the language of biology - Gonzaga College High School
... the menstrual cycle. other proteins are structural molecules, such as keratin (which forms fingernails and hair) and collagen (which is the connective tissue found in blood vessels and cartilage, and holds the inner organs together). there are many other functions for proteins. Together, they tell t ...
... the menstrual cycle. other proteins are structural molecules, such as keratin (which forms fingernails and hair) and collagen (which is the connective tissue found in blood vessels and cartilage, and holds the inner organs together). there are many other functions for proteins. Together, they tell t ...
Chapter 18 notes
... prevent other transcription factors from interacting with RNA pol. e} repressors may affect chromatin structure via recruitment of histone modifiers f} seems to be a common method for silencing genes ...
... prevent other transcription factors from interacting with RNA pol. e} repressors may affect chromatin structure via recruitment of histone modifiers f} seems to be a common method for silencing genes ...
Slide 1
... This copying process is called REPLICATION. It is carried out by a series of enzymes. These enzymes “unzip” the double-helix, insert the bases, and create links to extend the chain. ...
... This copying process is called REPLICATION. It is carried out by a series of enzymes. These enzymes “unzip” the double-helix, insert the bases, and create links to extend the chain. ...
Slide 1
... Genetic Mutations and Disease • A mutation in the gene that encodes the protein leptin leads to marked obesity in rodents and humans. ...
... Genetic Mutations and Disease • A mutation in the gene that encodes the protein leptin leads to marked obesity in rodents and humans. ...
Leukaemia Section t(3;11)(q25;q23) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Protein 431 kDa; contains two DNA binding motifs (a AT hook, and Zinc fingers), a DNA methyl transferase motif, a bromodomain; transcriptional regulatory factor; nuclear localisation. ...
... Protein 431 kDa; contains two DNA binding motifs (a AT hook, and Zinc fingers), a DNA methyl transferase motif, a bromodomain; transcriptional regulatory factor; nuclear localisation. ...
Lecture Three: Genes and Inheritance
... Ribonucleic Acid – RNA. This type of RNA is called messenger RNA, or mRNA. TRANSCRIPTION: Re-writing the DNA code into RNA When a cell needs to make protein, it “unzips” the DNA double helix, and reads the letters. As it reads, special proteins called enzymes manufacture a brand new strand of RNA th ...
... Ribonucleic Acid – RNA. This type of RNA is called messenger RNA, or mRNA. TRANSCRIPTION: Re-writing the DNA code into RNA When a cell needs to make protein, it “unzips” the DNA double helix, and reads the letters. As it reads, special proteins called enzymes manufacture a brand new strand of RNA th ...
DNA Test Review What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which
... 12. Why is tRNA important in translation? 13. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? 14. How many amino acids does this DNA sequence represent: TAAAGGCCC? 15. How can only 20 amino acids make thousands of proteins? 16. What is the ratio of A:T and C:G? 17. Why is DNA replication called semicons ...
... 12. Why is tRNA important in translation? 13. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? 14. How many amino acids does this DNA sequence represent: TAAAGGCCC? 15. How can only 20 amino acids make thousands of proteins? 16. What is the ratio of A:T and C:G? 17. Why is DNA replication called semicons ...
CH 14 notes - Lincoln Park High School
... Nucleotides join via dehydration synthesis to form a DNA strand o P of 1 nucleotide attaches to the sugar of another to form the sugar-phosphate backbone (sides of the ladder) Strands are antiparallel – they run in opposite directions ALL living things have DNA—differences are in the order of ...
... Nucleotides join via dehydration synthesis to form a DNA strand o P of 1 nucleotide attaches to the sugar of another to form the sugar-phosphate backbone (sides of the ladder) Strands are antiparallel – they run in opposite directions ALL living things have DNA—differences are in the order of ...
Chapter 2
... These recommendations have world-wide acceptance as the standard nomenclature for clinical diagnostics and are also widely used in other fields. The principal characteristics of the nomenclature aim for stability, meaningfulness, memorability and unambiguity. The nomenclature is documented using nat ...
... These recommendations have world-wide acceptance as the standard nomenclature for clinical diagnostics and are also widely used in other fields. The principal characteristics of the nomenclature aim for stability, meaningfulness, memorability and unambiguity. The nomenclature is documented using nat ...
Section 5.1
... RNA (3 types) - (pg 138) include functions – A molecule that carries genetic information from DNA (the code) to a ribosome, where the genetic information is used to form a protein. *mRNA (the codon) gets the code from DNA and carries it to a ribosome. Can travel from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. mR ...
... RNA (3 types) - (pg 138) include functions – A molecule that carries genetic information from DNA (the code) to a ribosome, where the genetic information is used to form a protein. *mRNA (the codon) gets the code from DNA and carries it to a ribosome. Can travel from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. mR ...
Dr Ishtiaq Regulation of gene expression
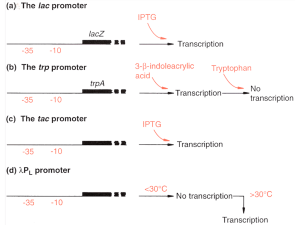
... IPTG (Isopropylthiogalactoside) - synthetic inducer, not metabolized, ...
... IPTG (Isopropylthiogalactoside) - synthetic inducer, not metabolized, ...
Transcription - Lake Station Community Schools
... called introns -they are extras and must be removed before the protein can be built Pre-mRNA also contains sections called exons -these contain the protein recipe and are joined to form the finished or mature mRNA ...
... called introns -they are extras and must be removed before the protein can be built Pre-mRNA also contains sections called exons -these contain the protein recipe and are joined to form the finished or mature mRNA ...
Plant RNA/DNA Purification Kit
... however this novel technology will allow for their simultaneous isolation from the same sample. This will not only save time, but will also be of a great benefit when isolating RNA and DNA from precious, difficult to obtain or very small samples. Furthermore, gene expression analysis will be more re ...
... however this novel technology will allow for their simultaneous isolation from the same sample. This will not only save time, but will also be of a great benefit when isolating RNA and DNA from precious, difficult to obtain or very small samples. Furthermore, gene expression analysis will be more re ...
DNA STRUCTURE - Teachers Network
... How does this shape allow the DNA to be copied easily? 2. The 4 bases that make up DNA are: _________________________, _________________________, _________________________, _________________________. The base-pairing rules are: A pairs with ____. T pairs with ____. ...
... How does this shape allow the DNA to be copied easily? 2. The 4 bases that make up DNA are: _________________________, _________________________, _________________________, _________________________. The base-pairing rules are: A pairs with ____. T pairs with ____. ...
Lectures by Erin Barley Kathleen Fitzpatrick From Gene to Protein
... RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription • The completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II bound to a promoter is called a transcription initiation complex • A promoter called a TATA box is crucial in forming the initiation complex in eukaryotes © 2011 Pearson Educati ...
... RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription • The completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II bound to a promoter is called a transcription initiation complex • A promoter called a TATA box is crucial in forming the initiation complex in eukaryotes © 2011 Pearson Educati ...
bio 1406 final exam review
... 49. What is cellular respiration 50. What is allosteric site 51. In genetic disorder testing, fetoscopy, ultrasound and sonogram are the least invasive procedures while amniocentesis is the most invasive procedure. 52. Nerve cells do not divide after they mature. 53. Gametic cells contain half the n ...
... 49. What is cellular respiration 50. What is allosteric site 51. In genetic disorder testing, fetoscopy, ultrasound and sonogram are the least invasive procedures while amniocentesis is the most invasive procedure. 52. Nerve cells do not divide after they mature. 53. Gametic cells contain half the n ...
Ch 12- DNA and RNA
... moves through ribosome, amino acid is brought into ribosome by tRNA, amino acid is transferred to growing polypeptide chain • tRNA has 3 unpaired bases (anticodon)- complementary to one mRNA codon ...
... moves through ribosome, amino acid is brought into ribosome by tRNA, amino acid is transferred to growing polypeptide chain • tRNA has 3 unpaired bases (anticodon)- complementary to one mRNA codon ...
DNA
... Levene’s work lead to the idea that the structure of DNA was a simple repeating unit of GATCGATCGATC This is why no one thought it could be the genetic material with a structure this simple • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymi ...
... Levene’s work lead to the idea that the structure of DNA was a simple repeating unit of GATCGATCGATC This is why no one thought it could be the genetic material with a structure this simple • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymi ...
Discovery of a “transforming principle”
... Levene’s work lead to the idea that the structure of DNA was a simple repeating unit of GATCGATCGATC This is why no one thought it could be the genetic material with a structure this simple • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymi ...
... Levene’s work lead to the idea that the structure of DNA was a simple repeating unit of GATCGATCGATC This is why no one thought it could be the genetic material with a structure this simple • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymi ...
regulation of cell cycle
... Sequences produced within the cell by transcription from individual miRNA genes, introns, or from polycistronic clusters of closely related miRNA genes. ‘pri-miRNAs’, are several thousand bases long. miRNAs only have complementarity in a crucial ‘seed’ region 2-8 bases long in the 5’ region. This ca ...
... Sequences produced within the cell by transcription from individual miRNA genes, introns, or from polycistronic clusters of closely related miRNA genes. ‘pri-miRNAs’, are several thousand bases long. miRNAs only have complementarity in a crucial ‘seed’ region 2-8 bases long in the 5’ region. This ca ...
splicing
... individual large rRNAs – RNase E is another ribonuclease that is responsible for removing the 5S rRNA from the precursor ...
... individual large rRNAs – RNase E is another ribonuclease that is responsible for removing the 5S rRNA from the precursor ...
DNase I (AMPD1) - Technical Bulletin - Sigma
... DNase I has been purified to remove RNase activity, and is suitable for eliminating DNA from RNA preparations prior to sensitive applications, such as RTPCR (Reverse Transcriptase – Polymerase Chain Reaction). No current RNA isolation procedure removes 100% of the DNA. Because PCR can detect even a ...
... DNase I has been purified to remove RNase activity, and is suitable for eliminating DNA from RNA preparations prior to sensitive applications, such as RTPCR (Reverse Transcriptase – Polymerase Chain Reaction). No current RNA isolation procedure removes 100% of the DNA. Because PCR can detect even a ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.