Chapter 12
... showed that DNA is the genetic material Until the 1940s, the case for proteins serving as the genetic material was stronger than the case for DNA. – Proteins are made from ____different amino acids. – DNA was known to be made from just ____ kinds of ...
... showed that DNA is the genetic material Until the 1940s, the case for proteins serving as the genetic material was stronger than the case for DNA. – Proteins are made from ____different amino acids. – DNA was known to be made from just ____ kinds of ...
26 120 515 Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes
... Nancy Craig et al., Molecular Biology: Principles of Genome Function ...
... Nancy Craig et al., Molecular Biology: Principles of Genome Function ...
PCB 6528 Exam – Organelle genomes and gene expression
... and/or environmental cues that are known to regulate the target gene. Based upon this knowledge, suggest a hypothesis about the nature of the retrograde signal, and how this retrograde regulation pathway might be adaptive for plant survival and/or reproductive success. ...
... and/or environmental cues that are known to regulate the target gene. Based upon this knowledge, suggest a hypothesis about the nature of the retrograde signal, and how this retrograde regulation pathway might be adaptive for plant survival and/or reproductive success. ...
notes - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... to make a pigment can control the color of a flower. A gene that codes for an enzyme (protein) adds carbohydrates to glycoproteins to produce your blood type. Enzymes catalyze and regulate chemical reactions so proteins build and operate all cell components. ...
... to make a pigment can control the color of a flower. A gene that codes for an enzyme (protein) adds carbohydrates to glycoproteins to produce your blood type. Enzymes catalyze and regulate chemical reactions so proteins build and operate all cell components. ...
Biological Basis PDF worksheet - UNC
... The sequence of bases from one nucleotide to the next in line is the code for the assembly of specific amino acids to make specific types of proteins. Therefore, a gene is essentially a specific sequence of these base pairs. The sequence need not be continuous but can be divided into different secti ...
... The sequence of bases from one nucleotide to the next in line is the code for the assembly of specific amino acids to make specific types of proteins. Therefore, a gene is essentially a specific sequence of these base pairs. The sequence need not be continuous but can be divided into different secti ...
Ch. 16 – Control of Gene Expression Sample Questions
... E.DNA kinase must have access to the DNA double helix and also must be capable of binding to the gene's promoter. ...
... E.DNA kinase must have access to the DNA double helix and also must be capable of binding to the gene's promoter. ...
Chapter 18 Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis
... structural gene is made of exons and introns. • A regulatory gene that controls transcription; the regulatory gene is not transcribed but has control elements, one of which is the promoter. A promoter is unique to each gene. • There is always a sequence of bases on the DNA strand called an initiatio ...
... structural gene is made of exons and introns. • A regulatory gene that controls transcription; the regulatory gene is not transcribed but has control elements, one of which is the promoter. A promoter is unique to each gene. • There is always a sequence of bases on the DNA strand called an initiatio ...
ACCURACY OF TRANSFER RNA SELECTION IN PROTEIN
... The ribosome is a rapid magnificent molecular machine that plays an important role in protein synthesis and it consists of RNA and protein. The 70S bacterial ribosome comprises two subunits, 30S and 50S. The 30S small subunit of the bacterial ribosome contains a protein called S12, encoded by the rp ...
... The ribosome is a rapid magnificent molecular machine that plays an important role in protein synthesis and it consists of RNA and protein. The 70S bacterial ribosome comprises two subunits, 30S and 50S. The 30S small subunit of the bacterial ribosome contains a protein called S12, encoded by the rp ...
Micro Lab Unit 1 Flashcards
... It is essential to a protein’s physiological function. If it does not fold properly, it will not be in the proper shape to perform its function. Sequences of nucleic acids on our chromosomes that contain information on how to build the thousands of different proteins in our body. Mutations. ...
... It is essential to a protein’s physiological function. If it does not fold properly, it will not be in the proper shape to perform its function. Sequences of nucleic acids on our chromosomes that contain information on how to build the thousands of different proteins in our body. Mutations. ...
Origin of life on Earth Two approaches: • bottom-up
... RNA (ribonucleic acid) can fulfill both functions: Both meteoritic amino acids and those synthesized in Miller-Urey type experiments tend to be almost racemic mixtures: equal amounts of left-handed and right-handed versions Additionally, the set of 20 amino acids used in biology today is not particu ...
... RNA (ribonucleic acid) can fulfill both functions: Both meteoritic amino acids and those synthesized in Miller-Urey type experiments tend to be almost racemic mixtures: equal amounts of left-handed and right-handed versions Additionally, the set of 20 amino acids used in biology today is not particu ...
Figure 19.5 A eukaryotic gene and its transcript
... Figure 19.8 Alternative RNA splicing Chromatin changes ...
... Figure 19.8 Alternative RNA splicing Chromatin changes ...
Questions chapter 15
... c. Describe the structural and sequence elements that are common to all tRNA molecules, addressing the function of each of the elements. What forces stabilize the tRNAs' structural features? d. Outline the steps by which aminoacyl tRNA synthetases charge tRNAs. How can some organisms get away with h ...
... c. Describe the structural and sequence elements that are common to all tRNA molecules, addressing the function of each of the elements. What forces stabilize the tRNAs' structural features? d. Outline the steps by which aminoacyl tRNA synthetases charge tRNAs. How can some organisms get away with h ...
BP 32: Posters - DNA/RNA - DPG
... In interphase cell nuclei, DNA forms a microstructure of interspersed high concentration and low concentration regions. Transcription of DNA is carried out by RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) in low DNA density regions. While this organization reflects a need to unfold DNA for Pol II access, the causal or ...
... In interphase cell nuclei, DNA forms a microstructure of interspersed high concentration and low concentration regions. Transcription of DNA is carried out by RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) in low DNA density regions. While this organization reflects a need to unfold DNA for Pol II access, the causal or ...
Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4
... You have discovered a new virus that contains only RNA as its genetic material. Curious as to how this virus works, you infect cells with this virus and discover that after infection, some DNA that encodes viral proteins is produced At a later time point, lots of viral RNA molecules and various vira ...
... You have discovered a new virus that contains only RNA as its genetic material. Curious as to how this virus works, you infect cells with this virus and discover that after infection, some DNA that encodes viral proteins is produced At a later time point, lots of viral RNA molecules and various vira ...
Gene Switches - Science Take-Out
... involved in lactose metabolism. Bacteria normally rely on glucose in their environment as a food source. However, if glucose is not available and lactose (a disaccharide) is present in the environment, bacteria can survive by switching on the genes that allow them to use lactose as a food sourc ...
... involved in lactose metabolism. Bacteria normally rely on glucose in their environment as a food source. However, if glucose is not available and lactose (a disaccharide) is present in the environment, bacteria can survive by switching on the genes that allow them to use lactose as a food sourc ...
Spotted arrays
... By allowing scientists to compare diseased cells with normal cells, arrays can be used to discover sets of genes that play key roles in diseases. Genes that are either overexpressed or underexpressed in the diseased cells often present excellent targets for therapeutic drugs. Pharmacology and Toxico ...
... By allowing scientists to compare diseased cells with normal cells, arrays can be used to discover sets of genes that play key roles in diseases. Genes that are either overexpressed or underexpressed in the diseased cells often present excellent targets for therapeutic drugs. Pharmacology and Toxico ...
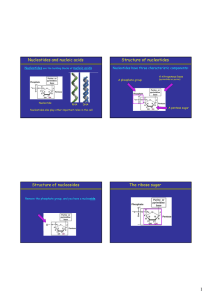
Nucleotides and nucleic acids Structure of nucleotides Structure of
... alternating phosphate and pentose residues. • The bases are analogous to side chains of amino acids; they vary without changing the covalent backbone structure. • Sequence is written from the 5' to 3' end: 5'-ATGCTAGC-3' • Note that the backbone is polyanionic. Phosphate groups pKa ~ 0. ...
... alternating phosphate and pentose residues. • The bases are analogous to side chains of amino acids; they vary without changing the covalent backbone structure. • Sequence is written from the 5' to 3' end: 5'-ATGCTAGC-3' • Note that the backbone is polyanionic. Phosphate groups pKa ~ 0. ...
Fig. 8.1. Amino acid structure
... Eukaryotic 1° transcript is processed to become mRNA RNA splicing (in other places) ...
... Eukaryotic 1° transcript is processed to become mRNA RNA splicing (in other places) ...
Nucleic Acids Notes
... (bases in nucleic acids) plays an important role in function. • Nucleic acid structure depends on the sequence of bases and on the type of ribose sugar (ribose, or 2'-deoxyribose). ...
... (bases in nucleic acids) plays an important role in function. • Nucleic acid structure depends on the sequence of bases and on the type of ribose sugar (ribose, or 2'-deoxyribose). ...
Isolating the Material of Heredity (Page 568
... further work on nucleic acids... 1. Isolated 2 types... - have different sugars as part of their structures One has a five carbon sugar molecule in it ( ribose ), Levene called it ribonucleic acid, or RNA. ( 1909) One has the same five carbon sugar, with one less oxygen atom attached to it ( deoxyri ...
... further work on nucleic acids... 1. Isolated 2 types... - have different sugars as part of their structures One has a five carbon sugar molecule in it ( ribose ), Levene called it ribonucleic acid, or RNA. ( 1909) One has the same five carbon sugar, with one less oxygen atom attached to it ( deoxyri ...
Chapter 2 Genes Encode RNAs and Polypeptides
... • allele – One of several alternative forms of a gene occupying a given locus on a chromosome. • locus – The position on a chromosome at which the gene for a particular trait resides; it may be occupied by any one of the alleles for the gene. • genetic recombination – A process by which separate DNA ...
... • allele – One of several alternative forms of a gene occupying a given locus on a chromosome. • locus – The position on a chromosome at which the gene for a particular trait resides; it may be occupied by any one of the alleles for the gene. • genetic recombination – A process by which separate DNA ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.