Biological information flow
... Prokaryote RNA Polymerase synthesizes mRNA, tRNA and rRNA Eukaryotes have three RNA Polymerases RNA Pol I: ...
... Prokaryote RNA Polymerase synthesizes mRNA, tRNA and rRNA Eukaryotes have three RNA Polymerases RNA Pol I: ...
Microbes in Medicine and Research
... mRNA can then Leave the Nucleus • mRNA leaves the nucleus to associate with a ribosome • While in the ribosome, transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to start ...
... mRNA can then Leave the Nucleus • mRNA leaves the nucleus to associate with a ribosome • While in the ribosome, transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to start ...
miRNA - apctp
... Small RNA mediated target RNA cleavage, post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanism. ...
... Small RNA mediated target RNA cleavage, post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanism. ...
Document
... 1. RNA-only genes produce functional RNA’s (tRNA, rRNA, miRNA, and more) 2. Protein-coding genes produce mRNA’s (17.3) 3. Transcription makes an RNA copy of a gene (17.4, 17.7) 4. Transcription begins when transcription factors bind to the promoter of a gene (17.8) G. Translation is the process of a ...
... 1. RNA-only genes produce functional RNA’s (tRNA, rRNA, miRNA, and more) 2. Protein-coding genes produce mRNA’s (17.3) 3. Transcription makes an RNA copy of a gene (17.4, 17.7) 4. Transcription begins when transcription factors bind to the promoter of a gene (17.8) G. Translation is the process of a ...
Introduction to molecular and cell biology
... Ulf Schmitz, Computational methods to discover ncRNA ...
... Ulf Schmitz, Computational methods to discover ncRNA ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... Unit of information = gene (a segment of DNA specifying a protein, rRNA or tRNA) Genes = coded by DNA or RNA (HIV) ...
... Unit of information = gene (a segment of DNA specifying a protein, rRNA or tRNA) Genes = coded by DNA or RNA (HIV) ...
DNA - Valhalla High School
... These strands of chromatin are made up of many genes. A gene can be hundreds or thousands of nucleotides long. (The entire human genome consists of 3 BILLION nucleotides). Each gene is a series of nucleotides which contains the information to make a protein. 1 gene = 1 protein. ...
... These strands of chromatin are made up of many genes. A gene can be hundreds or thousands of nucleotides long. (The entire human genome consists of 3 BILLION nucleotides). Each gene is a series of nucleotides which contains the information to make a protein. 1 gene = 1 protein. ...
Review sheet – Chapter 10
... Know that introns are the intervening sequences of DNA which do not code for any amino acid, whereas exons are the coding regions of DNA which remain and will code for specific amino acids ...
... Know that introns are the intervening sequences of DNA which do not code for any amino acid, whereas exons are the coding regions of DNA which remain and will code for specific amino acids ...
Biology II – Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
... o The complementary strands allow for exact self-replication (duplication) o This process of duplicating a DNA molecule is called replication. o During the process of replication, the strand unwinds – each strand providing a template to build a new complementary strand – therefore, producing two new ...
... o The complementary strands allow for exact self-replication (duplication) o This process of duplicating a DNA molecule is called replication. o During the process of replication, the strand unwinds – each strand providing a template to build a new complementary strand – therefore, producing two new ...
Biology and computers - Cal State LA
... Note the one letter and 3 letter abbreviations for you amino acid(s). Identify the atoms in red, blue, white, gray, and other colors Find the carboxy group, amino group, beta carbon, R group Categorize the amino acids – and be able to say why – some fit in more ...
... Note the one letter and 3 letter abbreviations for you amino acid(s). Identify the atoms in red, blue, white, gray, and other colors Find the carboxy group, amino group, beta carbon, R group Categorize the amino acids – and be able to say why – some fit in more ...
RNA-Seq - iPlant Pods
... All honeybees begin as worker bees, flying short distances. Some honeybees transition into foragers, flying long distances. This transition necessitates major changes in flight muscles. Goal is to identify the gene expression changes in flight muscles during this transition ...
... All honeybees begin as worker bees, flying short distances. Some honeybees transition into foragers, flying long distances. This transition necessitates major changes in flight muscles. Goal is to identify the gene expression changes in flight muscles during this transition ...
12-Transcription-The Relationship Between Genes and Proteins
... the 5′ cap is retained in mature mRNAs. ...
... the 5′ cap is retained in mature mRNAs. ...
PPR (pentatricopeptide repeat) proteins in mammals: important aids
... mutations in the gene encoding this PPR protein, LRPPRC (leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat cassette), were shown to cause a rare form of inherited COX (cytochrome c oxidase) deficiency that was termed ‘Leigh Syndrome French-Canadian type’ (or LSFC), as it was found in the population of the Sague ...
... mutations in the gene encoding this PPR protein, LRPPRC (leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat cassette), were shown to cause a rare form of inherited COX (cytochrome c oxidase) deficiency that was termed ‘Leigh Syndrome French-Canadian type’ (or LSFC), as it was found in the population of the Sague ...
OPERONS NOTES
... -In the absence of lactose, the Lac repressor protein binds to the operator and keeps RNA polymerase from transcribing the lac genes. -It would be wasteful for E. coli if the lac genes were expressed when lactose was not present. The effect of the Lac repressor on the lac genes is referred to as ne ...
... -In the absence of lactose, the Lac repressor protein binds to the operator and keeps RNA polymerase from transcribing the lac genes. -It would be wasteful for E. coli if the lac genes were expressed when lactose was not present. The effect of the Lac repressor on the lac genes is referred to as ne ...
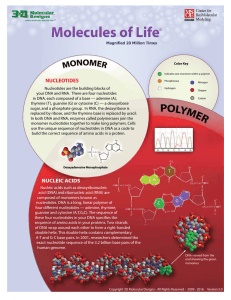
Nucleic Acids Placemat
... acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the sequence of amino acids in your protei ...
... acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the sequence of amino acids in your protei ...
nucleus
... build ribosome subunits from rRNA & proteins exit through nuclear pores to cytoplasm & combine to form functional ribosomes ...
... build ribosome subunits from rRNA & proteins exit through nuclear pores to cytoplasm & combine to form functional ribosomes ...
Ch 18
... Protein processing and degradation • Protein processing and degradation by proteasomes are subject to regulation. ...
... Protein processing and degradation • Protein processing and degradation by proteasomes are subject to regulation. ...
Definitions
... Adenine and Guanine are the two pyrimidine bases. They are single ring molecules Cytosine and Thymine are the two purine bases. They are double ring molecules Messenger RNA takes the complementary DNA strand out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA - As the mRNA moves through, tRNA mo ...
... Adenine and Guanine are the two pyrimidine bases. They are single ring molecules Cytosine and Thymine are the two purine bases. They are double ring molecules Messenger RNA takes the complementary DNA strand out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA - As the mRNA moves through, tRNA mo ...
Ch 18
... a major information-processing challenge: 1. the typical eukaryotic genome is much larger than that of a prokaryotic cell 2. cell specialization limits the expression of many genes to specific cells ...
... a major information-processing challenge: 1. the typical eukaryotic genome is much larger than that of a prokaryotic cell 2. cell specialization limits the expression of many genes to specific cells ...
CHIP-seq and RNA-seq
... • Goal: to measure RNA levels of all genes in a genome under various experimental conditions • RNA levels vary with: ...
... • Goal: to measure RNA levels of all genes in a genome under various experimental conditions • RNA levels vary with: ...
Genome evolution: a sequence
... snoRNA – small nucleolar RNA. Involved in the chemical modifications made in the construction of ribosomes. Often encode within the introns of ribosomal proteins genes tRNA – transfer RNA. Delivering amino-acid to the ribosome. piRNA - ??? ...
... snoRNA – small nucleolar RNA. Involved in the chemical modifications made in the construction of ribosomes. Often encode within the introns of ribosomal proteins genes tRNA – transfer RNA. Delivering amino-acid to the ribosome. piRNA - ??? ...
103 Lecture Ch22a
... synthesized, the ribosome reaches the the “stop” codon: UGA, UAA, or UAG • There is no tRNA with an anticodon for the “stop” codons • Therefore, protein synthesis ends (termination) • The polypeptide is released from the ribosome and the protein can take on it’s 3-D structure (some proteins begin fo ...
... synthesized, the ribosome reaches the the “stop” codon: UGA, UAA, or UAG • There is no tRNA with an anticodon for the “stop” codons • Therefore, protein synthesis ends (termination) • The polypeptide is released from the ribosome and the protein can take on it’s 3-D structure (some proteins begin fo ...
Document
... a. blood from a newborn baby b. a picture of a baby before it is born c. a picture of the chromosomes in a cell d. fluid that surrounds a baby before it is born How can genetic counselors predict genetic disorders? a. by studying karyotypes and pedigree charts b. by taking pictures of the baby befor ...
... a. blood from a newborn baby b. a picture of a baby before it is born c. a picture of the chromosomes in a cell d. fluid that surrounds a baby before it is born How can genetic counselors predict genetic disorders? a. by studying karyotypes and pedigree charts b. by taking pictures of the baby befor ...
Transcription Factors
... – diffusible proteins – act at numerous sites on many chromosomes – Influence transcription by interacting with other proteins or segments of DNA • “Upstream” = being 5’ to the start site – Negative numbers of bases ...
... – diffusible proteins – act at numerous sites on many chromosomes – Influence transcription by interacting with other proteins or segments of DNA • “Upstream” = being 5’ to the start site – Negative numbers of bases ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.