Comparative analyses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNAs using
... spectrophotometer. The RNA Nano Assay makes it possible to estimate RNA concentrations in the range from 1000 ng Wl31 to 17 ng Wl31 . The presence of impurities including traces of DNA within RNA samples does not influence the concentration measurements. Like agarose gel electrophoresis, RNA Nano As ...
... spectrophotometer. The RNA Nano Assay makes it possible to estimate RNA concentrations in the range from 1000 ng Wl31 to 17 ng Wl31 . The presence of impurities including traces of DNA within RNA samples does not influence the concentration measurements. Like agarose gel electrophoresis, RNA Nano As ...
Protocol
... Part I: Oocyte RNA with Stratagene’s “Absolutely RNA Miniprep Kit” The objective of this part of the experiment is to isolate high quality RNA, which means RNA that is not degraded and is free from DNA contamination. The Stratagene kit uses a spin column packed with a silica-based matrix that specif ...
... Part I: Oocyte RNA with Stratagene’s “Absolutely RNA Miniprep Kit” The objective of this part of the experiment is to isolate high quality RNA, which means RNA that is not degraded and is free from DNA contamination. The Stratagene kit uses a spin column packed with a silica-based matrix that specif ...
Unusual C-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA
... The significance of the acidic tail, which is present in all eukaryotic C-terminal domains (Figure 6), is unclear. Deletion mapping experiments in yeast and mouse showed that mutants in which the acidic tail was removed were viable (5,9), indicating that removal of the acidic tail as such does not i ...
... The significance of the acidic tail, which is present in all eukaryotic C-terminal domains (Figure 6), is unclear. Deletion mapping experiments in yeast and mouse showed that mutants in which the acidic tail was removed were viable (5,9), indicating that removal of the acidic tail as such does not i ...
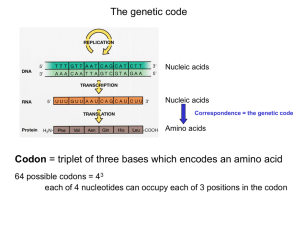
AUG
... Translation Initiation Initiation occurs at a special sequence on mRNA - ribosome binding site (RBS) or Shine-Dalgarno sequence - complementary to the 3’end of 16S rRNA 3’ end of 16S rRNA ...
... Translation Initiation Initiation occurs at a special sequence on mRNA - ribosome binding site (RBS) or Shine-Dalgarno sequence - complementary to the 3’end of 16S rRNA 3’ end of 16S rRNA ...
Chapter 18 PPT
... – It identified a specific protein required for some early steps in pattern formation – It increased understanding of the mother’s role in ...
... – It identified a specific protein required for some early steps in pattern formation – It increased understanding of the mother’s role in ...
Statistical analysis of simple repeats in the human genome
... E-mail addresses: francesco.piazza@epfl.ch (F. Piazza), pietro.lio@cl.cam.ac.uk (P. Liò). ...
... E-mail addresses: francesco.piazza@epfl.ch (F. Piazza), pietro.lio@cl.cam.ac.uk (P. Liò). ...
here - IMSS Biology 2014
... all the instructions to make skin, hair, digestive enzymes, immune system factors, everything! All this information, all of an organism’s DNA, is called the genome. A genome is sort of like a recipe book – it has all the instructions to make all different sorts of proteins, just like recipes have in ...
... all the instructions to make skin, hair, digestive enzymes, immune system factors, everything! All this information, all of an organism’s DNA, is called the genome. A genome is sort of like a recipe book – it has all the instructions to make all different sorts of proteins, just like recipes have in ...
QPCR Helpful Hints
... Lab typically uses the Nanodrop UV spectrophotometer which only requires 2 l of sample. Whatever method is used (UV or fluorescence) it is important to be consistent and not switch back and forth between quantification methods if data from multiple experiments is going to be compared. ...
... Lab typically uses the Nanodrop UV spectrophotometer which only requires 2 l of sample. Whatever method is used (UV or fluorescence) it is important to be consistent and not switch back and forth between quantification methods if data from multiple experiments is going to be compared. ...
Alignment of mRNA to genomic DNA Sequence
... then sequenced. The resulting EST sequences are compared with the nucleotide sequence of the entire genome (or the sequence of a single gene) to locate the gene (or parts of a gene) that contains each EST. ...
... then sequenced. The resulting EST sequences are compared with the nucleotide sequence of the entire genome (or the sequence of a single gene) to locate the gene (or parts of a gene) that contains each EST. ...
Supplementary Methods
... Poisson distributions for at least n hits for a transcript with detection frequency . For each transcript the detection frequency by shotgun sequencing will be dependent on the relative abundance of the gene, the length of the gene, and the uniformity of the ...
... Poisson distributions for at least n hits for a transcript with detection frequency . For each transcript the detection frequency by shotgun sequencing will be dependent on the relative abundance of the gene, the length of the gene, and the uniformity of the ...
Nonsense-suppressing mutation causes addition of amino acid at
... Exons – sequences found in a gene’s DNA and mature mRNA (expressed regions) Introns – sequences found in DNA but not in mRNA (intervening regions) Some eukaryotic genes have many introns ...
... Exons – sequences found in a gene’s DNA and mature mRNA (expressed regions) Introns – sequences found in DNA but not in mRNA (intervening regions) Some eukaryotic genes have many introns ...
PG1005 Lecture 18 Translation
... Initiation of Translation Recall that Met is always the first AA of a nascent polypeptide • A specific tRNA called the initiator is charged with Met • Initiator is bound to the small ribosomal subunit in association ...
... Initiation of Translation Recall that Met is always the first AA of a nascent polypeptide • A specific tRNA called the initiator is charged with Met • Initiator is bound to the small ribosomal subunit in association ...
Lecture16 Biol302 Spring 2011
... How often is this site found in the genome? 1/45 Once every 1000 nucleotides 109 nucleotides or 106 times ...
... How often is this site found in the genome? 1/45 Once every 1000 nucleotides 109 nucleotides or 106 times ...
Lecture 8: Life`s Information Molecule III
... MOLECULE III: TRANSLATION AND PROTEIN LOCALIZATION ...
... MOLECULE III: TRANSLATION AND PROTEIN LOCALIZATION ...
week 13_genetic information
... • They observed that during replication, each parental strands serves as a template for DNA synthesis. • After new strand is formed, it is hydrogen bonded to its parental strand. • Each of the double helix contains one parent DNA strand and one newly ...
... • They observed that during replication, each parental strands serves as a template for DNA synthesis. • After new strand is formed, it is hydrogen bonded to its parental strand. • Each of the double helix contains one parent DNA strand and one newly ...
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation | Principles of Biology from Nature
... tertiary structures, much like proteins can. This ability of RNA to adopt threedimensional structures allows mRNA to possess binding sites for other molecules and switch between conformations depending on whether these binding sites are occupied. The aptamer of a riboswitch is the region that binds ...
... tertiary structures, much like proteins can. This ability of RNA to adopt threedimensional structures allows mRNA to possess binding sites for other molecules and switch between conformations depending on whether these binding sites are occupied. The aptamer of a riboswitch is the region that binds ...
25.10 Translation: Transfer RNA and Protein
... tRNA carries only one amino acid. • Messenger RNAs (mRNA) carry information transcribed from DNA. They are formed in the nucleus and transported to ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized. They are polynucleotides that carry the same code for proteins as does the DNA. ...
... tRNA carries only one amino acid. • Messenger RNAs (mRNA) carry information transcribed from DNA. They are formed in the nucleus and transported to ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized. They are polynucleotides that carry the same code for proteins as does the DNA. ...
25.1-0 - Laurel County Schools
... 500 mya this relative of T. rex roamed Antarctica. Today the largest fully terrestrial animal found there is a 5 mm long fly! ...
... 500 mya this relative of T. rex roamed Antarctica. Today the largest fully terrestrial animal found there is a 5 mm long fly! ...
Lectures 1 & 2 (2010.03.05 & 2010.03.06)
... DNA must be replicated before a cell divides, so that each daughter cell inherits a copy of each gene • Cell missing a critical gene will die • Essential that the process of DNA replication produces an absolutely accurate copy of the original genetic information • Mistakes made in critical genes can ...
... DNA must be replicated before a cell divides, so that each daughter cell inherits a copy of each gene • Cell missing a critical gene will die • Essential that the process of DNA replication produces an absolutely accurate copy of the original genetic information • Mistakes made in critical genes can ...
Answers questions chapter 14
... huge challenge for those that include large numbers of introns (for example, well over a hundred in some cases), and/or introns of vast dimensions (for example, up to 500,000 nucleotides). This challenge is compounded by the relatively weak sequence requirements for splice sites, as this increases t ...
... huge challenge for those that include large numbers of introns (for example, well over a hundred in some cases), and/or introns of vast dimensions (for example, up to 500,000 nucleotides). This challenge is compounded by the relatively weak sequence requirements for splice sites, as this increases t ...
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.