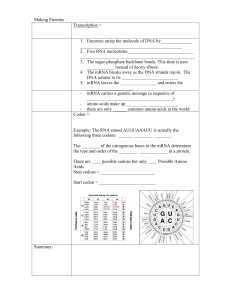
Transcription is the process by which RNA polymerase copies a
... scientists also noticed that DNA is like a zipper – in it can be split into a two single strands by separating the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. Check out this video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0CMIgZQakHY ...
... scientists also noticed that DNA is like a zipper – in it can be split into a two single strands by separating the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. Check out this video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0CMIgZQakHY ...
BIOL290
... A. Understand the changes that can occur in chromosomes, such as translocation, inversion, deletion, duplication, and loss/gain of genetic material. B. Review the terms euploidy and aneuploidy and be able to recognize examples of each. C. Understand the correlation between chromosome sets and size o ...
... A. Understand the changes that can occur in chromosomes, such as translocation, inversion, deletion, duplication, and loss/gain of genetic material. B. Review the terms euploidy and aneuploidy and be able to recognize examples of each. C. Understand the correlation between chromosome sets and size o ...
ppt - Duke Computer Science
... Ribozymes = RNA enzymes 1982 Tom Cech: Tetrahymena rRNA intron is self-spliced out (Guanosine [GR] + Mg++) Altman and Pace: Ribonuclease P is an RNP: RNA component alone can process the 5’ ends of tRNAs Mitochondrial group I introns (GR –catalyzed) also can self-splice Then group II introns in mitoc ...
... Ribozymes = RNA enzymes 1982 Tom Cech: Tetrahymena rRNA intron is self-spliced out (Guanosine [GR] + Mg++) Altman and Pace: Ribonuclease P is an RNP: RNA component alone can process the 5’ ends of tRNAs Mitochondrial group I introns (GR –catalyzed) also can self-splice Then group II introns in mitoc ...
RNA and DNA aptamers. Ribozymes and DNAzymes Daniel
... Ribozymes = RNA enzymes 1982 Tom Cech: Tetrahymena rRNA intron is self-spliced out (Guanosine [GR] + Mg++) Altman and Pace: Ribonuclease P is an RNP: RNA component alone can process the 5’ ends of tRNAs Mitochondrial group I introns (GR –catalyzed) also can self-splice Then group II introns in mitoc ...
... Ribozymes = RNA enzymes 1982 Tom Cech: Tetrahymena rRNA intron is self-spliced out (Guanosine [GR] + Mg++) Altman and Pace: Ribonuclease P is an RNP: RNA component alone can process the 5’ ends of tRNAs Mitochondrial group I introns (GR –catalyzed) also can self-splice Then group II introns in mitoc ...
First week lectures
... • RNA performs two functions coding information and synthesis – Like essentially all the important biological molecules RNA is a linear polymer that is made of a small number of monomers – The different monomers are attached to the same backbone (sugar rings (ribose) linked by phosphates) R T/U ...
... • RNA performs two functions coding information and synthesis – Like essentially all the important biological molecules RNA is a linear polymer that is made of a small number of monomers – The different monomers are attached to the same backbone (sugar rings (ribose) linked by phosphates) R T/U ...
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes - Bremen High School District 228
... AP Biology DNA packing movie ...
... AP Biology DNA packing movie ...
REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION
... so transcription and translation occur at different times Eukaryotic gene regulation can occur at transcription or after transcription Prokaryotic gene regulation can occur only at transcription Eukaryotic gene regulation can control how much transcription occurs Prokaryotic gene regulation ...
... so transcription and translation occur at different times Eukaryotic gene regulation can occur at transcription or after transcription Prokaryotic gene regulation can occur only at transcription Eukaryotic gene regulation can control how much transcription occurs Prokaryotic gene regulation ...
1-1 - We can offer most test bank and solution manual you need.
... that orthologous genes had between 60 to 80% amino acid identity between species. B. dulcis was found to have a set of genes encoding enzymes important for polysaccharide degradation that did not exist in the other species. Interestingly, sequence comparisons of these polysaccharide-degrading genes ...
... that orthologous genes had between 60 to 80% amino acid identity between species. B. dulcis was found to have a set of genes encoding enzymes important for polysaccharide degradation that did not exist in the other species. Interestingly, sequence comparisons of these polysaccharide-degrading genes ...
Slide 1
... Hannon, G. J., & Rossi, J. J. (2004). Unlocking the potential of the human genome with RNA interference. Nature , 371-378. Juliano, R., Alam, R., Dixit, V., & Kang, H. (2008). Mechanisms and strategies for effective delivery of antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Research , 1-14. ...
... Hannon, G. J., & Rossi, J. J. (2004). Unlocking the potential of the human genome with RNA interference. Nature , 371-378. Juliano, R., Alam, R., Dixit, V., & Kang, H. (2008). Mechanisms and strategies for effective delivery of antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Research , 1-14. ...
Ch 18 Lecture
... e.g. in newborn mammals, E.coli are bathed in milk, containing the milk sugar lactose The lactose operon contains three structural genes, each coding for an enzyme that aids in lactose metabolism lactose not present: repressor active, operon off; no transcription for lactose enzymes lactose pres ...
... e.g. in newborn mammals, E.coli are bathed in milk, containing the milk sugar lactose The lactose operon contains three structural genes, each coding for an enzyme that aids in lactose metabolism lactose not present: repressor active, operon off; no transcription for lactose enzymes lactose pres ...
Schol Biol: Genetics
... • Chitin synthase (shell structure) • HSP70 (stress) Biochemical measurements • Carbonic anhydrase activity ...
... • Chitin synthase (shell structure) • HSP70 (stress) Biochemical measurements • Carbonic anhydrase activity ...
How Genes Are Regulated
... • Describe how prokaryotic gene expression occurs at the transcriptional level • Understand that eukaryotic gene expression occurs at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels For a cell to function properly, necessary proteins must be synthe ...
... • Describe how prokaryotic gene expression occurs at the transcriptional level • Understand that eukaryotic gene expression occurs at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels For a cell to function properly, necessary proteins must be synthe ...
Hypothesis: Variations in the rate of DNA replication determine the
... genes and higher order structures compete for limited resources is a symmetrybreaking situation previously proposed to lead to differentiation. Recent experiments are consistent with an intimate relationship between metabolism and the rate of chromosome replication in bacteria. The process of chromo ...
... genes and higher order structures compete for limited resources is a symmetrybreaking situation previously proposed to lead to differentiation. Recent experiments are consistent with an intimate relationship between metabolism and the rate of chromosome replication in bacteria. The process of chromo ...
Competency Goal 2: The learner will develop an understanding of
... Goal 3 Key Concepts Review: The learner will develop an understanding of the continuity of life and the changes of organisms over time. 1. Define DNA and give its function. (Ch 12) 2. What is the shape of DNA? (293) 3. Who discovered the structure of DNA in 1953? (293) 4. What are the three main par ...
... Goal 3 Key Concepts Review: The learner will develop an understanding of the continuity of life and the changes of organisms over time. 1. Define DNA and give its function. (Ch 12) 2. What is the shape of DNA? (293) 3. Who discovered the structure of DNA in 1953? (293) 4. What are the three main par ...
Ch 12.DNA and RNA.Biology.Landis
... 33. Where does translation occur? 34. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation can occur, messenger RNA must be transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid i ...
... 33. Where does translation occur? 34. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation can occur, messenger RNA must be transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid i ...
Schedule
... rRNA is the RNA found in a ribosome and it is folded up with proteins to complete the structure; its function is to help ‘read’ the mRNA sequence. tRNA is a folded molecule with a clover leaf shape. It carries an amino acid at one end and has an anticodon (3 bases). The different anticodons code for ...
... rRNA is the RNA found in a ribosome and it is folded up with proteins to complete the structure; its function is to help ‘read’ the mRNA sequence. tRNA is a folded molecule with a clover leaf shape. It carries an amino acid at one end and has an anticodon (3 bases). The different anticodons code for ...
Unit 7 Molecular Genetics Chp 17 Protein Synthesis
... 3) The RNA transcript is cut to release the intron, and the exons are spliced together; the spliceosome then comes apart, releasing mRNA, which now contains only exons. ...
... 3) The RNA transcript is cut to release the intron, and the exons are spliced together; the spliceosome then comes apart, releasing mRNA, which now contains only exons. ...
Ch17WordLectureOutline w pics
... spliced together; the spliceosome then comes apart, releasing mRNA, which now contains only exons. ...
... spliced together; the spliceosome then comes apart, releasing mRNA, which now contains only exons. ...
C. The Synthesis of Protein
... 3) The RNA transcript is cut to release the intron, and the exons are spliced together; the spliceosome then comes apart, releasing mRNA, which now contains only exons. ...
... 3) The RNA transcript is cut to release the intron, and the exons are spliced together; the spliceosome then comes apart, releasing mRNA, which now contains only exons. ...
bch2ibm: molecular biology end of semester 1 exam notes 2014
... called? -‐ Hypothesised that AAs don’t bind directly to mRNA but need an adaptor molecule that could match the mRNA with a corresponding AA. -‐ One side of the adaptor could bind a specific AA to ...
... called? -‐ Hypothesised that AAs don’t bind directly to mRNA but need an adaptor molecule that could match the mRNA with a corresponding AA. -‐ One side of the adaptor could bind a specific AA to ...
Dna sequence and Cell Activity
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
DNA Transcription
... 6. A new _________ carrying an __________ ________ pairs with the second mRNA codon. 7. The first and second ________ ________ bond together in a _________ bond. 8. This process continues joining amino acids until the ribosome reaches a _______ codon on the mRNA strand. 9. The amino acid strand (now ...
... 6. A new _________ carrying an __________ ________ pairs with the second mRNA codon. 7. The first and second ________ ________ bond together in a _________ bond. 8. This process continues joining amino acids until the ribosome reaches a _______ codon on the mRNA strand. 9. The amino acid strand (now ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.