Chapter 10 - Mantachie High School
... Proteins are made up of one or more polypeptides; the polypeptides consist of amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids that make up proteins. The function of a protein depends on its 3-D structure, which is determined by its amino-acid sequence. The Genetic Code: Genetic code—triplets of nucl ...
... Proteins are made up of one or more polypeptides; the polypeptides consist of amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids that make up proteins. The function of a protein depends on its 3-D structure, which is determined by its amino-acid sequence. The Genetic Code: Genetic code—triplets of nucl ...
DNA & RNA - East Pennsboro High School
... Enzyme DNA polymerase unzips DNA Two new “complimentary” strands built ...
... Enzyme DNA polymerase unzips DNA Two new “complimentary” strands built ...
Chapter 17 Molecular Genetics
... – The genetic information contained in the DNA molecule is transferred to messenger RNA. – Messenger RNA molecules carry this information to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. – Messenger RNA serves as a template for protein synthesis. – Ribosomes are required to produce proteins on the ...
... – The genetic information contained in the DNA molecule is transferred to messenger RNA. – Messenger RNA molecules carry this information to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. – Messenger RNA serves as a template for protein synthesis. – Ribosomes are required to produce proteins on the ...
proteins
... The genetic code Degeneracy of the genetic code: 64 codons but only 20 aa’s plus stop codon ...
... The genetic code Degeneracy of the genetic code: 64 codons but only 20 aa’s plus stop codon ...
Powerpoint file - revised
... splicing of pre-mRNA; discovery of self-splicing of ribosomal RNA in Tetrahymena ...
... splicing of pre-mRNA; discovery of self-splicing of ribosomal RNA in Tetrahymena ...
A1991GH39300001
... I came to Philip Leder’s laboratory at the National labeled amino acids incorporated into protein ditnstitute of Child Health and Human Development rectedbymRNA. in 1970 after finishing my doctorate at the I immediately followed this ~ by runWeumann ln~tituteof Science in IsraeL The main ning throug ...
... I came to Philip Leder’s laboratory at the National labeled amino acids incorporated into protein ditnstitute of Child Health and Human Development rectedbymRNA. in 1970 after finishing my doctorate at the I immediately followed this ~ by runWeumann ln~tituteof Science in IsraeL The main ning throug ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... others are red blood cells that have lost their nuclei and are packed with hemoglobin? Why are cells so different in structure and function? If the characteristics of a cell depend upon the proteins that are synthesized, what does this tell you about protein synthesis? Work with a partner to discuss ...
... others are red blood cells that have lost their nuclei and are packed with hemoglobin? Why are cells so different in structure and function? If the characteristics of a cell depend upon the proteins that are synthesized, what does this tell you about protein synthesis? Work with a partner to discuss ...
RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA)
... • These so-called non-coding RNAs ("ncRNA") can be encoded by their own genes (RNA genes), but can also derive from mRNA introns • The most prominent examples of non-coding RNAs are transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), both of which are involved in the process of translation ...
... • These so-called non-coding RNAs ("ncRNA") can be encoded by their own genes (RNA genes), but can also derive from mRNA introns • The most prominent examples of non-coding RNAs are transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), both of which are involved in the process of translation ...
Transcription and Translation
... o Each polymerase transcribes only certain types of RNA in eukaryotes. o RNA polymerase II is the only polymerase that transcribes protein-coding genes. - Promoters in eukaryotic DNA are more diverse than bacterial promoters. o Eukaryotic promoters include the TATA box and other important diverse se ...
... o Each polymerase transcribes only certain types of RNA in eukaryotes. o RNA polymerase II is the only polymerase that transcribes protein-coding genes. - Promoters in eukaryotic DNA are more diverse than bacterial promoters. o Eukaryotic promoters include the TATA box and other important diverse se ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
Section 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
DNA Replication - cloudfront.net
... 17. What binds to the mRNA on 1 end and brings an amino acid on the other? 18. What makes up part of the ribosome and hold the mRNA during translation? 19. Which RNA makes the proteins? 20.What is the process that makes mRNA from DNA and where does it occur? 21. What are the 4 steps of transcription ...
... 17. What binds to the mRNA on 1 end and brings an amino acid on the other? 18. What makes up part of the ribosome and hold the mRNA during translation? 19. Which RNA makes the proteins? 20.What is the process that makes mRNA from DNA and where does it occur? 21. What are the 4 steps of transcription ...
Biology 105
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries specific info for making a protein Transfer RNA (tRNA) – bonds with only one specific amino acid and carries it to the ribosome Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – part of the structure of ribosomes and catalyzes functions during protein synthesis ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries specific info for making a protein Transfer RNA (tRNA) – bonds with only one specific amino acid and carries it to the ribosome Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – part of the structure of ribosomes and catalyzes functions during protein synthesis ...
1. Introduction Organisms are made up of the sum of their genes and
... CstF-64K binds to the downstream element via its N-terminal RNP type RNA recognition motif (RRM). Its C-terminal domain contains a long proline / glycine-rich region, which encloses 12 tandem copies of the MEARA / G amino acid (aa) motif. They form a long α-helical structure (Takagaki et al., 1992). ...
... CstF-64K binds to the downstream element via its N-terminal RNP type RNA recognition motif (RRM). Its C-terminal domain contains a long proline / glycine-rich region, which encloses 12 tandem copies of the MEARA / G amino acid (aa) motif. They form a long α-helical structure (Takagaki et al., 1992). ...
Central Dogma - We Heart Science
... In eukaryotes, many general are interrupted by introns and exons. • Introns – long segments of nucleotides that have no coding information. • Exons – are the portions of a gene that are translated (expressed) into proteins. ...
... In eukaryotes, many general are interrupted by introns and exons. • Introns – long segments of nucleotides that have no coding information. • Exons – are the portions of a gene that are translated (expressed) into proteins. ...
AP Protein Synthesis
... • For transcription to occur, RNA polymerase must first bind to a promoter (in eukaryotes this requires many transcription factors) • Once RNA polymerase is bound it will unwind the DNA and nucleotides can be added ...
... • For transcription to occur, RNA polymerase must first bind to a promoter (in eukaryotes this requires many transcription factors) • Once RNA polymerase is bound it will unwind the DNA and nucleotides can be added ...
Gene Expression Gene expression involves coded information on
... In the nucleus the DNA molecule is unwind by the enzyme helicase, exposing the nucleotides on the DNA strand. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the promotor region on the template strand. However, RNA polymerase alone cannot start transcription of the gene. Transcription factors must also bind to t ...
... In the nucleus the DNA molecule is unwind by the enzyme helicase, exposing the nucleotides on the DNA strand. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the promotor region on the template strand. However, RNA polymerase alone cannot start transcription of the gene. Transcription factors must also bind to t ...
Decoding mRNA
... Three types of RNA are involved in the process of protein synthesis. Each molecule has specific responsibilities. Identify the 3 different types of RNA in Figure 1. Also indicate by circling the correct answer where in the cell that type of RNA can be found. ...
... Three types of RNA are involved in the process of protein synthesis. Each molecule has specific responsibilities. Identify the 3 different types of RNA in Figure 1. Also indicate by circling the correct answer where in the cell that type of RNA can be found. ...
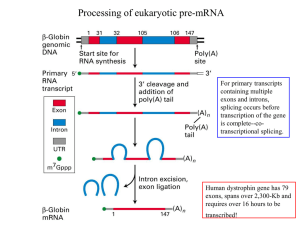
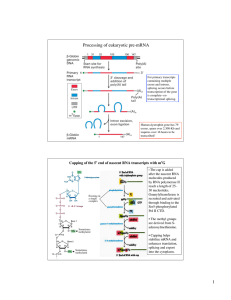
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.