The Christian Crusades
... Holy Land. Even though Moslems had ruled Jerusalem since 638, Christians were still allowed to visit the city. By the 11th century, however, the situation had changed. Just as the number and frequency of pilgrimages to Jerusalem was at new peaks, the Seljuk Turks took over control of Jerusalem and p ...
... Holy Land. Even though Moslems had ruled Jerusalem since 638, Christians were still allowed to visit the city. By the 11th century, however, the situation had changed. Just as the number and frequency of pilgrimages to Jerusalem was at new peaks, the Seljuk Turks took over control of Jerusalem and p ...
Religious Crusades - Cherry Creek Academy
... – Muslims were caught off guard by the First Crusade – He Muslim world was too divided politically to organize a strong defense – Muslims described their own campaigns in religious terms, as a holy war ...
... – Muslims were caught off guard by the First Crusade – He Muslim world was too divided politically to organize a strong defense – Muslims described their own campaigns in religious terms, as a holy war ...
The Causes of the Crusades
... European knights and others were willing to travel and fight a war in a foreign land. Why were Europeans willing to fight the Crusades? For centuries, Christian pilgrims traveled from Europe to Jerusalem. In the 11th century, however, the Seljuk Turks, who were Muslim, began to interfere with these ...
... European knights and others were willing to travel and fight a war in a foreign land. Why were Europeans willing to fight the Crusades? For centuries, Christian pilgrims traveled from Europe to Jerusalem. In the 11th century, however, the Seljuk Turks, who were Muslim, began to interfere with these ...
The Crusades “Let`s Retake Jerusalem”
... revive trade between the east and west, which led to the growth of towns and cities. • Barter to Money Economy – The Crusaders were far from home making bartering ...
... revive trade between the east and west, which led to the growth of towns and cities. • Barter to Money Economy – The Crusaders were far from home making bartering ...
Word - Saint Mary`s Press
... all of the Crusades, but the slogan adopted for the First Crusade—“Deus volt!” or “God wills it!”—gives us insight into what was in the hearts of the Pope, the French king, and all the Crusaders. The First Crusade was a military success; the Crusaders captured Jerusalem and other lands. They set up ...
... all of the Crusades, but the slogan adopted for the First Crusade—“Deus volt!” or “God wills it!”—gives us insight into what was in the hearts of the Pope, the French king, and all the Crusaders. The First Crusade was a military success; the Crusaders captured Jerusalem and other lands. They set up ...
Belief and Violence: The Crusades
... all of the Crusades, but the slogan adopted for the First Crusade—“Deus volt!” or “God wills it!”—gives us insight into what was in the hearts of the Pope, the French king, and all the Crusaders. The First Crusade was a military success; the Crusaders captured Jerusalem and other lands. They set up ...
... all of the Crusades, but the slogan adopted for the First Crusade—“Deus volt!” or “God wills it!”—gives us insight into what was in the hearts of the Pope, the French king, and all the Crusaders. The First Crusade was a military success; the Crusaders captured Jerusalem and other lands. They set up ...
Crusades
... The Muslims were led by Salah al Din (Saladin) The Christians were led by Richard the Lion-Hearted (Richard I) After many battles, a peace was negotiated The Muslims would control Jerusalem, but Christians had free access to the Holy Land ...
... The Muslims were led by Salah al Din (Saladin) The Christians were led by Richard the Lion-Hearted (Richard I) After many battles, a peace was negotiated The Muslims would control Jerusalem, but Christians had free access to the Holy Land ...
The Peasant`s Crusade
... • Before the first planned Crusade took off, Peter the Hermit (a monk) organized large numbers of peasants and low-ranking knights set off for Jerusalem. • Along the way they had a number of problems such as food shortages and lack of discipline. • About one-quarter of these troops died before reach ...
... • Before the first planned Crusade took off, Peter the Hermit (a monk) organized large numbers of peasants and low-ranking knights set off for Jerusalem. • Along the way they had a number of problems such as food shortages and lack of discipline. • About one-quarter of these troops died before reach ...
The Crusades Guided Notes Prezi
... a. November 1095 _________________- speech asking for volunteer army to take _____________ and _______________ from the _______________. “Deus Vult!”= God’s will it i. ___________- welcomed the opportunity to use their _____________________ ii. Peasants- freed from _______________ bonds while on the ...
... a. November 1095 _________________- speech asking for volunteer army to take _____________ and _______________ from the _______________. “Deus Vult!”= God’s will it i. ___________- welcomed the opportunity to use their _____________________ ii. Peasants- freed from _______________ bonds while on the ...
The Crusades
... and were advised to wait for help. The people rebelled and attacked the Turks. They were defeated as only a small part of his army survived. ...
... and were advised to wait for help. The people rebelled and attacked the Turks. They were defeated as only a small part of his army survived. ...
Who were the Crusaders?
... • Pope is head of the Catholic Church • Had enormous influence over all of Western Europe (Christiandom) • Popes supported & advised kings (Charlemagne) ...
... • Pope is head of the Catholic Church • Had enormous influence over all of Western Europe (Christiandom) • Popes supported & advised kings (Charlemagne) ...
11.4 Christians and the Crusades
... The impact of the Crusades reached far beyond those who fought, however. The Crusades brought many economic changes to Europe. Crusaders needed a way to pay for supplies. Their need increased the use of money in Europe. Some knights began performing banking functions, such as making loans or investm ...
... The impact of the Crusades reached far beyond those who fought, however. The Crusades brought many economic changes to Europe. Crusaders needed a way to pay for supplies. Their need increased the use of money in Europe. Some knights began performing banking functions, such as making loans or investm ...
The Crusades - Issaquah Connect
... Younger sons did not stand to inherit any fortune or family land Merchants profited by financing the journey ...
... Younger sons did not stand to inherit any fortune or family land Merchants profited by financing the journey ...
1/13 Aim: Why did Western Europe fight the Crusades
... to fight the Muslims for control of the holy land, Jerusalem. Why were many willing to fight in the Crusades knowing that there was good chance that they might never return? On your handout, match the people with the reason that best suits them for fighting in the Crusades. ...
... to fight the Muslims for control of the holy land, Jerusalem. Why were many willing to fight in the Crusades knowing that there was good chance that they might never return? On your handout, match the people with the reason that best suits them for fighting in the Crusades. ...
Crusades Lesson 1 of 2 Lesson 6
... Tear out a blank sheet of paper from your spiral. Write 3 causes of the Crusades Write 2 facts about the course of the ...
... Tear out a blank sheet of paper from your spiral. Write 3 causes of the Crusades Write 2 facts about the course of the ...
Crusades
... • King Richard I of England • King Philip II Augustus of France • Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa of Germany ...
... • King Richard I of England • King Philip II Augustus of France • Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa of Germany ...
Slide 1
... • King Richard I of England • King Philip II Augustus of France • Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa of Germany ...
... • King Richard I of England • King Philip II Augustus of France • Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa of Germany ...
The Crusades – Holy War or Invasion
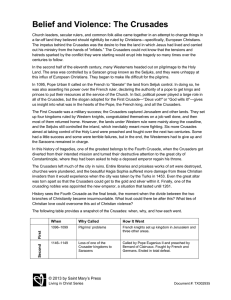
... In 1071, Muslims captured the holy city of Jerusalem. This made it difficult and dangerous for Christians to make a pilgrimage to the Holy Land. The leaders of the Roman Catholic Church were concerned and angry. In 1095, Pope Urban II took action. At a meeting with church leaders in Clermont, France ...
... In 1071, Muslims captured the holy city of Jerusalem. This made it difficult and dangerous for Christians to make a pilgrimage to the Holy Land. The leaders of the Roman Catholic Church were concerned and angry. In 1095, Pope Urban II took action. At a meeting with church leaders in Clermont, France ...
The Story of the Crusades (HA)
... movements of poor people, rather than organized military campaigns. In 1212, for example, thousands of peasant children from France and Germany marched in a Children’s Crusade. Few, if any, ever reached the Holy Land. Some made it to European port cities, only to be sold into slavery by merchants. S ...
... movements of poor people, rather than organized military campaigns. In 1212, for example, thousands of peasant children from France and Germany marched in a Children’s Crusade. Few, if any, ever reached the Holy Land. Some made it to European port cities, only to be sold into slavery by merchants. S ...
12th Grade, Ch. 9, Sec. 3, Notes
... Invaded the Byzantine Empire By 1071 controlled most Byzantine lands, Palestine and Holy Lands Attacked Christian pilgrims. ...
... Invaded the Byzantine Empire By 1071 controlled most Byzantine lands, Palestine and Holy Lands Attacked Christian pilgrims. ...
The Crusades! - Mrs. Abbott OPHS
... letter asking for help and called for a “holy war” or CRUSADE He said those who fought and died in the Crusades would be promised a spot in Heaven with all sins forgiven Remember the head of the Church is the Pope ...
... letter asking for help and called for a “holy war” or CRUSADE He said those who fought and died in the Crusades would be promised a spot in Heaven with all sins forgiven Remember the head of the Church is the Pope ...
THE CRUSADES
... thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected the waters to part and let them pass. When this did not hap ...
... thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected the waters to part and let them pass. When this did not hap ...
BalthazarMonastery.com Roman Catholic Crusades The First Crusade
... drawing upon earlier writers such as Ignatius of Melitene, Michael the Syrian had recorded that the Seljuqs subjected Coele-Syria and the Palestinian coast to "cruel destruction and pillage." Thomas Asbridge argues that the First Crusade was Pope Urban II's attempt to expand the power of the church ...
... drawing upon earlier writers such as Ignatius of Melitene, Michael the Syrian had recorded that the Seljuqs subjected Coele-Syria and the Palestinian coast to "cruel destruction and pillage." Thomas Asbridge argues that the First Crusade was Pope Urban II's attempt to expand the power of the church ...
First Crusade

The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a number of crusades that attempted to capture the Holy Lands, called by Pope Urban II in 1095. It started as a widespread pilgrimage in western christendom and ended as a military expedition by Roman Catholic Europe to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquests of the Levant (632–661), ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem in 1099. It was launched on 27 November 1095 by Pope Urban II with the primary goal of responding to an appeal from Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos, who requested that western volunteers come to his aid and help to repel the invading Seljuq Turks from Anatolia. An additional goal soon became the principal objective—the Christian reconquest of the sacred city of Jerusalem and the Holy Land and the freeing of the Eastern Christians from Muslim rule.During the crusade, knights, peasants and serfs from many nations of Western Europe travelled over land and by sea, first to Constantinople and then on towards Jerusalem. The Crusaders arrived at Jerusalem, launched an assault on the city, and captured it in July 1099, massacring many of the city's Muslim, Christian, and Jewish inhabitants. They also established the crusader states of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the County of Tripoli, the Principality of Antioch, and the County of Edessa.The First Crusade was followed by the Second to the Ninth Crusades. It was also the first major step towards reopening international trade in the West since the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Because the First Crusade was largely concerned with Jerusalem, a city which had not been under Christian dominion for 461 years, and the crusader army had refused to return the land to the control of the Byzantine Empire, the status of the First Crusade as defensive or as aggressive in nature remains controversial.