Cauliflower mosaic virus: still in the news
... et al., 2000). Recently, it has been shown that the function of P6 depends on its association with polysomes and the eukaryotic initiation factor eIF3 (Park et al., 2001). P6 physically interacts with the g subunit of eIF3 and three proteins of the 60S ribosomal subunit, namely L18 (Leh et al., 2000 ...
... et al., 2000). Recently, it has been shown that the function of P6 depends on its association with polysomes and the eukaryotic initiation factor eIF3 (Park et al., 2001). P6 physically interacts with the g subunit of eIF3 and three proteins of the 60S ribosomal subunit, namely L18 (Leh et al., 2000 ...
CHAPTER 11.1
... What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Which parts make up the backbone of a DNA strand? 2. List the two base pairs found in DNA. 3. If six bases on one strand of a DNA double helix are AGTCGG, what are the six bases on the complementary section of the other strand of DNA? ...
... What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Which parts make up the backbone of a DNA strand? 2. List the two base pairs found in DNA. 3. If six bases on one strand of a DNA double helix are AGTCGG, what are the six bases on the complementary section of the other strand of DNA? ...
Mader/Biology, 13/e – Chapter Outline
... b. Mature red blood cells eject their nucleus but synthesize hemoglobin for several months; the mRNAs must persist during this time. c. Ribonucleases are enzymes associated with ribosomes that degrade mRNA. d. Mature mRNA has non-coding segments at 3' cap and 5' poly-A tail ends; differences in thes ...
... b. Mature red blood cells eject their nucleus but synthesize hemoglobin for several months; the mRNAs must persist during this time. c. Ribonucleases are enzymes associated with ribosomes that degrade mRNA. d. Mature mRNA has non-coding segments at 3' cap and 5' poly-A tail ends; differences in thes ...
RNA polymerase
... the processes that link DNA sequences to the synthesis of a specific polypeptide chain. ...
... the processes that link DNA sequences to the synthesis of a specific polypeptide chain. ...
insightLMU RESEARCH
... which deliver the building blocks for proteins to the ribosomes. However, the sncRNAs play important regulatory roles. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), for instance, bind to specific mRNAs to form short double-stranded regions, inhibiting translation into protein and inducing their destruction. Micro ...
... which deliver the building blocks for proteins to the ribosomes. However, the sncRNAs play important regulatory roles. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), for instance, bind to specific mRNAs to form short double-stranded regions, inhibiting translation into protein and inducing their destruction. Micro ...
TD7: Gel Electrophoresis Photoaffinity probes GEL
... Negatively charged DNA runs to the cathode (cathode at bottom, anode at top) Note- mobility is proportional to size, because charge is proportional to size (unlike with proteins) For very high resolution, DNA can be analyzed by denaturing PAGE (urea is used to denature DNA instead of SDS) - gives si ...
... Negatively charged DNA runs to the cathode (cathode at bottom, anode at top) Note- mobility is proportional to size, because charge is proportional to size (unlike with proteins) For very high resolution, DNA can be analyzed by denaturing PAGE (urea is used to denature DNA instead of SDS) - gives si ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... ■ Principle of Dominant and Recessive – some genes can hide or mask others ■ Law of Segregation – Mendel’s genetics principle that states that genes in pairs separate during gamete formation and gene pairs are reformed during fertilization ...
... ■ Principle of Dominant and Recessive – some genes can hide or mask others ■ Law of Segregation – Mendel’s genetics principle that states that genes in pairs separate during gamete formation and gene pairs are reformed during fertilization ...
2013 DNA, Repl, Trans and Transl Review
... 1. What are the subunits called that make up DNA? 2. What three things make up a nucleotide? 3. Describe the structure of DNA. 4. An organism's characteristics and directions for proteins synthesis are coded for by molecules of __________. 5. What are the monomers of proteins? How many of these mono ...
... 1. What are the subunits called that make up DNA? 2. What three things make up a nucleotide? 3. Describe the structure of DNA. 4. An organism's characteristics and directions for proteins synthesis are coded for by molecules of __________. 5. What are the monomers of proteins? How many of these mono ...
CH 17 PPT
... intervene between coding sequences (exons); are initially transcribed but are not translated because they are excised before mRNA leaves the nucleus • Exons—coding sequences of a gene that are transcribed and expressed. • RNA splicing—RNA processing that removes introns and joins exons from eukaryot ...
... intervene between coding sequences (exons); are initially transcribed but are not translated because they are excised before mRNA leaves the nucleus • Exons—coding sequences of a gene that are transcribed and expressed. • RNA splicing—RNA processing that removes introns and joins exons from eukaryot ...
Clustering
... 2. Genome sequencing projects. These generated a large number of gene probes that can be used to analyse global transcription. ...
... 2. Genome sequencing projects. These generated a large number of gene probes that can be used to analyse global transcription. ...
DNA Recap
... H. Identical strands of DNA that appear at the end of DNA Replication I. A mistake that occurs during DNA replication that does not affect the chances of survival of an organism ...
... H. Identical strands of DNA that appear at the end of DNA Replication I. A mistake that occurs during DNA replication that does not affect the chances of survival of an organism ...
RNA polymerase I
... • Only a small fraction of DNA codes for proteins, rRNA, and tRNA. • A significant amount of the genome may be transcribed into noncoding RNAs. • Noncoding RNAs regulate gene expression at two points: mRNA translation and chromatin configuration. ...
... • Only a small fraction of DNA codes for proteins, rRNA, and tRNA. • A significant amount of the genome may be transcribed into noncoding RNAs. • Noncoding RNAs regulate gene expression at two points: mRNA translation and chromatin configuration. ...
RNAi, Penetrance and Expressivity Genetics 322, Fall 2008
... Scientists studying many different organisms, including petunia, soon discovered that this system of inactivating gene expression was a highly conserved mechanism. Furthermore, they found that the function of virtually all genes could be down-regulated through the RNAi mechanism simply by introducin ...
... Scientists studying many different organisms, including petunia, soon discovered that this system of inactivating gene expression was a highly conserved mechanism. Furthermore, they found that the function of virtually all genes could be down-regulated through the RNAi mechanism simply by introducin ...
Validation of microarray gene expression analysis
... Human lymphoblasts (Coriell, Camden, NJ, catalogue # GM 15851) and human Tacute lymphoblastic leukemia Jurkat cells (procured from ATCC) were grown on RPMI-1640 medium with L-glutamine (Cellgro) supplemented with 15% FBS (Gibco) and Antibiotic-Antimycotic solution (Cellgro) at 37°C in the atmosphere ...
... Human lymphoblasts (Coriell, Camden, NJ, catalogue # GM 15851) and human Tacute lymphoblastic leukemia Jurkat cells (procured from ATCC) were grown on RPMI-1640 medium with L-glutamine (Cellgro) supplemented with 15% FBS (Gibco) and Antibiotic-Antimycotic solution (Cellgro) at 37°C in the atmosphere ...
Imprinted green beards: a little less than kin and more than kind The
... one-quarter for genes of maternal grandmaternal origin but are unrelated for all ...
... one-quarter for genes of maternal grandmaternal origin but are unrelated for all ...
Molecular Biology
... of a cell in structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes are small, granular structures where protein synthesis takes place. Each ribosome is a complex consisting of about 60% ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 40% protein. 2. Messenger RNAs-are the nucleic acids that "record“ information from DNA in the cell nucl ...
... of a cell in structures called ribosomes. Ribosomes are small, granular structures where protein synthesis takes place. Each ribosome is a complex consisting of about 60% ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 40% protein. 2. Messenger RNAs-are the nucleic acids that "record“ information from DNA in the cell nucl ...
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are one of the most abundant groups of
... One subject we are most interested is the Bioinformatics, where I have a small but a capable group. The specific reason I write to you concerns one of the topics we work on – miRNA and gene regulation. As it is known now, the microRNAs (miRNAs) are one of the most abundant groups of regulatory molec ...
... One subject we are most interested is the Bioinformatics, where I have a small but a capable group. The specific reason I write to you concerns one of the topics we work on – miRNA and gene regulation. As it is known now, the microRNAs (miRNAs) are one of the most abundant groups of regulatory molec ...
Biology Slide 1 of 39 End Show
... RNA Editing Some DNA within a gene is not needed to produce a protein. These areas are called introns. The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called exons. ...
... RNA Editing Some DNA within a gene is not needed to produce a protein. These areas are called introns. The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called exons. ...
S2452302X16000073_mmc1 - JACC: Basic to Translational
... (Abcam 6994) and α-smooth muscle actin (Abcam 32575). Arterioles were identified by von Willebrand factor and α-smooth muscle actin positive staining and capillaries by von Willebrand factor positive staining only. For cardiomyocyte cross sectional area, slides were immunostained with wheat-germ agg ...
... (Abcam 6994) and α-smooth muscle actin (Abcam 32575). Arterioles were identified by von Willebrand factor and α-smooth muscle actin positive staining and capillaries by von Willebrand factor positive staining only. For cardiomyocyte cross sectional area, slides were immunostained with wheat-germ agg ...
problem set
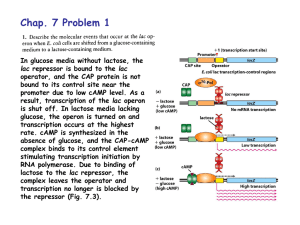
... promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex binds to its control element stimu ...
... promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex binds to its control element stimu ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.