Ribosome - Mrs. J. Malito
... from degradation and to help small ribosomal subunits recognize the attachment site on mRNA’s 5’ end. • A poly-A tail is sequence of 30 – 200 A nucleotides added to the 3’ end of mRNA before it exits to: ...
... from degradation and to help small ribosomal subunits recognize the attachment site on mRNA’s 5’ end. • A poly-A tail is sequence of 30 – 200 A nucleotides added to the 3’ end of mRNA before it exits to: ...
DNA - Center on Disability Studies
... • Some genes are dominant (stronger) • Some genes are recessive (weaker) • Each organism inherits a gene from each parent. • Each organism has 2 genes per trait. ...
... • Some genes are dominant (stronger) • Some genes are recessive (weaker) • Each organism inherits a gene from each parent. • Each organism has 2 genes per trait. ...
Heredity and Genes
... Non coding DNA inside genes are called ________. What is transcription? What is translation? In what parts of the cell does transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes? In what parts of the cell does transcription and translation occur in eukaryotes? Put in order of amount of DNA (from least ...
... Non coding DNA inside genes are called ________. What is transcription? What is translation? In what parts of the cell does transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes? In what parts of the cell does transcription and translation occur in eukaryotes? Put in order of amount of DNA (from least ...
BIO S - Chapter 13 RNA
... The Genetic Code The first step in decoding genetic messages is to transcribe a nucleotide base sequence from DNA to RNA The transcript contains a code for making ...
... The Genetic Code The first step in decoding genetic messages is to transcribe a nucleotide base sequence from DNA to RNA The transcript contains a code for making ...
RNA Structure, Function, and Synthesis RNA - Rose
... RNA Structure, Function, and Synthesis RNA RNA differs from DNA in both structural and functional respects. RNA has two major structural differences: each of the ribose rings contains a 2´-hydroxyl, and RNA uses uracil in place of thymine. RNA molecules are capable of base pairing, but generally wil ...
... RNA Structure, Function, and Synthesis RNA RNA differs from DNA in both structural and functional respects. RNA has two major structural differences: each of the ribose rings contains a 2´-hydroxyl, and RNA uses uracil in place of thymine. RNA molecules are capable of base pairing, but generally wil ...
CHAPTERS 21 AND 22
... material in ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis ► Ribosome - a sub cellular particle that serves as the site of protein synthesis in all organisms ...
... material in ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis ► Ribosome - a sub cellular particle that serves as the site of protein synthesis in all organisms ...
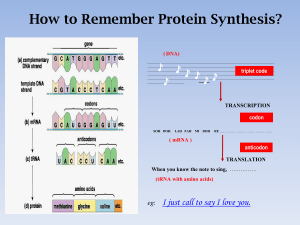
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
Chap2 DNA RNA and Protein
... shorter with each cell division eventually DNA damage occurs at chromosome ends sends a signal to stabilize p53transcription of several genes (e.g. p21) CKI (cdk inhibitor protein) bind to and inhibit G1/S-cdk and S-cdk.=> block entry into S phase (Alberts, p10071018). ...
... shorter with each cell division eventually DNA damage occurs at chromosome ends sends a signal to stabilize p53transcription of several genes (e.g. p21) CKI (cdk inhibitor protein) bind to and inhibit G1/S-cdk and S-cdk.=> block entry into S phase (Alberts, p10071018). ...
26 DNA Transcription - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... between a given amino acid and the correct (cognate) tRNA is catalyzed by a specific aminoacyltRNA synthetase (one for each amino acid). The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases establish and enforce the genetic code. 4)MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are around 22 nucleotides in length and are found only in eukaryotic ce ...
... between a given amino acid and the correct (cognate) tRNA is catalyzed by a specific aminoacyltRNA synthetase (one for each amino acid). The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases establish and enforce the genetic code. 4)MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are around 22 nucleotides in length and are found only in eukaryotic ce ...
Inheritance and the Structure of DNA
... • Each sequence of 3 bases on mRNA encodes for either an amino acid or stop/start signal • Some amino acids will have 1,2,or 3 different codons – No codon codes for more than one amino acid – 64 mRNA codons • There are special codons that act as start and stop to the sequence • For example, AUG acts ...
... • Each sequence of 3 bases on mRNA encodes for either an amino acid or stop/start signal • Some amino acids will have 1,2,or 3 different codons – No codon codes for more than one amino acid – 64 mRNA codons • There are special codons that act as start and stop to the sequence • For example, AUG acts ...
Chapter 16
... one or more of the following processes: 1) cleavage of the mRNA strand into two pieces, 2) destabilization of the mRNA through shortening of its poly(A) tail, and 3) less efficient translation of the mRNA into proteins by ribosomes. 2. Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfer ...
... one or more of the following processes: 1) cleavage of the mRNA strand into two pieces, 2) destabilization of the mRNA through shortening of its poly(A) tail, and 3) less efficient translation of the mRNA into proteins by ribosomes. 2. Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfer ...
mRNA
... and sequences regulatory within the elements that, gene that together do that that not encode combine encode with transcription the the toprotein result proteinfactors, structure instructure a protein Transcription: process tosequences produce RNA from the gene determine the amount of gene expressio ...
... and sequences regulatory within the elements that, gene that together do that that not encode combine encode with transcription the the toprotein result proteinfactors, structure instructure a protein Transcription: process tosequences produce RNA from the gene determine the amount of gene expressio ...
DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid
... Chromosome Duplication • During S-phase = “Synthesis” Why?.... • So that later, the sister chromatids can separate into different (new) cells! ...
... Chromosome Duplication • During S-phase = “Synthesis” Why?.... • So that later, the sister chromatids can separate into different (new) cells! ...
From DNA to Protein
... • translation: process of converting information in mRNA into sequence of amino acids to make a protein • occurs at the ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum ...
... • translation: process of converting information in mRNA into sequence of amino acids to make a protein • occurs at the ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum ...
Chapter 14 Guided Reading
... 21. Use the diagram below to demonstrate initiation of transcription at a eukaryotic promoter. Label all parts of the diagram and discuss what is occurring at each step.. ...
... 21. Use the diagram below to demonstrate initiation of transcription at a eukaryotic promoter. Label all parts of the diagram and discuss what is occurring at each step.. ...
compgenomics
... Digital gene expression from RNA-seq studies Prediction of ncRNAs and their function Global mapping of alternative splicing regulation Integration of multi-level signaling (TFs, miRNA, chromatin) Association studies for combinations of alleles ...
... Digital gene expression from RNA-seq studies Prediction of ncRNAs and their function Global mapping of alternative splicing regulation Integration of multi-level signaling (TFs, miRNA, chromatin) Association studies for combinations of alleles ...
CH7 DNAtoProtein
... …because the DNA is not separated from the ribosomes (like in eukaryotic cells!) ...
... …because the DNA is not separated from the ribosomes (like in eukaryotic cells!) ...
THE DEVELOPMENT OF AN RNA BASED ASSAY SYSTEM TO
... Five saliva-specific genes have been identified so far, including statherin, histatin, proline-rich proteins BstNI subfamily 1 (PRB1), proline-rich proteins BstNI subfamily 2 (PRB2), and proline-rich proteins BstNI ...
... Five saliva-specific genes have been identified so far, including statherin, histatin, proline-rich proteins BstNI subfamily 1 (PRB1), proline-rich proteins BstNI subfamily 2 (PRB2), and proline-rich proteins BstNI ...
Lecture 8 - Brandeis Life Sciences
... Data mining and visualization Controls and normalization of results Statistical validation Linkage between gene expression data and gene sequence/function/metabolic pathways databases • Clustering and pattern detection • Discovery of common sequences in coregulated genes ...
... Data mining and visualization Controls and normalization of results Statistical validation Linkage between gene expression data and gene sequence/function/metabolic pathways databases • Clustering and pattern detection • Discovery of common sequences in coregulated genes ...
Tutorial_9_NEW
... -other efficient algorithms for identifying stem loops Concentrating on intragenic regions and introns - Filtering coding regions Filtering out non conserved candidates -Mature and pre-miRNA is usually evolutionary conserved ...
... -other efficient algorithms for identifying stem loops Concentrating on intragenic regions and introns - Filtering coding regions Filtering out non conserved candidates -Mature and pre-miRNA is usually evolutionary conserved ...
DNA Structure and Function
... 2. A tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid matches up to a complementary triplet on mRNA on the ribosome 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attached to the growing chain of amin ...
... 2. A tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid matches up to a complementary triplet on mRNA on the ribosome 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attached to the growing chain of amin ...
m5zn_a4ac3a22336dedd
... the flow (or transcription) of genetic information from DNA to mRNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of ge ...
... the flow (or transcription) of genetic information from DNA to mRNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of ge ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.