
Entodermal derivatives: formation of the gut, liver, and pancreas
... Duodenum proximal to ampulla of Vater Liver Biliary Apparatus Pancreas ...
... Duodenum proximal to ampulla of Vater Liver Biliary Apparatus Pancreas ...
Duodenal Injuries - The American Association for the Surgery of
... •Not always very sensitive Extravasation of oral contrast from the duodenum with a retroperitoneal hematoma Extraluminal gas/fluid around the duodenum Focal bowel wall thickening Interruption of progress of the bowel contrast medium ...
... •Not always very sensitive Extravasation of oral contrast from the duodenum with a retroperitoneal hematoma Extraluminal gas/fluid around the duodenum Focal bowel wall thickening Interruption of progress of the bowel contrast medium ...
Accessory Organs of the Small Intestine
... Common Bile Duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla. The hepatopancreatic ampulla opens onto an elevation of the duodenal mucosa called the Duodenal Papilla. The ...
... Common Bile Duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla. The hepatopancreatic ampulla opens onto an elevation of the duodenal mucosa called the Duodenal Papilla. The ...
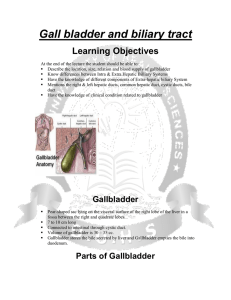
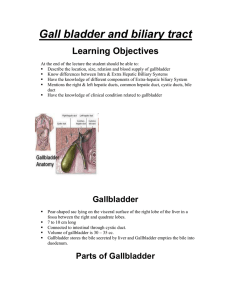
Relations of Gallbladder
... When the gallbladder relaxes, the stone may pass back into the gallbladder. If the stone blocks the cystic duct, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) occurs because of bile accumulation, causing enlargement of the gallbladder. Pain develops in the epigastric region and later shifts to the ...
... When the gallbladder relaxes, the stone may pass back into the gallbladder. If the stone blocks the cystic duct, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) occurs because of bile accumulation, causing enlargement of the gallbladder. Pain develops in the epigastric region and later shifts to the ...
Gall bladder and biliary tract
... When the gallbladder relaxes, the stone may pass back into the gallbladder. If the stone blocks the cystic duct, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) occurs because of bile accumulation, causing enlargement of the gallbladder. Pain develops in the epigastric region and later shifts to the ...
... When the gallbladder relaxes, the stone may pass back into the gallbladder. If the stone blocks the cystic duct, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) occurs because of bile accumulation, causing enlargement of the gallbladder. Pain develops in the epigastric region and later shifts to the ...
Practical Approach to Lower Extremity Edema
... liver disease (ascites, spider hemangiomas, and jaundice) may be helpful in detecting a systemic cause ...
... liver disease (ascites, spider hemangiomas, and jaundice) may be helpful in detecting a systemic cause ...
THE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION IN CARDIOLOGY
... Pulsatile liver: tricuspid regurgitation or other cause of elevated R sided pressures Hard liver may be more serious than large, soft liver ...
... Pulsatile liver: tricuspid regurgitation or other cause of elevated R sided pressures Hard liver may be more serious than large, soft liver ...
PAC01 Abdomen
... artery, a branch of the femoral artery, and from the inferior epigastric artery. Scrotal veins are of the same name as the arteries they parallel. Nerves are associated with the genitofemoral nerves from L1 & L2, ilioinguinal from L1, pudental nerve from S2,S3,&S4, and posterior femoral cutaneous n ...
... artery, a branch of the femoral artery, and from the inferior epigastric artery. Scrotal veins are of the same name as the arteries they parallel. Nerves are associated with the genitofemoral nerves from L1 & L2, ilioinguinal from L1, pudental nerve from S2,S3,&S4, and posterior femoral cutaneous n ...
Unit 24: Abdominal and Peritoneal Cavities
... Below the right costal margin and xiphoid process one can see the lower margin of the liver (Plates 260, 278; 2.1A, 2.19). In the region where the lateral rectus line crosses the right ninth costal margin is the fundus of the gall bladder, unless it has been surgically removed. Below the lower liver ...
... Below the right costal margin and xiphoid process one can see the lower margin of the liver (Plates 260, 278; 2.1A, 2.19). In the region where the lateral rectus line crosses the right ninth costal margin is the fundus of the gall bladder, unless it has been surgically removed. Below the lower liver ...
Lecture 19 - Vessels and Circulation
... the only which goes off to the right) 2. Superior mesenteric supplies most of intestines Definition of mesenteries: double layered sheets of peritoneum that support most organs in the abdominopelvic cavity ...
... the only which goes off to the right) 2. Superior mesenteric supplies most of intestines Definition of mesenteries: double layered sheets of peritoneum that support most organs in the abdominopelvic cavity ...
THE ABDOMEN -Located bt thorax and pelvis is surrounded by the
... -Occlusion of the Vasa Recta (branch of the SMA) to the SI results in ischemia to the affected part of the intestine - if obstruction is severe, necrosis can occur -Ileus - severe pain usually accompanied by vomiting, fever, dehydration - if early dx, then obstructed vessels can be cleared -Dx via a ...
... -Occlusion of the Vasa Recta (branch of the SMA) to the SI results in ischemia to the affected part of the intestine - if obstruction is severe, necrosis can occur -Ileus - severe pain usually accompanied by vomiting, fever, dehydration - if early dx, then obstructed vessels can be cleared -Dx via a ...
Recommendations - Canadian Cardiovascular Society
... This recommendation reflects the panel preferences that high risk revascularization is likely to best occur in higher volume centres with significant experience, known outcomes, and similar to participating in clinical trials involving high-risk coronary revascularization. Practical Tip: Assessment ...
... This recommendation reflects the panel preferences that high risk revascularization is likely to best occur in higher volume centres with significant experience, known outcomes, and similar to participating in clinical trials involving high-risk coronary revascularization. Practical Tip: Assessment ...
use of quadruped models in thoraco- abdominal
... impact experiments are modified to account for postural effects. Pope et al. (1979) investigated postural influences on thoracic impact utilizing the porcine model in a normal porcine posture (the spine oriented in a horizontal plane). They compared the results to a porcine experiment under similar ...
... impact experiments are modified to account for postural effects. Pope et al. (1979) investigated postural influences on thoracic impact utilizing the porcine model in a normal porcine posture (the spine oriented in a horizontal plane). They compared the results to a porcine experiment under similar ...
Isolated posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
... Hughston and Degenhardt9 advocated a dynamic secondary reconstruction using the medial tendon of the gastrocnemius. However, their results were mixed, with only 33% objective good results. Clancy et al.,2 in 1983, reported their PCL secondary reconstruction results of using the medial one third of t ...
... Hughston and Degenhardt9 advocated a dynamic secondary reconstruction using the medial tendon of the gastrocnemius. However, their results were mixed, with only 33% objective good results. Clancy et al.,2 in 1983, reported their PCL secondary reconstruction results of using the medial one third of t ...
Indications of Coronary Angiography
... (level of evidence: C). 2- Serial non-invasive testing with identical testing protocols, at the same level of medical therapy, showing progressively worsening abnormalities (level of evidence: C). 3- Patients with angina and suspected coronary disease who, due to disability, illness, or physical cha ...
... (level of evidence: C). 2- Serial non-invasive testing with identical testing protocols, at the same level of medical therapy, showing progressively worsening abnormalities (level of evidence: C). 3- Patients with angina and suspected coronary disease who, due to disability, illness, or physical cha ...
Full Text [Download PDF]
... Methods and Results: Four hundred patients with first AMI were catheterized for possible coronary intervention and measurement of LV filling pressure (LVFP). Although E/regional e¢ correlated linearly with LVFP, it was not a sufficient correlation to identify an elevated LVFP in AMI. For purposes of ...
... Methods and Results: Four hundred patients with first AMI were catheterized for possible coronary intervention and measurement of LV filling pressure (LVFP). Although E/regional e¢ correlated linearly with LVFP, it was not a sufficient correlation to identify an elevated LVFP in AMI. For purposes of ...
Evaluation of Abdominal Trauma
... Equivocal physical findings in patients who have sustained high-energy forces to the torso ...
... Equivocal physical findings in patients who have sustained high-energy forces to the torso ...
Digestive System
... It’s the longest porCon of the gland and runs from the neck to the tail. It’s slightly triangular in cross secCon, becoming thinner and less broad toward the tail. The Anterosuperior surface is per ...
... It’s the longest porCon of the gland and runs from the neck to the tail. It’s slightly triangular in cross secCon, becoming thinner and less broad toward the tail. The Anterosuperior surface is per ...
page1
... Radioiodine studies should be performed as the initial imaging procedure, although falsenegative results do occur. ...
... Radioiodine studies should be performed as the initial imaging procedure, although falsenegative results do occur. ...
Candidate - Palestine Medical Council
... E Molar pregnancy can be reliable exclude before 10 weeks. 8) Regarding gynaecological ultrasound A Normal post menopausal endometrial thikness is 10 mm or less. B Endometrial polyps are detected more readily when fluid is instilled into the uterinecavity. C Low velocity high impedance flow on Doppl ...
... E Molar pregnancy can be reliable exclude before 10 weeks. 8) Regarding gynaecological ultrasound A Normal post menopausal endometrial thikness is 10 mm or less. B Endometrial polyps are detected more readily when fluid is instilled into the uterinecavity. C Low velocity high impedance flow on Doppl ...
Chapter 2 / The Thoracic Cavity
... Direct Tests When you push the central part of the liver posterosuperiorly as described above, it should move by 1-2cm. Of all mobilizations, that of the liver is the most objective because no other solid organ directly interferes with or gets in the way of its movement. Depending on the location an ...
... Direct Tests When you push the central part of the liver posterosuperiorly as described above, it should move by 1-2cm. Of all mobilizations, that of the liver is the most objective because no other solid organ directly interferes with or gets in the way of its movement. Depending on the location an ...
奇美醫學中心胸腔內,外,放射科臨床病例綜合討論會
... upper part of the body to the vessels below the level of coarctation may be seen; these may be present as early as a few weeks to a few months of life. The most commonly associated clinically significant defects include patent ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, and aortic stenosis. The ea ...
... upper part of the body to the vessels below the level of coarctation may be seen; these may be present as early as a few weeks to a few months of life. The most commonly associated clinically significant defects include patent ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, and aortic stenosis. The ea ...
奇美醫學中心胸腔內,外,放射科臨床病例綜合討論會
... upper part of the body to the vessels below the level of coarctation may be seen; these may be present as early as a few weeks to a few months of life. The most commonly associated clinically significant defects include patent ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, and aortic stenosis. The ea ...
... upper part of the body to the vessels below the level of coarctation may be seen; these may be present as early as a few weeks to a few months of life. The most commonly associated clinically significant defects include patent ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, and aortic stenosis. The ea ...
奇美醫學中心胸腔內,外,放射科臨床病例綜合討論會
... Collateral vessels that connect arteries from the upper part of the body to the vessels below the level of coarctation may be seen; these may be present as early as a few weeks to a few months of life. The most commonly associated clinically significant defects include patent ductus arteriosus, vent ...
... Collateral vessels that connect arteries from the upper part of the body to the vessels below the level of coarctation may be seen; these may be present as early as a few weeks to a few months of life. The most commonly associated clinically significant defects include patent ductus arteriosus, vent ...
Acute liver failure

Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs of liver disease (such as jaundice), and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage (loss of function of 80–90% of liver cells). The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis (as measured by the levels of serum albumin and the prothrombin time in the blood). The 1993 classification defines hyperacute as within 1 week, acute as 8–28 days and subacute as 4–12 weeks. It reflects the fact that the pace of disease evolution strongly influences prognosis. Underlying etiology is the other significant determinant of outcome.











![Full Text [Download PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001685190_1-c6da98f3872ede87149ebf3f50d19137-300x300.png)








