J. Ullrich et al. Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 (2003) 1463-1545
... decisively. Now, not only ‘kinematically complete’ measurements have become feasible but moreover, FDCSs can be projected out of huge data sets. In parallel, despite of general problems, substantial progress has been achieved in the theoretical treatment of fragmenting Coulomb systems, driven by con ...
... decisively. Now, not only ‘kinematically complete’ measurements have become feasible but moreover, FDCSs can be projected out of huge data sets. In parallel, despite of general problems, substantial progress has been achieved in the theoretical treatment of fragmenting Coulomb systems, driven by con ...
Quantum fluctuations in modulated nonlinear oscillators Vittorio Peano and M I Dykman
... electrodynamics. Vibrational systems of the new generation are mesoscopic. On the one hand, they can be individually accessed, similar to macroscopic systems, and are well-characterized. On the other hand, since they are small, they experience comparatively strong fluctuations of thermal and quantum ...
... electrodynamics. Vibrational systems of the new generation are mesoscopic. On the one hand, they can be individually accessed, similar to macroscopic systems, and are well-characterized. On the other hand, since they are small, they experience comparatively strong fluctuations of thermal and quantum ...
Computational Complexity: A Modern Approach
... “The only difference between a probabilistic classical world and the equations of the quantum world is that somehow or other it appears as if the probabilities would have to go negative..” Richard Feynman, in “Simulating physics with computers,” 1982 Quantum computing is a new computational model th ...
... “The only difference between a probabilistic classical world and the equations of the quantum world is that somehow or other it appears as if the probabilities would have to go negative..” Richard Feynman, in “Simulating physics with computers,” 1982 Quantum computing is a new computational model th ...
SELF-CONSISTENT SIMULATION OF RADIATION AND SPACE-CHARGE IN HIGH-BRIGHTNESS RELATIVISTIC ELECTRON BEAMS
... offset in both coordinates is due to the net energy loss of the beam. The normalized rms emittance, which is corrected for the offsets in centroids, is 18.5 mm-mrad (initial was 2 mm-mrad). . . . . . . . . . 113 5.13 Longitudinal phase-space at exit of SDL bunch compressor. The bunch charge is 0.3 n ...
... offset in both coordinates is due to the net energy loss of the beam. The normalized rms emittance, which is corrected for the offsets in centroids, is 18.5 mm-mrad (initial was 2 mm-mrad). . . . . . . . . . 113 5.13 Longitudinal phase-space at exit of SDL bunch compressor. The bunch charge is 0.3 n ...
Quantum computing Markus Kiili Opinnäytetyö
... resources can run out solving hard problems. In chapter four it is shown that some important problems that are hard on classical computers turn out to be easy on quantum computers. 2.2 Models of computation There are different mathematical models that describe computation. They differ by the basic o ...
... resources can run out solving hard problems. In chapter four it is shown that some important problems that are hard on classical computers turn out to be easy on quantum computers. 2.2 Models of computation There are different mathematical models that describe computation. They differ by the basic o ...
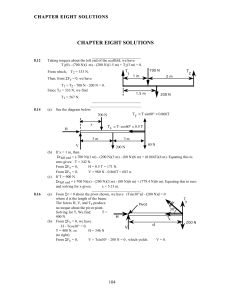
chapter eight solutions - Jay Mathy Science Wiki
... Now in six seconds, ω changes from 0 to 10 rad/s. Using ω = ω0 + α1t, we have 10 rad/s = 0 + α1(6 s), giving α1 = 1.67 rad/s2. Then, 36 N m= (1.67 rad/s2)I, or I = 21.6 kg m2. When the applied torque is removed, we have τfriction = Iα2. Using ω = ω0 + α2t we have 0 = 10 rad/s + α2(60 s), so α2 = -0. ...
... Now in six seconds, ω changes from 0 to 10 rad/s. Using ω = ω0 + α1t, we have 10 rad/s = 0 + α1(6 s), giving α1 = 1.67 rad/s2. Then, 36 N m= (1.67 rad/s2)I, or I = 21.6 kg m2. When the applied torque is removed, we have τfriction = Iα2. Using ω = ω0 + α2t we have 0 = 10 rad/s + α2(60 s), so α2 = -0. ...
RESEARCH ARTICLE Bottles as models
... negatively buoyant particle to leave the streamline and impact a filtering surface (Rubenstein and Koehl, 1977). Gravitational deposition is similar to inertial impaction except that particles are not separated from the fluid by a sharp acceleration of the streamline, but rather by a constant gravit ...
... negatively buoyant particle to leave the streamline and impact a filtering surface (Rubenstein and Koehl, 1977). Gravitational deposition is similar to inertial impaction except that particles are not separated from the fluid by a sharp acceleration of the streamline, but rather by a constant gravit ...
Use of Spatially Non-Uniform Electric Fields for Contact-Free Assembly of Three-Dimensional
... The use of spatially non-uniform electric fields for the contact-free assembly of structures from colloidal building blocks is explored in this thesis. Specifically, the use of dielectrophoretic forces (electric field-induced dipole force) and electrohydrodynamic forces (electric field force on a fl ...
... The use of spatially non-uniform electric fields for the contact-free assembly of structures from colloidal building blocks is explored in this thesis. Specifically, the use of dielectrophoretic forces (electric field-induced dipole force) and electrohydrodynamic forces (electric field force on a fl ...
Explanation - Physicsland
... The force on the cannonball will be the same for a short- or long-barreled cannon. The longer barrel provides for a longer time for the force to act, and therefore, a greater impulse. (The long barrel also provides a longer distance for the force to act, providing greater work and greater kinetic en ...
... The force on the cannonball will be the same for a short- or long-barreled cannon. The longer barrel provides for a longer time for the force to act, and therefore, a greater impulse. (The long barrel also provides a longer distance for the force to act, providing greater work and greater kinetic en ...
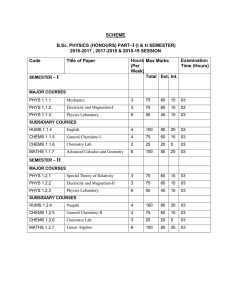
Sample Papers 1 - Entrance
... b) The behavior of solids, liquids and gases is different under the action of deforming forces. 4. When the deforming forces are withdrawn, the body may regain its original shape and dimension. This is because of the restoring forces (internal forces) acting within the body, which oppose changes in ...
... b) The behavior of solids, liquids and gases is different under the action of deforming forces. 4. When the deforming forces are withdrawn, the body may regain its original shape and dimension. This is because of the restoring forces (internal forces) acting within the body, which oppose changes in ...
Electron production in proton collisions with atoms and
... The collision of a fast charged particle with a neutral atom or molecule may result in the ejection of one or more secondary electrons, which, in the case of proton impact, must come from the target. These electrons are ejected over a range of energies and directions. The differential cross section ...
... The collision of a fast charged particle with a neutral atom or molecule may result in the ejection of one or more secondary electrons, which, in the case of proton impact, must come from the target. These electrons are ejected over a range of energies and directions. The differential cross section ...
Physics Mechanics
... R.A. Serway, J.S. Faughn, College Physics, Fifth Edition, Saunders College Publishing, ...
... R.A. Serway, J.S. Faughn, College Physics, Fifth Edition, Saunders College Publishing, ...