Lecture 4-5 Outline
... Transcription units (genes) contain the transcribed information and all associated regulatory sequences for the production of an RNA transcript. Structure of eukaryotic gene: (i) Promoter region, DNA elements that bind transcription regulatory proteins; (ii) 5' untranslated region; (iii) coding regi ...
... Transcription units (genes) contain the transcribed information and all associated regulatory sequences for the production of an RNA transcript. Structure of eukaryotic gene: (i) Promoter region, DNA elements that bind transcription regulatory proteins; (ii) 5' untranslated region; (iii) coding regi ...
Transcription
... • critical steps involved in producing functional proteins in the cell. • Transcription involves synthesis of an RNA from the DNA template provided by the non-coding strand. • RNA polymerase In prokaryotes there is a single RNA polymerase enzyme, but in eukaryotes there are three types of RNA polyme ...
... • critical steps involved in producing functional proteins in the cell. • Transcription involves synthesis of an RNA from the DNA template provided by the non-coding strand. • RNA polymerase In prokaryotes there is a single RNA polymerase enzyme, but in eukaryotes there are three types of RNA polyme ...
Document
... Fe(H2O)63+ ---> Fe(OH)3 + 3H+ + 3H2O Ksp = [Fe3+][OH-]3 ≈ 10-38 M [Fe3+] = 10-38/[OH-]3 ...
... Fe(H2O)63+ ---> Fe(OH)3 + 3H+ + 3H2O Ksp = [Fe3+][OH-]3 ≈ 10-38 M [Fe3+] = 10-38/[OH-]3 ...
notes File - selu moodle
... Transcription uses the template strand of DNA to make a mRNA strand that has the same sequence as the coding strand (except that there are U’s in RNA and T’s in DNA) Translation uses a ribosome to read the mRNA and synthesize proteins RNA’s mRNA – carries the code rRNA – component of ribosomes tRNA ...
... Transcription uses the template strand of DNA to make a mRNA strand that has the same sequence as the coding strand (except that there are U’s in RNA and T’s in DNA) Translation uses a ribosome to read the mRNA and synthesize proteins RNA’s mRNA – carries the code rRNA – component of ribosomes tRNA ...
Bio 313 worksheet 14 - Iowa State University
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
RNA - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 4. How does a cell know it is making RNA from DNA instead of making more DNA from DNA ? 5. Change the following DNA strand into mRNA T-T-A-A-G-C-G-A-T-C 6. RNA is used in the making of ___________. 7. There are 20 different kinds of this type of RNA. ...
... 4. How does a cell know it is making RNA from DNA instead of making more DNA from DNA ? 5. Change the following DNA strand into mRNA T-T-A-A-G-C-G-A-T-C 6. RNA is used in the making of ___________. 7. There are 20 different kinds of this type of RNA. ...
Transcription
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... nitrogen bases, (U vs. T), and the structure (single stranded vs. double helix.) 5. What are the three types of RNA and what is their function? Messenger RNA (mRNA)-Transcribes the code from DNA and takes it from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA (tRNA)- Transfers amino acids from the cytop ...
... nitrogen bases, (U vs. T), and the structure (single stranded vs. double helix.) 5. What are the three types of RNA and what is their function? Messenger RNA (mRNA)-Transcribes the code from DNA and takes it from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA (tRNA)- Transfers amino acids from the cytop ...
(A) + RNA
... two or more samples and require uniform sampling conditions for this comparison to be valid. Many factors can contribute to variability in the analysis of samples, making the results difficult to reproduce between experiments: Sample degradation, extraction efficiency, contamination → RNA isolation ...
... two or more samples and require uniform sampling conditions for this comparison to be valid. Many factors can contribute to variability in the analysis of samples, making the results difficult to reproduce between experiments: Sample degradation, extraction efficiency, contamination → RNA isolation ...
Central Dogma of Cell Biology
... Translation • The mRNA leaves the nucleus cytoplasm • Message is read at the ribosome • 1 Codon (3 letter message) is translated into 1 amino acid • tRNA molecule has one end (anticodon) that matches the mRNA . Each anticodon specifies an amino acid. • The amino acids are bonded together as pept ...
... Translation • The mRNA leaves the nucleus cytoplasm • Message is read at the ribosome • 1 Codon (3 letter message) is translated into 1 amino acid • tRNA molecule has one end (anticodon) that matches the mRNA . Each anticodon specifies an amino acid. • The amino acids are bonded together as pept ...
Student work sheets for Power Point Slides
... 13) The protein structure is three dimensional because of the folding of the amino acids. 14) Endoplasmic reticulum is located outside the nucleus. 15) An anticodon consists of three base pairs which are opposite to the base pairs in the mRNA. Slide 4 16) Describe what you see from this slide. Slide ...
... 13) The protein structure is three dimensional because of the folding of the amino acids. 14) Endoplasmic reticulum is located outside the nucleus. 15) An anticodon consists of three base pairs which are opposite to the base pairs in the mRNA. Slide 4 16) Describe what you see from this slide. Slide ...
notes
... • RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and makes a complementary RNA copy from one DNA strand. • Once the RNA sequence has been synthesized, RNA polymerase will detach from the DNA molecule and the double helix will reform • The sequence of DNA that is transcribed into RNA is called a gene • Tra ...
... • RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and makes a complementary RNA copy from one DNA strand. • Once the RNA sequence has been synthesized, RNA polymerase will detach from the DNA molecule and the double helix will reform • The sequence of DNA that is transcribed into RNA is called a gene • Tra ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... like much of the DNA. Also, just like the DNA, it has to be edited to make it sensible. ...
... like much of the DNA. Also, just like the DNA, it has to be edited to make it sensible. ...
Transcription and Translation Candy Activity
... Notes labels Other? RNA: RNA has some key differences from DNA. List them below and make a key for the 4 RNA nucleotides. Paste a picture of the 4 RNA nucleotides clearly labeling: ribose, base, phosphate group and nucleotide name. ...
... Notes labels Other? RNA: RNA has some key differences from DNA. List them below and make a key for the 4 RNA nucleotides. Paste a picture of the 4 RNA nucleotides clearly labeling: ribose, base, phosphate group and nucleotide name. ...
Slide 1
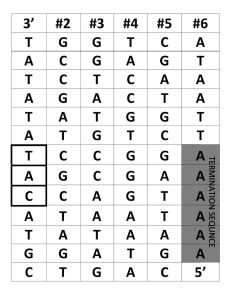
... Where are Polymerases? Where are transcription start/stop sites? Where are the 3’ and 5’ ends of the transcript? Which direction are the RNA polymerases moving? Why are the RNA transcripts so much shorter than the length of the DNA that encodes them? ...
... Where are Polymerases? Where are transcription start/stop sites? Where are the 3’ and 5’ ends of the transcript? Which direction are the RNA polymerases moving? Why are the RNA transcripts so much shorter than the length of the DNA that encodes them? ...
PPT: Mitosis, Meiosis, DNA, PS
... • Gametes = haploid = with only one set of chromosomes • For humans: – haploid number is 23 (n = 23) – Each set of 23 consists of 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome ...
... • Gametes = haploid = with only one set of chromosomes • For humans: – haploid number is 23 (n = 23) – Each set of 23 consists of 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome ...
Making Proteins - Hbwbiology.net
... Nucleic acid - A macromolecule made of nucleotides linked together. Ribonucleic acid - A nucleic acid of a single strand of nucleotides containing the five-carbon sugar ribose, which contains an additional H than deoxyribose. Instead of thymine (T), RNA contains uracil (U). transcription - The trans ...
... Nucleic acid - A macromolecule made of nucleotides linked together. Ribonucleic acid - A nucleic acid of a single strand of nucleotides containing the five-carbon sugar ribose, which contains an additional H than deoxyribose. Instead of thymine (T), RNA contains uracil (U). transcription - The trans ...
RNA - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 4. How does a cell know it is making RNA from DNA instead of making more DNA from DNA ? 5. Change the following DNA strand into mRNA T-T-A-A-G-C-G-A-T-C 6. RNA is used in the making of ___________. 7. There are 20 different kinds of this type of RNA. ...
... 4. How does a cell know it is making RNA from DNA instead of making more DNA from DNA ? 5. Change the following DNA strand into mRNA T-T-A-A-G-C-G-A-T-C 6. RNA is used in the making of ___________. 7. There are 20 different kinds of this type of RNA. ...
Regulating Protein Synthesis
... ! siRNAs and miRNAs (smallinterfering RNAs and micro RNAs) can regulate translation ! siRNAs and miRNAs are cut from double-stranded RNA; one strand joins a protein complex ! The protein-siRNA complex breaks down mRNAs that contain complementary sequences ! The protein-miRNA complex breaks down mRNA ...
... ! siRNAs and miRNAs (smallinterfering RNAs and micro RNAs) can regulate translation ! siRNAs and miRNAs are cut from double-stranded RNA; one strand joins a protein complex ! The protein-siRNA complex breaks down mRNAs that contain complementary sequences ! The protein-miRNA complex breaks down mRNA ...
Name: Protein Synthesis PRICE DNA DNA contains ______
... • Copies DNA & leaves through __________ pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, ____ ( no T ) • Carries the information for a ___________ protein • Made up of 500 to 1000 nucleotides long • Sequence of ____ bases called codon • AUG – methionine or start ________ • UAA, UAG, or UGA – ______ cod ...
... • Copies DNA & leaves through __________ pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, ____ ( no T ) • Carries the information for a ___________ protein • Made up of 500 to 1000 nucleotides long • Sequence of ____ bases called codon • AUG – methionine or start ________ • UAA, UAG, or UGA – ______ cod ...
CHAPTER 10 - Protein Synthesis The DNA genotype is expressed
... The genetic code is the Rosetta stone of life • Virtually all organisms share the same genetic code ...
... The genetic code is the Rosetta stone of life • Virtually all organisms share the same genetic code ...
Matt Reuter
... Role of RNA in the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Information Storage in the DNA Double Helix Consequences of Mutation and Cancer ...
... Role of RNA in the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Information Storage in the DNA Double Helix Consequences of Mutation and Cancer ...
Chapter 12 Notes - White Plains Public Schools
... Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Base pairing- Adenine (A)= Thymine (T) Cytosine(C)= Guanine (G) ...
... Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Base pairing- Adenine (A)= Thymine (T) Cytosine(C)= Guanine (G) ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.