Interacting Fermionic Atoms in Optical Lattices
... Starting with the first realization of a quantum degenerate gas of fermionic atoms in 1999 [3], ultracold fermions became an important subfield, especially in the presence of strong interactions: Fermions cannot Bose condense due to the Pauli principle (cf. sec. 2.2) and superfluidity of fermionic part ...
... Starting with the first realization of a quantum degenerate gas of fermionic atoms in 1999 [3], ultracold fermions became an important subfield, especially in the presence of strong interactions: Fermions cannot Bose condense due to the Pauli principle (cf. sec. 2.2) and superfluidity of fermionic part ...
Topology of Bands in Solids: From Insulators to Dirac Matter
... of crystals was found to be inadequate and restrictive (in particular translations on the crystal do not commute due to the magnetic field and require the definition of a magnetic unit cell) and soon the initial topological characterization evolved to a more general form [4, 5]. In this context it l ...
... of crystals was found to be inadequate and restrictive (in particular translations on the crystal do not commute due to the magnetic field and require the definition of a magnetic unit cell) and soon the initial topological characterization evolved to a more general form [4, 5]. In this context it l ...
Title Goes Here
... nature of 1D system where the OS concentrates into the lowest bound state. At higher ne, we observed the metal-insulator crossover where the trion peak evolves to the typical single absorption onset of the band-toband transition. In this crossover region, we found a double absorption peak structure ...
... nature of 1D system where the OS concentrates into the lowest bound state. At higher ne, we observed the metal-insulator crossover where the trion peak evolves to the typical single absorption onset of the band-toband transition. In this crossover region, we found a double absorption peak structure ...
Chapter 2 - Motion in One Dimension
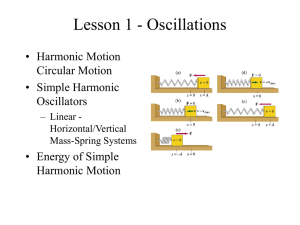
... • A mass of 200 grams is connected to a light spring that has a spring constant (k) of 5.0 N/m and is free to oscillate on a horizontal, frictionless surface. If the mass is displaced 5.0 cm from the rest position and released from rest find: • a) the period of its motion, • b) the maximum speed and ...
... • A mass of 200 grams is connected to a light spring that has a spring constant (k) of 5.0 N/m and is free to oscillate on a horizontal, frictionless surface. If the mass is displaced 5.0 cm from the rest position and released from rest find: • a) the period of its motion, • b) the maximum speed and ...
Here - 21st International Conference on General Relativity and
... On the conditions for the formation of exotic compact objects from gravitational collapse (Daniele Malafarina) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Universal Walker metrics (Tomas Malek ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . The Cartan Algorithm in Higher Dimensions with Applications (David McNutt) . ...
... On the conditions for the formation of exotic compact objects from gravitational collapse (Daniele Malafarina) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Universal Walker metrics (Tomas Malek ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . The Cartan Algorithm in Higher Dimensions with Applications (David McNutt) . ...
Emergent Gravity and the Dark Universe
... These ideas are best understood in Anti-de Sitter space, where they rely on the area law for entanglement entropy. The extension to de Sitter space requires taking into account the entropy and temperature associated with the cosmological horizon. Using insights from string theory, black hole physics ...
... These ideas are best understood in Anti-de Sitter space, where they rely on the area law for entanglement entropy. The extension to de Sitter space requires taking into account the entropy and temperature associated with the cosmological horizon. Using insights from string theory, black hole physics ...
No Slide Title
... function can be changed at all points in space and in time only at once and only with the same number. The Standard model does not give any physical meaning for the wave function. Dtheory explains geometrically with help of its space model what are the wave function and its complex phase and how doe ...
... function can be changed at all points in space and in time only at once and only with the same number. The Standard model does not give any physical meaning for the wave function. Dtheory explains geometrically with help of its space model what are the wave function and its complex phase and how doe ...
Quantum Proofs for Classical Theorems
... is to go to complex numbers: using the identity eix = cos x + i sin x we have ei(x+y) = eix eiy = (cos x + i sin x)(cos y + i sin y) = cos x cos y − sin x sin y + i(cos x sin y + sin x cos y) . Taking the real parts of the two sides gives our identity. Another example is the probabilistic method, as ...
... is to go to complex numbers: using the identity eix = cos x + i sin x we have ei(x+y) = eix eiy = (cos x + i sin x)(cos y + i sin y) = cos x cos y − sin x sin y + i(cos x sin y + sin x cos y) . Taking the real parts of the two sides gives our identity. Another example is the probabilistic method, as ...