Protein Synthesis Notes Review
... 2. To make proteins, what does the DNA have to be decoded into? 3. What are the three parts that make up a RNA nucleotide? 4. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA? 5. If a DNA chain had the following sequence, CCGTAATAGCAT, what RNA nucleotides would attach to this sequence? 6. What is ...
... 2. To make proteins, what does the DNA have to be decoded into? 3. What are the three parts that make up a RNA nucleotide? 4. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA? 5. If a DNA chain had the following sequence, CCGTAATAGCAT, what RNA nucleotides would attach to this sequence? 6. What is ...
1, 2, 5, 6, 7 Time: 08:00
... -Summarize the role of RNA polymerase in the synthesis of messenger RNA. -Describe how the code of DNA is translated into messenger RNA and is utilized to synthesize a particular protein. ...
... -Summarize the role of RNA polymerase in the synthesis of messenger RNA. -Describe how the code of DNA is translated into messenger RNA and is utilized to synthesize a particular protein. ...
Chapter 13: The Genetic Code and Transcription
... Three other codons serve as termination codons (UAG, UAA, and UGA) but do not code for an amino acid. They are not recognized by the tRNA performing translation, so the process ends when they are reached. 13.8 Transcription synthesizes RNA on a DNA template During the studies of DNA, it was clea ...
... Three other codons serve as termination codons (UAG, UAA, and UGA) but do not code for an amino acid. They are not recognized by the tRNA performing translation, so the process ends when they are reached. 13.8 Transcription synthesizes RNA on a DNA template During the studies of DNA, it was clea ...
How Did Life Begin? And What is Life?
... numerous small molecules and four classes of macromolecules: • Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA; polymers of nucleotides) • Proteins (polymers of amino acids) • Polysaccharides (polymers of sugars) ...
... numerous small molecules and four classes of macromolecules: • Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA; polymers of nucleotides) • Proteins (polymers of amino acids) • Polysaccharides (polymers of sugars) ...
No Slide Title
... 1) “Transcription stuff” binds to a promoter region of the DNA. 2) An enzyme “slices” the DNA, making it single stranded. 3) Another enzyme (polymerase) synthesizes a strand of RNA using one of the DNA strands as a template. ...
... 1) “Transcription stuff” binds to a promoter region of the DNA. 2) An enzyme “slices” the DNA, making it single stranded. 3) Another enzyme (polymerase) synthesizes a strand of RNA using one of the DNA strands as a template. ...
Bio-261-chapter-7
... • The coding regions are called exons and the non-coding regions are called introns. • The introns are removed by an enzymeRNA complex known as the spliceosome. • A tail of adenine bases is added to the 3 prime end and a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5 prime end. ...
... • The coding regions are called exons and the non-coding regions are called introns. • The introns are removed by an enzymeRNA complex known as the spliceosome. • A tail of adenine bases is added to the 3 prime end and a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5 prime end. ...
Test 4
... proofreading occur, and are there any differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems? This process is carried out by Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. A cell will usually have one synthetase for each amino acid, even when there are several tRNAs for the same amino acid. The synthetase will charge ...
... proofreading occur, and are there any differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems? This process is carried out by Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. A cell will usually have one synthetase for each amino acid, even when there are several tRNAs for the same amino acid. The synthetase will charge ...
C - TeacherWeb
... • The coding regions are called exons and the non-coding regions are called introns. • The introns are removed by an enzymeRNA complex known as the spliceosome. • A tail of adenine bases is added to the 3 prime end and a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5 prime end. ...
... • The coding regions are called exons and the non-coding regions are called introns. • The introns are removed by an enzymeRNA complex known as the spliceosome. • A tail of adenine bases is added to the 3 prime end and a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5 prime end. ...
ch 19 gene expression in eukaryotes
... Cancers result from a series of genetic changes in a cell lineage – The incidence of cancer increases with age because multiple somatic mutations are required to produce a cancerous cell – As in many cancers, the development of colon cancer is gradual ...
... Cancers result from a series of genetic changes in a cell lineage – The incidence of cancer increases with age because multiple somatic mutations are required to produce a cancerous cell – As in many cancers, the development of colon cancer is gradual ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... Translation begins when a small ribosomal subunit recognizes a start codon. Then, an initiator tRNA-MET pairs with the start codon, and a large ribosomal subunit completes the initiation complex. ...
... Translation begins when a small ribosomal subunit recognizes a start codon. Then, an initiator tRNA-MET pairs with the start codon, and a large ribosomal subunit completes the initiation complex. ...
NEW revision booklt - Eduspace
... ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ What is similar about the two ? ______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ What is similar about the two ? ______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
8.4 Transcription - Issaquah Connect
... 8.4 Transcription The transcription process is similar to replication. • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a g ...
... 8.4 Transcription The transcription process is similar to replication. • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a g ...
Protein Synthesis Powerpoint
... brings it to the ribosome. It is made during first step called transcription. - rRNA= Ribosomal RNA: combines with proteins to make the structure of the ribosome. - tRNA= Transfer RNA: carries an amino acid to the ribosome to be able to synthesize the protein during translation. ...
... brings it to the ribosome. It is made during first step called transcription. - rRNA= Ribosomal RNA: combines with proteins to make the structure of the ribosome. - tRNA= Transfer RNA: carries an amino acid to the ribosome to be able to synthesize the protein during translation. ...
Document
... Cut plasmid with an enzyme that recognizes restriction site in lacZ’ gene (codes for -galactosidase). Cut donor DNA with same enzyme. Transform bacterial cells with ...
... Cut plasmid with an enzyme that recognizes restriction site in lacZ’ gene (codes for -galactosidase). Cut donor DNA with same enzyme. Transform bacterial cells with ...
RNA and transcription
... 1- transport amino acids to ribosome for protein synthesis. Each tRNA carry only one amino acid. The specific amino acid is attached enzymatically to 3' end of tRNA. 2- recognize the specified codon on mRNA to ensure the insertion of the correct amino acid in the growing polypeptide chain. This func ...
... 1- transport amino acids to ribosome for protein synthesis. Each tRNA carry only one amino acid. The specific amino acid is attached enzymatically to 3' end of tRNA. 2- recognize the specified codon on mRNA to ensure the insertion of the correct amino acid in the growing polypeptide chain. This func ...
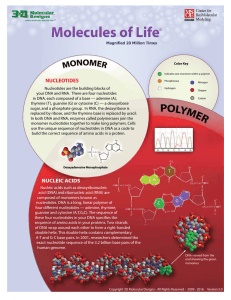
Nucleic Acids Placemat
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
CHAPTER 12
... • Activity of certain genes, called imprinted genes, depends on whether they originated with the sperm or egg. • Active and inactive versions of imprinted genes differ in their methylation patterns. • Disturbances in imprinting patterns have been implicated in a number of rare human genetic disorder ...
... • Activity of certain genes, called imprinted genes, depends on whether they originated with the sperm or egg. • Active and inactive versions of imprinted genes differ in their methylation patterns. • Disturbances in imprinting patterns have been implicated in a number of rare human genetic disorder ...
Bench Guide
... out by ribosomes, which consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. Amino acids for protein synthesis are delivered to the ribosome on transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. RNAs are also part of riboproteins involved in RNA processing. In addition, many viruses contain RNA as their genome instead of DNA, ...
... out by ribosomes, which consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. Amino acids for protein synthesis are delivered to the ribosome on transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. RNAs are also part of riboproteins involved in RNA processing. In addition, many viruses contain RNA as their genome instead of DNA, ...
Chapter 12 Notes - White Plains Public Schools
... Anticodon- the 3 bases (AUGC) on mRNA are paired with ones on tRNA o Examples: AGU-UCC-AAG (codon) UCA-AGG-CGA (Anticodon) RNA and DNA DNA= “Master plan” -Stays in the nucleus RNA= “Blueprint” – Leaves the nucleus to go to protein building sites (Ribosomes) in cytoplasm Chapter 12 Lesson 4 Mutat ...
... Anticodon- the 3 bases (AUGC) on mRNA are paired with ones on tRNA o Examples: AGU-UCC-AAG (codon) UCA-AGG-CGA (Anticodon) RNA and DNA DNA= “Master plan” -Stays in the nucleus RNA= “Blueprint” – Leaves the nucleus to go to protein building sites (Ribosomes) in cytoplasm Chapter 12 Lesson 4 Mutat ...
AP Biology Discussion Notes
... Nirenberg "for their interpretation of the genetic code and its function in protein synthesis". ...
... Nirenberg "for their interpretation of the genetic code and its function in protein synthesis". ...
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to a messenger RNA The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene finishes, or terminates. The 3'-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3' end. In some genes, these proteins may add a poly(A) tail at any one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing.The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation, and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic non-coding RNAs.mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3'-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and less mRNA molecules polyadenylated.