Transcription PPT
... mRNA… • DNA contains many non-coding regions, also known as “junk DNA” • RNA is not made from the junk DNA • Only 1 of the 2 DNA strands is used to make the mRNA; this strand is called the DNA template • DNA code on the mRNA is read three bases at once, and these three letter base combinations on th ...
... mRNA… • DNA contains many non-coding regions, also known as “junk DNA” • RNA is not made from the junk DNA • Only 1 of the 2 DNA strands is used to make the mRNA; this strand is called the DNA template • DNA code on the mRNA is read three bases at once, and these three letter base combinations on th ...
Chapter 17 Presentation
... Bread mold is hearty. It can grow on minimal medium because it can use various pathways to synthesize everything it needs to survive. Minimal medium is culture medium that contains everything necessary for growth of the wild type: usually inorganic salts, a carbon source including vitamins and water ...
... Bread mold is hearty. It can grow on minimal medium because it can use various pathways to synthesize everything it needs to survive. Minimal medium is culture medium that contains everything necessary for growth of the wild type: usually inorganic salts, a carbon source including vitamins and water ...
here - VCU
... exon codes for a specific portion of the complete protein. In some species (including humans), a gene's exons are separated by long regions of DNA (called introns or sometimes "junk DNA") that have no apparent function. The DNA that makes up the human genome can be subdivided into information bytes ...
... exon codes for a specific portion of the complete protein. In some species (including humans), a gene's exons are separated by long regions of DNA (called introns or sometimes "junk DNA") that have no apparent function. The DNA that makes up the human genome can be subdivided into information bytes ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • Different proteins are made by combining these 20 amino acids in different combinations ...
... • Different proteins are made by combining these 20 amino acids in different combinations ...
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Three forms of RNA involved in protein synthesis 1. mRNA (messenger): copies instructions in DNA and carries these to the ribosome. 2. tRNA (transfer): carries amino acids to the ribosome. 3. rRNA (ribosomal): composes the ribosome. ...
... Three forms of RNA involved in protein synthesis 1. mRNA (messenger): copies instructions in DNA and carries these to the ribosome. 2. tRNA (transfer): carries amino acids to the ribosome. 3. rRNA (ribosomal): composes the ribosome. ...
Topic 12 (Ch9/7) – Microbial Genetics Genetics Chromosome
... Lac operon example for regulation of sugar metabolism ...
... Lac operon example for regulation of sugar metabolism ...
BILD 10.Problem Set 3 KEY
... electrophorese the two samples on a gel, you see that two bands are present in the sample from Individual 1, while only one band is present in the sample from Individual 2. What is a likely explanation for this outcome? a) Individual 1 is homozygous, while Individual 2 is heterozygous. b) Individual ...
... electrophorese the two samples on a gel, you see that two bands are present in the sample from Individual 1, while only one band is present in the sample from Individual 2. What is a likely explanation for this outcome? a) Individual 1 is homozygous, while Individual 2 is heterozygous. b) Individual ...
第一次课件第八章
... purpose is to ensure that the activation domain is in the vicinity of the initiation complex. The notion of tethering is a more general idea that initiation requires a high concentration of transcription factors in the vicinity of the promoter. This may be achieved when activators bind to enhancers, ...
... purpose is to ensure that the activation domain is in the vicinity of the initiation complex. The notion of tethering is a more general idea that initiation requires a high concentration of transcription factors in the vicinity of the promoter. This may be achieved when activators bind to enhancers, ...
Agilent TapeStation 2200 FAQ
... At this time there has been little information to determine the benefits of using one system over the other. Both systems provide accurate, reliable information on your sample quality. However, recent study has revealed differences between the two technologies in their capabilities to determine appr ...
... At this time there has been little information to determine the benefits of using one system over the other. Both systems provide accurate, reliable information on your sample quality. However, recent study has revealed differences between the two technologies in their capabilities to determine appr ...
Applications of RNA minimum free energy computations
... Markov models (Baldi et al., 1994; Eddy et al. 1995) (see g409201), neural networks (Nielsen et al., 1997)(see g409201) and support vector machines (Vert, 2002) (see g409416). While accurate detection of protein coding genes can be achieved using hidden Markov models (Borodovsky and McIninch, 1993), ...
... Markov models (Baldi et al., 1994; Eddy et al. 1995) (see g409201), neural networks (Nielsen et al., 1997)(see g409201) and support vector machines (Vert, 2002) (see g409416). While accurate detection of protein coding genes can be achieved using hidden Markov models (Borodovsky and McIninch, 1993), ...
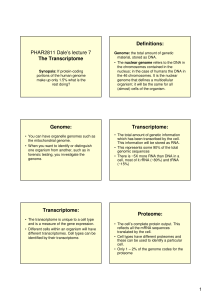
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 7 The Transcriptome Definitions: Genome
... Lariat formed when 5’ p of the intron G attaches to 2’ OH of A ...
... Lariat formed when 5’ p of the intron G attaches to 2’ OH of A ...
Slides PPT
... • Occurs in the nucleus • Capping (meG at 5’ head) and polyA tailing at 3’ end carried out first • Splice sites are defined by a sequence • Formation of a “lariat” by the spliceosome (U1, U2, U4, U5 & U6 and ~10 proteins) ...
... • Occurs in the nucleus • Capping (meG at 5’ head) and polyA tailing at 3’ end carried out first • Splice sites are defined by a sequence • Formation of a “lariat” by the spliceosome (U1, U2, U4, U5 & U6 and ~10 proteins) ...
Chapter 9
... 9.6 Effects of Protein Processing Humans have more than 25,000 protein-coding genes, but can make over 100,000 different proteins Taking into account alternative splicing and protein modification in the Golgi (Chp 2) it is estimated that each gene can make 6 or 7 different proteins Proteome • ...
... 9.6 Effects of Protein Processing Humans have more than 25,000 protein-coding genes, but can make over 100,000 different proteins Taking into account alternative splicing and protein modification in the Golgi (Chp 2) it is estimated that each gene can make 6 or 7 different proteins Proteome • ...
Identification of RNAi-Related Genes in Archaea
... Using the idea that protein structure is more conserved than the primary sequence of amino acids, I will next perform structure-based searches. For RNAi-related proteins with known structures, I will search for proteins of similar structure (and thus presumably of similar function) in Archaea. Not m ...
... Using the idea that protein structure is more conserved than the primary sequence of amino acids, I will next perform structure-based searches. For RNAi-related proteins with known structures, I will search for proteins of similar structure (and thus presumably of similar function) in Archaea. Not m ...
protein synthesis
... A transfer RNA with the proper (complementary) anticodon and its correct amino acid line up on the codon of the mRNA The ribosome moves along the mRNA the space of one codon A second tRNA with its correct amino acid lines up on the second codon The ribosome checks the codon / anticodons for a correc ...
... A transfer RNA with the proper (complementary) anticodon and its correct amino acid line up on the codon of the mRNA The ribosome moves along the mRNA the space of one codon A second tRNA with its correct amino acid lines up on the second codon The ribosome checks the codon / anticodons for a correc ...
RNA notes 2015 - OG
... Gene Sequencing – Determining the order of nucleotide bases within a gene DNA Fingerprinting – technique used in criminal investigations. DNA Fingerprinting takes the DNA out of a cell and separates it. This will allow investigators to distinguish body cells of different individuals (since they are ...
... Gene Sequencing – Determining the order of nucleotide bases within a gene DNA Fingerprinting – technique used in criminal investigations. DNA Fingerprinting takes the DNA out of a cell and separates it. This will allow investigators to distinguish body cells of different individuals (since they are ...
Transcription
... • Cells usually synthesize only proteins that are required. • Turning genes “off” and “on” is highly controlled in cells. • In prokaryotes, control occurs at the level of transcription initiation. • Eukaryotes are more complex. There are many regulatory proteins and controls occur at many levels in ...
... • Cells usually synthesize only proteins that are required. • Turning genes “off” and “on” is highly controlled in cells. • In prokaryotes, control occurs at the level of transcription initiation. • Eukaryotes are more complex. There are many regulatory proteins and controls occur at many levels in ...
Chapter 17 Presentation
... carries the genetic information from the DNA to the protein synthesizing machinery. RNA polymerase pries apart the DNA and joins RNA nucleotides together in the 5’-->3’ direction (adding, again, to the free 3’ end). RNA polymerase is just like DNA ...
... carries the genetic information from the DNA to the protein synthesizing machinery. RNA polymerase pries apart the DNA and joins RNA nucleotides together in the 5’-->3’ direction (adding, again, to the free 3’ end). RNA polymerase is just like DNA ...
Transcription
... DNA is a selfreplicating molecule containing genetic information that can be transcribed into an RNA message that can be translated into a polypeptide (protein). ...
... DNA is a selfreplicating molecule containing genetic information that can be transcribed into an RNA message that can be translated into a polypeptide (protein). ...
This is going to be a long journey, but it is crucial
... 49. Now its time to put al of the elements of transcription together. Write an essay to describe the process by which mRNA is formed IN EUKARYOTES. Use the following terms correctly in your essay and underline each: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3’, termination, initiation, ...
... 49. Now its time to put al of the elements of transcription together. Write an essay to describe the process by which mRNA is formed IN EUKARYOTES. Use the following terms correctly in your essay and underline each: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3’, termination, initiation, ...
17. Gene regulation
... control determines whether or not transcription is initiated requires promoter of gene transcription factors bind to promoter and recruit RNA polymerase to initiate transcription post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression control after pre-mRNA synthesis can involve control of RNA ...
... control determines whether or not transcription is initiated requires promoter of gene transcription factors bind to promoter and recruit RNA polymerase to initiate transcription post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression control after pre-mRNA synthesis can involve control of RNA ...
Slide 1
... subunit of RNA polymerase. These promoters have very similar sequences. • Eukarya: the major classes of RNA are transcribed by three different RNA polymerases, with RNA polymerase II producing most mRNA. • Archaea: have a single RNA that resembles in structure and function the RNA polymerase II. ...
... subunit of RNA polymerase. These promoters have very similar sequences. • Eukarya: the major classes of RNA are transcribed by three different RNA polymerases, with RNA polymerase II producing most mRNA. • Archaea: have a single RNA that resembles in structure and function the RNA polymerase II. ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.