Protein Synthesis
... What are the 3 types of RNA? A sequence of 3 nucleotides on the mRNA strand that codes for a specific amino acid is called a what? What is the name of the bond that is formed between two amino acids? How do amino acids get into the body in the ...
... What are the 3 types of RNA? A sequence of 3 nucleotides on the mRNA strand that codes for a specific amino acid is called a what? What is the name of the bond that is formed between two amino acids? How do amino acids get into the body in the ...
Transcription
... Recognized by small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs) that catalyze the cutting and splicing reactions. Internal intron sequences are highly variable even between closely related homologous genes. Alternative splicing allows different proteins from a single original transcript ...
... Recognized by small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs) that catalyze the cutting and splicing reactions. Internal intron sequences are highly variable even between closely related homologous genes. Alternative splicing allows different proteins from a single original transcript ...
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein 1. Overview of Gene Expression 2. Transcription
... • 5’ cap, poly-A tail, intron, exon, splicing, spliceosome • rho protein, stem-loop, codon, anti-codon, translation • aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, polyribosome, signal ...
... • 5’ cap, poly-A tail, intron, exon, splicing, spliceosome • rho protein, stem-loop, codon, anti-codon, translation • aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, polyribosome, signal ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... back together to form the final messenger RNA. A mutation in a series of genes, called the ____________________, can change the organs that develop in specific parts of an embryo. Short Answer In Figure 12-2, which molecule is tRNA, and what is its function? (2 points) ...
... back together to form the final messenger RNA. A mutation in a series of genes, called the ____________________, can change the organs that develop in specific parts of an embryo. Short Answer In Figure 12-2, which molecule is tRNA, and what is its function? (2 points) ...
Introduction to molecular biology
... – Actually, since almost all the cells in an organism share the same genome, it contains all the information needed by ANY cell to perform their functions. – It stays (almost) always in the nucleus. ...
... – Actually, since almost all the cells in an organism share the same genome, it contains all the information needed by ANY cell to perform their functions. – It stays (almost) always in the nucleus. ...
DNA→ RNA
... the cell • Hormones – chemical messengers that regulate body functions • Provide structure • Energy source • Transport other molecules • Part of our immune system ...
... the cell • Hormones – chemical messengers that regulate body functions • Provide structure • Energy source • Transport other molecules • Part of our immune system ...
Bio 220 MiniQuiz 1
... _____1. Organic growth factors include amino acids and vitamins. _____2. Chemoautotrophs use the light from the sun as their primary energy source. _____3. Both chocolate agar and blood agar contain blood. _____4. Transcription refers to the process of DNA synthesis. Multiple choice _____5. An oblig ...
... _____1. Organic growth factors include amino acids and vitamins. _____2. Chemoautotrophs use the light from the sun as their primary energy source. _____3. Both chocolate agar and blood agar contain blood. _____4. Transcription refers to the process of DNA synthesis. Multiple choice _____5. An oblig ...
Slide 1
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA formed is immediately ready for protein synthesis • In eukaryotes, the mRNA formed in nucleus is very large & not fully processed. • It contains additional non-coding (interrupting) sequences called Introns. • The coding regions (exons) have to be cut and spliced together to f ...
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA formed is immediately ready for protein synthesis • In eukaryotes, the mRNA formed in nucleus is very large & not fully processed. • It contains additional non-coding (interrupting) sequences called Introns. • The coding regions (exons) have to be cut and spliced together to f ...
Summer Internship project
... The use of RNA measurements to estimate the abundance of microorganisms in samples would be both powerful and convenient. Combined with gene expression analysis, a single RNA extraction would provide answers to a number of different questions: (i) How many microorganisms are present?; (ii) What type ...
... The use of RNA measurements to estimate the abundance of microorganisms in samples would be both powerful and convenient. Combined with gene expression analysis, a single RNA extraction would provide answers to a number of different questions: (i) How many microorganisms are present?; (ii) What type ...
Objectives Unit 5
... 1) How do living systems store, retrieve, and transmit genetic information critical to life processes? 2) How does the expression of genetic material control cell products which, in turn, determine the metabolism and nature of the cell? 3) What is the relationship between changes in genotype and phe ...
... 1) How do living systems store, retrieve, and transmit genetic information critical to life processes? 2) How does the expression of genetic material control cell products which, in turn, determine the metabolism and nature of the cell? 3) What is the relationship between changes in genotype and phe ...
Chapter 8 Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... the single-base mutation, the sixth amino acid in the chain is valine, rather than glutamic acid. This type of mutation is: _________________________ *Mutations – favorable, neutral or harmful? 1. Antibiotics, drugs that target specific features of bacteria, are used to treat infections. Bacteria ev ...
... the single-base mutation, the sixth amino acid in the chain is valine, rather than glutamic acid. This type of mutation is: _________________________ *Mutations – favorable, neutral or harmful? 1. Antibiotics, drugs that target specific features of bacteria, are used to treat infections. Bacteria ev ...
PowerPoint Notes
... Hershey and Chase offered further evidence that DNA, not proteins, is the genetic material. Only the DNA of the old generation of viruses is incorporated into the new generation. ...
... Hershey and Chase offered further evidence that DNA, not proteins, is the genetic material. Only the DNA of the old generation of viruses is incorporated into the new generation. ...
SEG exam 2 1
... The full chemical name of DNA is ______________________________________. A chart that displays all the chromosome pairs in size order is called a __________________. _________________ are alterations in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule that can occur randomly and modify the genome. When a ...
... The full chemical name of DNA is ______________________________________. A chart that displays all the chromosome pairs in size order is called a __________________. _________________ are alterations in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule that can occur randomly and modify the genome. When a ...
Chapter 13, 14 Rev
... a. small proteins that function in translation. b. proteins and small RNAs that function in translation. c. proteins and tRNAs that function in transcription. d. proteins and mRNAs that function in translation. e. mRNAs and tRNAs that function in translation. The adaptors that allow translation of t ...
... a. small proteins that function in translation. b. proteins and small RNAs that function in translation. c. proteins and tRNAs that function in transcription. d. proteins and mRNAs that function in translation. e. mRNAs and tRNAs that function in translation. The adaptors that allow translation of t ...
Gene Regulation - Cloudfront.net
... genes through regulatory molecules (ex. steroids may stimulate the production of certain proteins) certain parts of eukaryotic chromosomes are in a highly condensed, compact state making it inaccessible to RNA polymerase some of these areas are structural and don’t contain genes other of these regio ...
... genes through regulatory molecules (ex. steroids may stimulate the production of certain proteins) certain parts of eukaryotic chromosomes are in a highly condensed, compact state making it inaccessible to RNA polymerase some of these areas are structural and don’t contain genes other of these regio ...
Control of Gene Expression
... – Operon: series of genes that code for specific products, including regulators that control whether these genes are transcribed • Example: lac operon (bacteria) – genes for lactose metabolism only activated if lactose is present (when lactose not present, a repressor blocks transcription; if presen ...
... – Operon: series of genes that code for specific products, including regulators that control whether these genes are transcribed • Example: lac operon (bacteria) – genes for lactose metabolism only activated if lactose is present (when lactose not present, a repressor blocks transcription; if presen ...
Complementary base pairing Hydrogen bonding between purines
... Environmental influences causing mutations in humans genetic disorder An illness caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome eg.sicsickle eg. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation initiation First step of protein synthesis, in which all the translation components are brought t ...
... Environmental influences causing mutations in humans genetic disorder An illness caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome eg.sicsickle eg. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation initiation First step of protein synthesis, in which all the translation components are brought t ...
Genes and How They Work
... Start & Stop Signals: Where to read the blueprint Regulatory Sequences: When to read the blueprint: operators, enhancers, promotors ...
... Start & Stop Signals: Where to read the blueprint Regulatory Sequences: When to read the blueprint: operators, enhancers, promotors ...
3.1 Teacher Notes
... b. Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. i. These are often proteins ...
... b. Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. i. These are often proteins ...
Gene, Protein Synthesis & Gene Regulation
... • Each cell in the human contains all the genetic material for the growth and development of a human • Some of these genes will be need to be expressed all the time called Constitutive genes • These are the genes that are involved in of vital ...
... • Each cell in the human contains all the genetic material for the growth and development of a human • Some of these genes will be need to be expressed all the time called Constitutive genes • These are the genes that are involved in of vital ...
Genetics Review
... The DNA triplets help code for amino acids during translation because DNA is in control of the triplets of mRNA (the codon). The anticodon of the tRNA matches this codon on the ribosome and brings with it an amino acid. ...
... The DNA triplets help code for amino acids during translation because DNA is in control of the triplets of mRNA (the codon). The anticodon of the tRNA matches this codon on the ribosome and brings with it an amino acid. ...
File
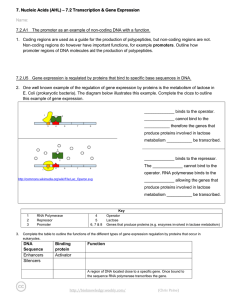
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.