Genes to Proteins Nucleic Acid Structure
... • Recombinant DNA serves as a cloning vector – Incorporate into cells – Select cells that have been transformed ...
... • Recombinant DNA serves as a cloning vector – Incorporate into cells – Select cells that have been transformed ...
No Slide Title
... From Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants (W.Gruissem, B. Buchanan and R.Jones p.416. [/425 ASPP, Rockville MD, 2000 ...
... From Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants (W.Gruissem, B. Buchanan and R.Jones p.416. [/425 ASPP, Rockville MD, 2000 ...
Genomes
... Humans and other mammals have the lowest gene density, or number of genes, in a given length of DNA Multicellular eukaryotes have many introns within genes and noncoding DNA between genes ...
... Humans and other mammals have the lowest gene density, or number of genes, in a given length of DNA Multicellular eukaryotes have many introns within genes and noncoding DNA between genes ...
TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION
... can cause the wrong amino acids to be added to the chain. This usually results in the assembly of a nonfunctional protein. Mutations happen on a daily basis. Some are caused by errors in the cell replication process. Others are caused by exposure to chemicals or ionizing radiation. There are protein ...
... can cause the wrong amino acids to be added to the chain. This usually results in the assembly of a nonfunctional protein. Mutations happen on a daily basis. Some are caused by errors in the cell replication process. Others are caused by exposure to chemicals or ionizing radiation. There are protein ...
File
... • A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. • There are 20 different amino acids codon for methionine (Met) ...
... • A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. • There are 20 different amino acids codon for methionine (Met) ...
Gene Section NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... This article is an update of: Huret JL. NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol.1998;2(1):7. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 1999 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
... This article is an update of: Huret JL. NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol.1998;2(1):7. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 1999 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
Chapter 10: Microbial Systematics and the Domains Bacteria and
... Microbial evolution is very difficult to understand without an ability to interpret phylogenetic trees. Many systematic studies rely on the principles of monophyly • A clade is a group of organims that includes a common ancestor Mutations are a major source of species variation • Account for t ...
... Microbial evolution is very difficult to understand without an ability to interpret phylogenetic trees. Many systematic studies rely on the principles of monophyly • A clade is a group of organims that includes a common ancestor Mutations are a major source of species variation • Account for t ...
GENERAL PATHOLOGY Human Genetics
... protein synthesis takes place. Ribosomal RNA forms 60% of the ribosome, with the remainder of the ribosome composed of the structural proteins and enzymes needed for protein synthesis. As with the other types of RNA, rRNA is synthesized in the nucleus. Unlike other RNAs, ribosomal RNA is produced in ...
... protein synthesis takes place. Ribosomal RNA forms 60% of the ribosome, with the remainder of the ribosome composed of the structural proteins and enzymes needed for protein synthesis. As with the other types of RNA, rRNA is synthesized in the nucleus. Unlike other RNAs, ribosomal RNA is produced in ...
DNA and RNA - Xavier High School
... (E. coli) • Operator bound – RNA polymerase can’t transcribe genetic information(not expressed) • Operator free – gene(s) expressed ...
... (E. coli) • Operator bound – RNA polymerase can’t transcribe genetic information(not expressed) • Operator free – gene(s) expressed ...
Marshall Nirenberg and the discovery of the Genetic Code
... • RNA is a cousin to DNA, it is also a nucleic acid, but it has a different sugar component • This gives it a different structure to DNA • Three kinds of RNA were then known – • Ribsomal or rRNA that made up the ribosomes in combination with some proteins • Soluble RNA or sRNA that was later identif ...
... • RNA is a cousin to DNA, it is also a nucleic acid, but it has a different sugar component • This gives it a different structure to DNA • Three kinds of RNA were then known – • Ribsomal or rRNA that made up the ribosomes in combination with some proteins • Soluble RNA or sRNA that was later identif ...
How Genes Work - Cochise College
... P site tRNA transfers amino acids to A site Ribosome shifts to open A site ...
... P site tRNA transfers amino acids to A site Ribosome shifts to open A site ...
how mutations affect gene function
... Most eukaryotic genes contain introns, which are removed by a process called splicing splice donor sequence ...
... Most eukaryotic genes contain introns, which are removed by a process called splicing splice donor sequence ...
Grading rubric DNA Project Unit
... Requirements: complete sentences, word processed, correct 2. Project DNA chart Requirements: shows 6 codons for DNA and RNA, 6 amino acids, 6 traits 3. DNA transcribed into RNA Requirements: all DNA translated correctly into RNA 6 traits should be visible 4. Colored picture of the person Requirement ...
... Requirements: complete sentences, word processed, correct 2. Project DNA chart Requirements: shows 6 codons for DNA and RNA, 6 amino acids, 6 traits 3. DNA transcribed into RNA Requirements: all DNA translated correctly into RNA 6 traits should be visible 4. Colored picture of the person Requirement ...
CHAPTER 17
... Concept check: Which of these levels is the most energy-efficient way to regulate gene expression? Answer: Transcriptional regulation is the most energy-efficient, because a cell avoids wasting energy making RNA or protein. FIGURE 17.3 Concept check: Explain how an alpha helix is able to function as ...
... Concept check: Which of these levels is the most energy-efficient way to regulate gene expression? Answer: Transcriptional regulation is the most energy-efficient, because a cell avoids wasting energy making RNA or protein. FIGURE 17.3 Concept check: Explain how an alpha helix is able to function as ...
Example-Abstract
... USA. b)Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center,USA c)Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, USA Eukaryotic RNases H2 comprise three different subunits. In this report we determine the composition a ...
... USA. b)Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center,USA c)Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, USA Eukaryotic RNases H2 comprise three different subunits. In this report we determine the composition a ...
Sem título-2
... High cost and a total time for analysis of the order of (at least) several hours. ...
... High cost and a total time for analysis of the order of (at least) several hours. ...
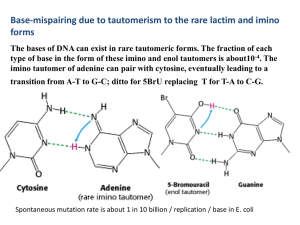
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... Why not polyamide backbone as illustrated in PNA (Peptide Nucleic Acid) TOO MUCH inter-chain binding (H-bonds and other forces as found in protein secondary structures; also no electrostatic repulsion as present in phosphate ...
... Why not polyamide backbone as illustrated in PNA (Peptide Nucleic Acid) TOO MUCH inter-chain binding (H-bonds and other forces as found in protein secondary structures; also no electrostatic repulsion as present in phosphate ...
`Genes` Like That, Who Needs an Environment?
... sequences that are targeted by transcription and splicing factors (proteins and noncoding RNAs) that bind to them and (2) the specific environmental signals that cue these factors or otherwise influence the gene’s expression. I understand ‘genetic information’ in its original meaning as it was spell ...
... sequences that are targeted by transcription and splicing factors (proteins and noncoding RNAs) that bind to them and (2) the specific environmental signals that cue these factors or otherwise influence the gene’s expression. I understand ‘genetic information’ in its original meaning as it was spell ...
Lesson 4 - Translation
... Students will practice the skills of transcribing and translating, including using a codon chart by playing codon bingo. Students will work individually. Each student will receive a codon chart and a blank bingo card and instructed to write the name of all 20 amino acids on the card. Then the teache ...
... Students will practice the skills of transcribing and translating, including using a codon chart by playing codon bingo. Students will work individually. Each student will receive a codon chart and a blank bingo card and instructed to write the name of all 20 amino acids on the card. Then the teache ...
Chapter 6 Microbial Genetics
... binds to the second code word on mRNA. A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. The first tRNA leaves, and the enzyme translocase moves the ribosome down one code word of mRNA at a time. This repeats ~ 300X. ...
... binds to the second code word on mRNA. A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. The first tRNA leaves, and the enzyme translocase moves the ribosome down one code word of mRNA at a time. This repeats ~ 300X. ...
CSE 181 Project guidelines
... molecule binds to vacant site • P-site: site where the new peptide bond is formed. • E-site: the exit site Two subunits join together on a mRNA molecule near the 5’ end. The ribosome will read the codons until AUG is reached and then the initiator tRNA binds to the P-site of the ribosome. Stop codon ...
... molecule binds to vacant site • P-site: site where the new peptide bond is formed. • E-site: the exit site Two subunits join together on a mRNA molecule near the 5’ end. The ribosome will read the codons until AUG is reached and then the initiator tRNA binds to the P-site of the ribosome. Stop codon ...
Long noncoding RNAs and human disease - e
... detail, lncRNAs participate in diverse biological processes through distinct mechanisms. Generally, lncRNAs have been implicated in gene-regulatory roles, such as chromosome dosage-compensation, imprinting, epigenetic regulation, cell cycle control, nuclear and cytoplasmic trafficking, transcription ...
... detail, lncRNAs participate in diverse biological processes through distinct mechanisms. Generally, lncRNAs have been implicated in gene-regulatory roles, such as chromosome dosage-compensation, imprinting, epigenetic regulation, cell cycle control, nuclear and cytoplasmic trafficking, transcription ...
BIOMI/PLAA 608 Bacterium
... and knowledge gained through genomics has revolutionized our understanding of pathogenesis. These activities have combined to spawn the new discipline of "pathogenomics". In essence, pathogenomics involves identifying and characterizing the subset of genes in a pathogen that confer virulence, the "v ...
... and knowledge gained through genomics has revolutionized our understanding of pathogenesis. These activities have combined to spawn the new discipline of "pathogenomics". In essence, pathogenomics involves identifying and characterizing the subset of genes in a pathogen that confer virulence, the "v ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.