A November, 2003 paper on the Pavlovian roots of the approach
... thought, cognition, and feelings to the realm of the unreal, leaving behavior or observable responses to stimuli in the realm of real explanations. Psychology, in Watson's view, could only become a science if, in its explanations, it 'emptied' the organism of all mental concepts. The most explicit ...
... thought, cognition, and feelings to the realm of the unreal, leaving behavior or observable responses to stimuli in the realm of real explanations. Psychology, in Watson's view, could only become a science if, in its explanations, it 'emptied' the organism of all mental concepts. The most explicit ...
Cognitive Neurosciences and Strategic Management: Challenges
... region, which is measured using high-field magnetic resonance scanners (Huettel, Song, & McCarthy, 2004). Thus, the BOLD signal represents an indirect and correlative measure of local neuronal activity. The typical fMRI response to a single trial or event, known as the hemodynamic response, begins a ...
... region, which is measured using high-field magnetic resonance scanners (Huettel, Song, & McCarthy, 2004). Thus, the BOLD signal represents an indirect and correlative measure of local neuronal activity. The typical fMRI response to a single trial or event, known as the hemodynamic response, begins a ...
Rodolphe Gouin - Hal-SHS
... But we still can attest the reality of non observable objects (like reasons, desires, intentions and beliefs) because we can feel them. We consciously experience their existence and their causal power. On the contrary biases, heuristics and cognitive dissonance reduction for instance can neither be ...
... But we still can attest the reality of non observable objects (like reasons, desires, intentions and beliefs) because we can feel them. We consciously experience their existence and their causal power. On the contrary biases, heuristics and cognitive dissonance reduction for instance can neither be ...
Proposal: Creation of an Honours Minor Program in Cognitive Science
... be completed in as few as two years. In the first year of the minor, students would typically complete PSYC 1010 and LING 1000. Then in the second year, they would typically complete COGS/PHIL 2160 and six credits from category B, while in the third year, they would complete PSYC 3260 and six credit ...
... be completed in as few as two years. In the first year of the minor, students would typically complete PSYC 1010 and LING 1000. Then in the second year, they would typically complete COGS/PHIL 2160 and six credits from category B, while in the third year, they would complete PSYC 3260 and six credit ...
Paper Title (use style: paper title)
... properties then same sentence is produced. Generation of novel sentences from images was not achieved from these annotations. Natural language generation (NLG) is a deep-seated problem and some classic approaches which are basically based on selection, planning and realization were introduced [11]. ...
... properties then same sentence is produced. Generation of novel sentences from images was not achieved from these annotations. Natural language generation (NLG) is a deep-seated problem and some classic approaches which are basically based on selection, planning and realization were introduced [11]. ...
A Revision and Experience using Cognitive Mapping and
... fourth and final part of the traditional travel demand analysis process: route choice. In contrast, the first three steps: trip generation, trip distribution, and in particular, mode choice, have been given far less attention by cognitive mapping researchers [6]. Existing opinion appears to specify ...
... fourth and final part of the traditional travel demand analysis process: route choice. In contrast, the first three steps: trip generation, trip distribution, and in particular, mode choice, have been given far less attention by cognitive mapping researchers [6]. Existing opinion appears to specify ...
Module10OperantandCognitiveApproaches
... – focused on how humans learn through observing things • Social cognitive learning – results from watching, and modeling and does not require the observer to perform any observable behavior or receive any observable reward ...
... – focused on how humans learn through observing things • Social cognitive learning – results from watching, and modeling and does not require the observer to perform any observable behavior or receive any observable reward ...
Hierarchical models
... Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a good model for studying the alteration of emotional disturbance because it involves the amygdala which plays an important role in emotions as demonstrated by functional neuroimaging studies (Cahill et al. 1996; Canli et al. 2000). In the present topic, we shall focus ou ...
... Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a good model for studying the alteration of emotional disturbance because it involves the amygdala which plays an important role in emotions as demonstrated by functional neuroimaging studies (Cahill et al. 1996; Canli et al. 2000). In the present topic, we shall focus ou ...
Dimensions of integration in embedded and extended cognitive
... this framework. These dimensions are all matters of degree and jointly they constitute a multidimensional space in which situated cognitive systems can be located and have certain dimensional configurations. The higher a particular system scores on these dimensions, the more deeply the functional in ...
... this framework. These dimensions are all matters of degree and jointly they constitute a multidimensional space in which situated cognitive systems can be located and have certain dimensional configurations. The higher a particular system scores on these dimensions, the more deeply the functional in ...
Re-Examining the Mental Imagery Debate with Neuropsychological
... There has been empirical findings in support of this theory (Shepard and Feng 1972 and Finke and Pinker 1982) as well as recent developments in neurobiology (fMRI primarily) which have lend support to the concept of topographically organized areas (Finke, Ward, and Smith 1992), primarily by findings ...
... There has been empirical findings in support of this theory (Shepard and Feng 1972 and Finke and Pinker 1982) as well as recent developments in neurobiology (fMRI primarily) which have lend support to the concept of topographically organized areas (Finke, Ward, and Smith 1992), primarily by findings ...
Executive function
... At an abstract level of processing, least tied to routine behaviour, are flexible representations of goals and intentions. Such ‘higher-level’ representations are often contrasted with ‘lower-level’ cognitive processes involved in analysing specific perceptual inputs (such as visual processing of st ...
... At an abstract level of processing, least tied to routine behaviour, are flexible representations of goals and intentions. Such ‘higher-level’ representations are often contrasted with ‘lower-level’ cognitive processes involved in analysing specific perceptual inputs (such as visual processing of st ...
Localization of Cognitive Operations
... patients with injury of the same three brain areas suggested by the monkey studies. When the efficiency of processing is measured precisely by a reaction time test, the nature ofthe deficits in the three areas differs. Patients with lesions in the parietal lobe show very long reaction times to targe ...
... patients with injury of the same three brain areas suggested by the monkey studies. When the efficiency of processing is measured precisely by a reaction time test, the nature ofthe deficits in the three areas differs. Patients with lesions in the parietal lobe show very long reaction times to targe ...
Is Political Cognition Like Riding a Bicycle?
... which considerations are accessible (Higgins & King, 1981) to consciousness at the moment that an attitude must be provided. Thinking takes effort; hence, individuals usually make judgments on the basis of the information that comes easily to mind, without conducting an exhaustive search of memory f ...
... which considerations are accessible (Higgins & King, 1981) to consciousness at the moment that an attitude must be provided. Thinking takes effort; hence, individuals usually make judgments on the basis of the information that comes easily to mind, without conducting an exhaustive search of memory f ...
Two Kinds of Reverse Inference in Cognitive Neuroscience
... makes essentially the same prediction but, in this case, the uniformity is due to partially overlapping motor processes being engaged in both conditions, as opposed to tokenings of the same concept.4 In short, TT and ST both predict an overlap in part of the neural pattern observed in both conditio ...
... makes essentially the same prediction but, in this case, the uniformity is due to partially overlapping motor processes being engaged in both conditions, as opposed to tokenings of the same concept.4 In short, TT and ST both predict an overlap in part of the neural pattern observed in both conditio ...
to get the file
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology, 2e by Ronald T. Kellogg ©SAGE Publications, Inc. ...
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology, 2e by Ronald T. Kellogg ©SAGE Publications, Inc. ...
Definitions of cognitive science
... brain), in the better case neuroscience would not be eliminated but considered to be only secondary. We know that both mentioned ways of treating neuroscience within cognitive science of mind are not in accordance with the current cognitive science. On the contrary, neuroscience plays these days in ...
... brain), in the better case neuroscience would not be eliminated but considered to be only secondary. We know that both mentioned ways of treating neuroscience within cognitive science of mind are not in accordance with the current cognitive science. On the contrary, neuroscience plays these days in ...
A Moderate Approach to Embodied Cognitive Science
... greater number of widely scattered brain areas than evolutionarily older functions, because the later a function comes on board, the more likely it is that there will already be useful neural circuits that can be incorporated in the service of the new function (2010: 246). In several publications An ...
... greater number of widely scattered brain areas than evolutionarily older functions, because the later a function comes on board, the more likely it is that there will already be useful neural circuits that can be incorporated in the service of the new function (2010: 246). In several publications An ...
Cognitive Mapping of Organic Vegetable Production in Flanders to
... construct the maps based on people’s knowledge. Therefore there is no need for scientific data (Özesmi and Özesmi, 2004). Application mapping method for the case-study For this study, 21 stakeholders (12 farmers, 4 experts, 2 advisers and 3 researchers) from the arable agriculture and horticulture o ...
... construct the maps based on people’s knowledge. Therefore there is no need for scientific data (Özesmi and Özesmi, 2004). Application mapping method for the case-study For this study, 21 stakeholders (12 farmers, 4 experts, 2 advisers and 3 researchers) from the arable agriculture and horticulture o ...
What can cognitive psychology and sensory evaluation learn from
... illustrated by our ‘‘inordinate proclivity’’ for chili pepper (or other capsaicin products), mustards, as well as carbonated beverages. Carsten and collaborators (in press) suggest several possible (nonexclusive) explanations for this paradoxical preference. They encompass a wide range, and go from ...
... illustrated by our ‘‘inordinate proclivity’’ for chili pepper (or other capsaicin products), mustards, as well as carbonated beverages. Carsten and collaborators (in press) suggest several possible (nonexclusive) explanations for this paradoxical preference. They encompass a wide range, and go from ...
LiebermanSSSP2002REV - Sydney Symposium of Social
... phenomenology rather than the qualitatively distinct representations that are utilized in the two kinds of processing. There is a tendency for us to believe that the same kind of underlying symbolic representations are used regardless of the automaticity of their use in terms of effort, intention, a ...
... phenomenology rather than the qualitatively distinct representations that are utilized in the two kinds of processing. There is a tendency for us to believe that the same kind of underlying symbolic representations are used regardless of the automaticity of their use in terms of effort, intention, a ...
Cognitive Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience/Motivation and
... recognise changes rather than stable states? An answer could be that changes are an important indicator of our situation. They show that our situation is unstable. Paying attention or focusing on that might increase the chance to survive. A change bears more information than repetitive events. This ...
... recognise changes rather than stable states? An answer could be that changes are an important indicator of our situation. They show that our situation is unstable. Paying attention or focusing on that might increase the chance to survive. A change bears more information than repetitive events. This ...
Psychology in Cognitive Science: 19782038
... disciplines not only provides useful tools but also suggests different accounts within our own field. For example, Linguistics has offered detailed theories of linguistic structure and phenomena that suggest psychological processes; and especially in recent times, empirical methods that originated i ...
... disciplines not only provides useful tools but also suggests different accounts within our own field. For example, Linguistics has offered detailed theories of linguistic structure and phenomena that suggest psychological processes; and especially in recent times, empirical methods that originated i ...
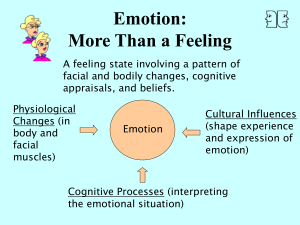
Emotion: More Than a Feeling
... An emotion-provoking stimulus activates a brain center called the “thalamus”, which simultaneously sends messages to the cortex, producing the feeling of an emotion, to the viscera, producing arousal, and to the skeletal muscles, producing behavior. Fear ...
... An emotion-provoking stimulus activates a brain center called the “thalamus”, which simultaneously sends messages to the cortex, producing the feeling of an emotion, to the viscera, producing arousal, and to the skeletal muscles, producing behavior. Fear ...
Failure to mobilize cognitive control for
... control network for volitional saccades. In a prior magnetoencephalography (MEG) study, we found that compared with healthy individuals, schizophrenia patients failed to increase preparatory activation in the dACC in response to cues that indicated an impending antisaccade (high control) versus pros ...
... control network for volitional saccades. In a prior magnetoencephalography (MEG) study, we found that compared with healthy individuals, schizophrenia patients failed to increase preparatory activation in the dACC in response to cues that indicated an impending antisaccade (high control) versus pros ...