Unit 1 - Moodle
... Identify the triplet code nature of the genetic code Define the term gene Outline the process the process of protein synthesis, including the role of transcription, translation, messenger RNA, transfer RNA and the template (antisense) DNA strand ...
... Identify the triplet code nature of the genetic code Define the term gene Outline the process the process of protein synthesis, including the role of transcription, translation, messenger RNA, transfer RNA and the template (antisense) DNA strand ...
3.4 C: Transcription Quiz PROCTOR VERSION
... This answer suggests the student may understand the base-pairing rules of DNA, but does not understand that when DNA is transcribed, the mRNA pairs uracil (U) with adenine (A) instead of with thymine (T), and that uracil (U) is not present in DNA because DNA uses thymine (T) instead of uracil (U). A ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand the base-pairing rules of DNA, but does not understand that when DNA is transcribed, the mRNA pairs uracil (U) with adenine (A) instead of with thymine (T), and that uracil (U) is not present in DNA because DNA uses thymine (T) instead of uracil (U). A ...
2012
... What amino acid will be charged to this tRNA? Leu 17. [8 points] In 1-2 sentences, briefly describe the role of the following components in bacterial protein synthesis: A) Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases Aminoacyl-tRNA sythetases both activate an amino acid for protein synthesis and pair an amino acid wi ...
... What amino acid will be charged to this tRNA? Leu 17. [8 points] In 1-2 sentences, briefly describe the role of the following components in bacterial protein synthesis: A) Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases Aminoacyl-tRNA sythetases both activate an amino acid for protein synthesis and pair an amino acid wi ...
Genomics – The Language of DNA
... Both ends of the transposon, which consist of inverted repeats; that is, identical sequences reading in ...
... Both ends of the transposon, which consist of inverted repeats; that is, identical sequences reading in ...
Reading Guide: The Origins of Life
... acids. Some of the concentrated amino acids then bond together and form polypeptides. Clay, in particular, concentrates amino acids and other organic monomers and could have held monomers close together. These experiments suggest that organic polymers such as polypeptides could have formed under th ...
... acids. Some of the concentrated amino acids then bond together and form polypeptides. Clay, in particular, concentrates amino acids and other organic monomers and could have held monomers close together. These experiments suggest that organic polymers such as polypeptides could have formed under th ...
William Yin
... which separates it into two strands (cutting dsRNA into 22-25nt siRNAs). It then proceeds to destroy other single-stranded RNA molecules that are complementary to one of those segments. The siRNAs that form from dsRNA target RNA-degrading enzymes (RNAse) through RISC to destroy transcripts complemen ...
... which separates it into two strands (cutting dsRNA into 22-25nt siRNAs). It then proceeds to destroy other single-stranded RNA molecules that are complementary to one of those segments. The siRNAs that form from dsRNA target RNA-degrading enzymes (RNAse) through RISC to destroy transcripts complemen ...
Identify which nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) contains each of the
... Problem 2 Condensation of the Components Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions: a. ...
... Problem 2 Condensation of the Components Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions: a. ...
DNA Workshop_Protein_Synthesis
... same as DNA. But instead of thymine (T), the fourth base is uracil (U). Each base has a complement -- another base that it can connect to. A complements U, and C complements G. Drag bases from the left to their complementary bases on the DNA strand. Description: Nucleotides are dragged from one area ...
... same as DNA. But instead of thymine (T), the fourth base is uracil (U). Each base has a complement -- another base that it can connect to. A complements U, and C complements G. Drag bases from the left to their complementary bases on the DNA strand. Description: Nucleotides are dragged from one area ...
The human genome: gene structure and function
... • Some (very few) genes do not have introns. One example is the histone genes, which encode the small DNA-binding proteins, histones H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. • Shown here is a histone gene that is only 400 base pairs (bp) in length and is composed of only one exon. • The beta-globin gene has three ...
... • Some (very few) genes do not have introns. One example is the histone genes, which encode the small DNA-binding proteins, histones H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. • Shown here is a histone gene that is only 400 base pairs (bp) in length and is composed of only one exon. • The beta-globin gene has three ...
Document
... 2’ hydroxyl – H-bonding in RNA structure – Reactions of catalytic RNA (rare) – Hydrolysis ...
... 2’ hydroxyl – H-bonding in RNA structure – Reactions of catalytic RNA (rare) – Hydrolysis ...
Molecular Structure of DNA and RNA part 1 powerpoint
... His findings suggested that there was a ‘factor’ which was transmitted from parent to offspring and inherited. This factor was not understood at that time and not until the middle of the 20th century. ...
... His findings suggested that there was a ‘factor’ which was transmitted from parent to offspring and inherited. This factor was not understood at that time and not until the middle of the 20th century. ...
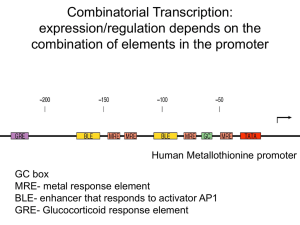
Combinatorial Transcription: expression/regulation depends on the
... domain is now free to form other domains with alternative boundary elements (in this case containing genes Z1and Z2). Enhancer 1(en1) is now unable to act on the promoter of gene Y because of the new location of the gypsy insulator. Nevertheless, this enhancer is still functional and competent to ac ...
... domain is now free to form other domains with alternative boundary elements (in this case containing genes Z1and Z2). Enhancer 1(en1) is now unable to act on the promoter of gene Y because of the new location of the gypsy insulator. Nevertheless, this enhancer is still functional and competent to ac ...
Parallel human genome analysis: Microarray
... Human cDNA from human T mRNA transformed by the Epstein Barr Virus with 5’ amino acid modification, amplified by PCR, and arrayed onto silyated microscope slides Probes labeled with fluorescin and Cy5-dCTP are hybridized to 1056-element array and scanned Verify expression patterns with RNA Blot ...
... Human cDNA from human T mRNA transformed by the Epstein Barr Virus with 5’ amino acid modification, amplified by PCR, and arrayed onto silyated microscope slides Probes labeled with fluorescin and Cy5-dCTP are hybridized to 1056-element array and scanned Verify expression patterns with RNA Blot ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Subunit IIa is the primary product in yeast – Can be converted to IIb by proteolytic removal of the carboxylterminal domain (CTD) which is 7aa-peptide repeated over and over. Enzyme with IIa binds to the promoter – Converts to IIo by phosphorylating 2 ser in the repeating heptad of the CTD. Enzyme ...
... • Subunit IIa is the primary product in yeast – Can be converted to IIb by proteolytic removal of the carboxylterminal domain (CTD) which is 7aa-peptide repeated over and over. Enzyme with IIa binds to the promoter – Converts to IIo by phosphorylating 2 ser in the repeating heptad of the CTD. Enzyme ...
NATIONAL BRAIN RESEARCH CENTRE(NBRC) NH-8, Manesar-122050, HARYANA
... Mohr’s salt is prepared in warm distilled water by the reaction of (NH4)2SO4 and: ...
... Mohr’s salt is prepared in warm distilled water by the reaction of (NH4)2SO4 and: ...
Test Review on DNA Structure, DNA Replication
... Be able to define mutation. Know the difference between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. The website http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/dna/# has a practice activity on DNA replication and protein synthesis. Be able to define homeostasis. Be able to explain what positive and negative feedb ...
... Be able to define mutation. Know the difference between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. The website http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/dna/# has a practice activity on DNA replication and protein synthesis. Be able to define homeostasis. Be able to explain what positive and negative feedb ...
DNA Structure and Function
... • At Initiation RNA polymerase binds start of gene and uncoils DNA. • At Elongation RNA polymerase moves along the gene briefly binding nucleotides to DNA (only about 10 nucleotides at a time), as the RNA nucleotides join together in a making a single complimentary strand • At Termination the mRNA m ...
... • At Initiation RNA polymerase binds start of gene and uncoils DNA. • At Elongation RNA polymerase moves along the gene briefly binding nucleotides to DNA (only about 10 nucleotides at a time), as the RNA nucleotides join together in a making a single complimentary strand • At Termination the mRNA m ...
Text S1.
... Several plant virus RNAi suppressors influence the miRNA pathway, thereby inducing strong developmental defects in transgenic plants that express RNAi suppressors during development [1,2]. This effect may be due to convergence of the antiviral RNAi and miRNA pathways on Argonaute-1 (AGO1) in plants. ...
... Several plant virus RNAi suppressors influence the miRNA pathway, thereby inducing strong developmental defects in transgenic plants that express RNAi suppressors during development [1,2]. This effect may be due to convergence of the antiviral RNAi and miRNA pathways on Argonaute-1 (AGO1) in plants. ...
mRNA
... How is RNA Assembled? • Transcription begins when an RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a DNA site called a promoter – RNA polymerase moves over a gene region and unwinds the double helix a bit so it can “read” the base sequence of the DNA strand – The polymerase joins free RNA nucleo ...
... How is RNA Assembled? • Transcription begins when an RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a DNA site called a promoter – RNA polymerase moves over a gene region and unwinds the double helix a bit so it can “read” the base sequence of the DNA strand – The polymerase joins free RNA nucleo ...
DNA to mRNA to Protein Assignment
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as ...
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations
... DNA polymerase also “proofreads” each new DNA strand, ensuring that each molecule is a perfect copy of the original ...
... DNA polymerase also “proofreads” each new DNA strand, ensuring that each molecule is a perfect copy of the original ...
Ch11_lecture students
... encode essential proteins, like the electron transport chain of mitochondria. • Other genes are transcribed only in specific types of cells. • How do cells regulate which genes are transcribed? • Proteins bind to “control regions” near gene promotors and block or enhance the binding of RNA polymeras ...
... encode essential proteins, like the electron transport chain of mitochondria. • Other genes are transcribed only in specific types of cells. • How do cells regulate which genes are transcribed? • Proteins bind to “control regions” near gene promotors and block or enhance the binding of RNA polymeras ...
RNA Interference Provides New Approach for Finding Cancer Genes
... mechanism. They’ve now made short hairpin RNAs that can silence every gene in the human and mouse genomes. For their experiments reported in Science, the pair first identified 3,000 genes important in cell signaling, growth, and other essential processes. Next, they inserted a genetic code for short h ...
... mechanism. They’ve now made short hairpin RNAs that can silence every gene in the human and mouse genomes. For their experiments reported in Science, the pair first identified 3,000 genes important in cell signaling, growth, and other essential processes. Next, they inserted a genetic code for short h ...
CHEM 482
... 4. What is the energetic cost, in ATPs, for the E. coli synthesis of a polypeptide chain of 100 amino acid residues starting from amino acids and mRNA? Assume that no losses are incurred as a result of proofreading. ...
... 4. What is the energetic cost, in ATPs, for the E. coli synthesis of a polypeptide chain of 100 amino acid residues starting from amino acids and mRNA? Assume that no losses are incurred as a result of proofreading. ...
Exam II Notes DNA
... composed of both DNA and protein, we didn’t know which material coded for traits. (Now we know that DNA is wrapped around spooling proteins called histones (8.5, p.124), which explains why chromosomes are composed of both DNA and protein.) B. While DNA was discovered in 1868 by Swiss biochemist Frie ...
... composed of both DNA and protein, we didn’t know which material coded for traits. (Now we know that DNA is wrapped around spooling proteins called histones (8.5, p.124), which explains why chromosomes are composed of both DNA and protein.) B. While DNA was discovered in 1868 by Swiss biochemist Frie ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.