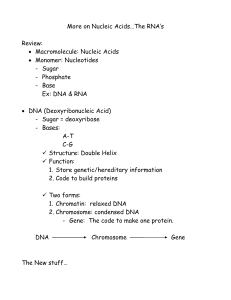
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... from DNA and carry those instructions to the ribosome/ “workbench” 3. tRNA: [“t” = transfer] - structure: upside down hair-pin loop or upside down “t”. - function: locate and transfer the correct amino acid to the mRNA on the rRNA (ribosome) and place them in the correct order and location. Differen ...
... from DNA and carry those instructions to the ribosome/ “workbench” 3. tRNA: [“t” = transfer] - structure: upside down hair-pin loop or upside down “t”. - function: locate and transfer the correct amino acid to the mRNA on the rRNA (ribosome) and place them in the correct order and location. Differen ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes
... •Long _______________ of _______________ •3 main differences between DNA and RNA ...
... •Long _______________ of _______________ •3 main differences between DNA and RNA ...
No Slide Title
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the DNA message out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm to ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis. ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the DNA message out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm to ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Kent City School District
... Initiation at the promoter site by RNA polymerase opens up the DNA molecule Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
... Initiation at the promoter site by RNA polymerase opens up the DNA molecule Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
DNA versus RNA Notes File
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
Chapter 10 Section 3 Notes Answer Key
... 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins to the nucleus for the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acid bond. b. Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to bu ...
... 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins to the nucleus for the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acid bond. b. Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to bu ...
Crossword Puzzle: Protein Synthesis
... 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The numbe ...
... 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The numbe ...
Protein Synthesis - Biology Junction
... transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The number of amino acids that exist 16. Number of strands making up RNA 19. DNA to RNA ...
... transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The number of amino acids that exist 16. Number of strands making up RNA 19. DNA to RNA ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
... up with the mRNA in the ribosome and an amino acids are joined together in a long polypeptide line which will form the protein • This process continues until the stop codon on the mRNA is reached at which point all the translation machinery separates and the protein is released and it folds up into ...
... up with the mRNA in the ribosome and an amino acids are joined together in a long polypeptide line which will form the protein • This process continues until the stop codon on the mRNA is reached at which point all the translation machinery separates and the protein is released and it folds up into ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
Expressing Genetic Information
... 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in a certain way. What is that way? 4. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA. 5. What is the genetic code? 6. What is the Human Genome Project? 7. What percentage of RNA is rRNA? Why is it so hig ...
... 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in a certain way. What is that way? 4. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA. 5. What is the genetic code? 6. What is the Human Genome Project? 7. What percentage of RNA is rRNA? Why is it so hig ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.