Lec:1 Dr.Mohammed Alhamdany Molecular and genetic factors in
... transcribed RNA molecules do not code for proteins. There are various categories of non-coding RNA (ncRNA), including transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and microRNA (miRNA). There is increasing evidence to suggest that miRNAs ...
... transcribed RNA molecules do not code for proteins. There are various categories of non-coding RNA (ncRNA), including transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and microRNA (miRNA). There is increasing evidence to suggest that miRNAs ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Organizer
... 2. RNA, like DNA, is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides. What are the four differences between DNA and RNA? a. ...
... 2. RNA, like DNA, is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides. What are the four differences between DNA and RNA? a. ...
proteins
... How the information in the DNA results in proteins Promoter – AUG Transcription: copy of the gene made on an RNA molecule (messenger RNA, or mRNA ). This resulting RNA will have exactly the same sequence as one of the strands of the gene but substituting U for T The strand identical to the ...
... How the information in the DNA results in proteins Promoter – AUG Transcription: copy of the gene made on an RNA molecule (messenger RNA, or mRNA ). This resulting RNA will have exactly the same sequence as one of the strands of the gene but substituting U for T The strand identical to the ...
Question How does DNA control a cell?By controlling Protein
... between the new AA and the polypeptide chain in the P-site. ...
... between the new AA and the polypeptide chain in the P-site. ...
Lecture 3 - Transcription (student)
... • mRNA acts as the middle man – It can take the DNA message out of the nucleus to synthesis polypeptides ...
... • mRNA acts as the middle man – It can take the DNA message out of the nucleus to synthesis polypeptides ...
Slide ()
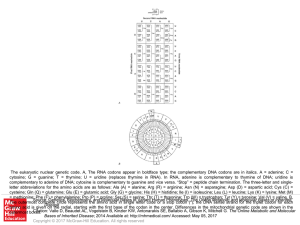
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
INHERITANCE
... Designate each color of gumdrops a different base (A=red, T=green, for example) Designate the toothpicks as the bonds between the bases Give the students a list of bases that ranges from 10 to 15 bases long The students will then lay out the sequence using the gumdrops and the sticking toothpicks in ...
... Designate each color of gumdrops a different base (A=red, T=green, for example) Designate the toothpicks as the bonds between the bases Give the students a list of bases that ranges from 10 to 15 bases long The students will then lay out the sequence using the gumdrops and the sticking toothpicks in ...
The four types of nucleotides in DNA are Adenine, Thymine
... B) Transfer RNA reads the information stored in mRNA and uses it to synthesize a protein C) Transfer RNA carries information from genes into the ribosome for protein synthesis D) Transfer RNA analyzes a protein in order to create an exact duplicate ...
... B) Transfer RNA reads the information stored in mRNA and uses it to synthesize a protein C) Transfer RNA carries information from genes into the ribosome for protein synthesis D) Transfer RNA analyzes a protein in order to create an exact duplicate ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: Cells cannot make
... 3. It involves three major processes in a eukaryotic cell: __________________________ (copies DNA) __________________________ (converts DNA to RNA) __________________________ (interprets an RNA message to a string of amino acids which make up proteins) 4. The double helix structure explains how DNA ...
... 3. It involves three major processes in a eukaryotic cell: __________________________ (copies DNA) __________________________ (converts DNA to RNA) __________________________ (interprets an RNA message to a string of amino acids which make up proteins) 4. The double helix structure explains how DNA ...
The 11th lecture in molecular biology
... structure in 5 end (Eukaryotic )and poly A at 3 end this will protect m RNA from degradation at lest few days ...
... structure in 5 end (Eukaryotic )and poly A at 3 end this will protect m RNA from degradation at lest few days ...
Notes
... Components and Structure of DNA: This was deduced by Watson and Crick using 3 pieces of information: 1) DNA is made of 4 nucleotides 2) Chargaff’s Rules, and 3) X-Ray evidence. DNA is a nucleic acid polymer made of 4 different monomers called nucleotides. The 4 nucleotides are: Each nucleotide conta ...
... Components and Structure of DNA: This was deduced by Watson and Crick using 3 pieces of information: 1) DNA is made of 4 nucleotides 2) Chargaff’s Rules, and 3) X-Ray evidence. DNA is a nucleic acid polymer made of 4 different monomers called nucleotides. The 4 nucleotides are: Each nucleotide conta ...
All Living things pass on their genetic heritage by common
... RNA polymerase makes a single stranded RNA transcript from one strand of the unwound DNA helix. Activated A, U, G and C ribonucleotide triphosphates base pair with the DNA and are linked by the RNA polymerase into RNA polynucleotides. RNA transcripts 1. rRNA, ribosomal RNA: In large and small riboso ...
... RNA polymerase makes a single stranded RNA transcript from one strand of the unwound DNA helix. Activated A, U, G and C ribonucleotide triphosphates base pair with the DNA and are linked by the RNA polymerase into RNA polynucleotides. RNA transcripts 1. rRNA, ribosomal RNA: In large and small riboso ...
RNA
... mRNA (messenger RNA) tRNA (transfer RNA) rRNA (ribosomal RNA) Transcription produces three general classes* of RNA, each of which plays a role in translation (protein synthesis) * actually, there are many more classes of small RNA molecules that perform important functions in the cell, including gen ...
... mRNA (messenger RNA) tRNA (transfer RNA) rRNA (ribosomal RNA) Transcription produces three general classes* of RNA, each of which plays a role in translation (protein synthesis) * actually, there are many more classes of small RNA molecules that perform important functions in the cell, including gen ...
Chapter 14
... DNA is like a book of instructions in each cell • The instructions are written in the alphabet of A,T,G,C. But merely knowing the letter does not tell us how the genes work • DNA consist of two strands of nucleotides twisted together in a double helix. – In replication, the two strands unwind to se ...
... DNA is like a book of instructions in each cell • The instructions are written in the alphabet of A,T,G,C. But merely knowing the letter does not tell us how the genes work • DNA consist of two strands of nucleotides twisted together in a double helix. – In replication, the two strands unwind to se ...
Ch. 10 Vocabs
... -Ribose: a five-carbon sugar present in RNA. -Messenger RNA (mRNA): a single-stranded RNA molecule that encodes the information to make a protein. -Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): an organelle that contains most of the RNA in the cell an that is responsible for ribosome function. -Transfer RNA (tRNA): an RNA ...
... -Ribose: a five-carbon sugar present in RNA. -Messenger RNA (mRNA): a single-stranded RNA molecule that encodes the information to make a protein. -Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): an organelle that contains most of the RNA in the cell an that is responsible for ribosome function. -Transfer RNA (tRNA): an RNA ...
Biology 211 Intro Molecular and Cell Biology
... AUG serves as the start codon: signal to start translation ...
... AUG serves as the start codon: signal to start translation ...
Chapter 17 - Madeira City Schools
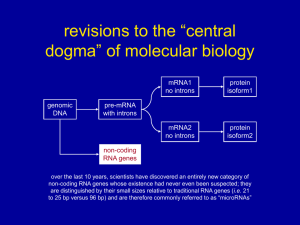
... b. many genes give rise to 2 or more different proteins depending on which segments are treated as exons during processing. c. introns may play role in variation of genes d. About 60% of genes are estimated to have alternative splicing sites. e. One gene does not equal one polypeptide ...
... b. many genes give rise to 2 or more different proteins depending on which segments are treated as exons during processing. c. introns may play role in variation of genes d. About 60% of genes are estimated to have alternative splicing sites. e. One gene does not equal one polypeptide ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... Once the mRNA strand is formed, it separates from the original DNA molecule and moves into the cytoplasm. It is now time for the next step in protein synthesis. STEP 2- ___________________________________________________ WHERE IT OCCURS- ___________________________________________________ OVERALL FU ...
... Once the mRNA strand is formed, it separates from the original DNA molecule and moves into the cytoplasm. It is now time for the next step in protein synthesis. STEP 2- ___________________________________________________ WHERE IT OCCURS- ___________________________________________________ OVERALL FU ...
Genetic Information DNA - Barnegat Township School District
... Only one chain of nucleotides – one strand Made of nucleotides that have A, C, G and U as nitrogenous bases • U replaces T • C pairs with G, A with U • Carries the coded message of DNA from the nucleus to the ribosomes (cytoplasm) – where this message is used to make proteins ...
... Only one chain of nucleotides – one strand Made of nucleotides that have A, C, G and U as nitrogenous bases • U replaces T • C pairs with G, A with U • Carries the coded message of DNA from the nucleus to the ribosomes (cytoplasm) – where this message is used to make proteins ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • When RNA molecules are formed, both the introns and the exons are copied from the DNA. • The introns are cut out of RNA molecules while they are still in the nucleus. • The remaining exons are then spliced back together to form the final mRNA. ...
... • When RNA molecules are formed, both the introns and the exons are copied from the DNA. • The introns are cut out of RNA molecules while they are still in the nucleus. • The remaining exons are then spliced back together to form the final mRNA. ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Questions
... What does Translation mean? What organelle makes proteins? What role does tRNA play in making proteins? What is an "anticodon"? What structure is it on? How is mRNA used to make proteins. Why are proteins so important to life? Given a strand of mRNA, be able to make an amino acid chain. (You will be ...
... What does Translation mean? What organelle makes proteins? What role does tRNA play in making proteins? What is an "anticodon"? What structure is it on? How is mRNA used to make proteins. Why are proteins so important to life? Given a strand of mRNA, be able to make an amino acid chain. (You will be ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.