Mood Disorders DSM V Handout
... B. During the period of mood disturbance and increased energy or activity, three (or more) of the following symptoms (four if the mood is only irritable) are present to a significant degree and represent a noticeable change from usual behavior: 1. Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity. 2. Decreased ne ...
... B. During the period of mood disturbance and increased energy or activity, three (or more) of the following symptoms (four if the mood is only irritable) are present to a significant degree and represent a noticeable change from usual behavior: 1. Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity. 2. Decreased ne ...
Vanessa Price Trauma Informed Responses in Specialty Courts
... what they are like as a person, and how they handle stress. Some personality disorders can be a challenge for law enforcement, such as people prone to interpersonal conflicts. ...
... what they are like as a person, and how they handle stress. Some personality disorders can be a challenge for law enforcement, such as people prone to interpersonal conflicts. ...
Antidepressants and neuroleptic
... risk of acute increases in ocular pressure. The other antidepressants all lack antagonist activity at the muscarinic receptor. ...
... risk of acute increases in ocular pressure. The other antidepressants all lack antagonist activity at the muscarinic receptor. ...
Downloadable PowerPoint Presentation
... 1 in 10 children and adolescents have a mental illness severe enough to cause impairment. Only 1 in 5 of these children receives any treatment. For nearly half of the children who do receive services, the school was the only provider. ...
... 1 in 10 children and adolescents have a mental illness severe enough to cause impairment. Only 1 in 5 of these children receives any treatment. For nearly half of the children who do receive services, the school was the only provider. ...
Lecture 2
... starves him/herself or uses other techniques such as vomiting, to induce weight loss. It is motivated by a false perception of being fat and/or phobia about becoming fat. It can be life threatening. ...
... starves him/herself or uses other techniques such as vomiting, to induce weight loss. It is motivated by a false perception of being fat and/or phobia about becoming fat. It can be life threatening. ...
Types of Depression Abraham Lincoln called it a terrible melancholy
... Bipolar Disorder (also called Manic Depression) - This is diagnosed when a person cycles between states of depression and mania, or when a person experiences only the mania. A manic episode lasts for at least one week and features an extremely elevated or irritable mood. At least three (or four if o ...
... Bipolar Disorder (also called Manic Depression) - This is diagnosed when a person cycles between states of depression and mania, or when a person experiences only the mania. A manic episode lasts for at least one week and features an extremely elevated or irritable mood. At least three (or four if o ...
Bipolar Disorder: Causes, Effects, and Possibilities
... damage a person’s finances, career, and reputation. This form of self-destructive mania may require containment and family support. Hypomanic episodes involve ...
... damage a person’s finances, career, and reputation. This form of self-destructive mania may require containment and family support. Hypomanic episodes involve ...
Depression and Anxiety - The Fraternal Twins of
... combination of symptoms that interfere with one’s ability to work, sleep, study, eat and enjoy once-pleasurable activities Dysthymic Disorder, or Dysthymia: long-term (two years or longer), but less severe symptoms that may not disable a person, but can prevent one from functioning normally or feeli ...
... combination of symptoms that interfere with one’s ability to work, sleep, study, eat and enjoy once-pleasurable activities Dysthymic Disorder, or Dysthymia: long-term (two years or longer), but less severe symptoms that may not disable a person, but can prevent one from functioning normally or feeli ...
Depression and Anxiety Disorders
... Mood and anxiety disorders are common, and the mortality risk is due primarily to suicide, cardiovascular disease, and substance abuse. Risk is highest early in the course of the disorder or within 2 years of a hospitalization. Mood disorders are divided into Depressive Disorders (unipolar) and Bipo ...
... Mood and anxiety disorders are common, and the mortality risk is due primarily to suicide, cardiovascular disease, and substance abuse. Risk is highest early in the course of the disorder or within 2 years of a hospitalization. Mood disorders are divided into Depressive Disorders (unipolar) and Bipo ...
321 mood no pic
... Depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all or almost all activities most of the day, nearly every day (anhedonia) Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain (more than 5% of body weight in a month) or decrease in appetite nearly ever ...
... Depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all or almost all activities most of the day, nearly every day (anhedonia) Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain (more than 5% of body weight in a month) or decrease in appetite nearly ever ...
Officials: Depression can affect anyone
... latest statistics show that 90 percent or more people who have committed suicide have had a mental disorder at the time of their death. "And most frequently, it's bipolar disorder or a major depressive disorder." Young children can also suffer from depression. The child may exhibit symptoms, such as ...
... latest statistics show that 90 percent or more people who have committed suicide have had a mental disorder at the time of their death. "And most frequently, it's bipolar disorder or a major depressive disorder." Young children can also suffer from depression. The child may exhibit symptoms, such as ...
Mood Disorders
... There is substantial likelihood that in the near future he or she will inflict serious bodily harm on himself or herself or another person, as evidenced by recent behavior ...
... There is substantial likelihood that in the near future he or she will inflict serious bodily harm on himself or herself or another person, as evidenced by recent behavior ...
Mood Disorders
... 4 interpersonal problem areas: interpersonal loss (explore grief and relationship with the lost person & explore feelings of anger-develop new ways of remembering the lost person), interpersonal role dispute (ways of resolving them), interpersonal role transition (develop social support and skills t ...
... 4 interpersonal problem areas: interpersonal loss (explore grief and relationship with the lost person & explore feelings of anger-develop new ways of remembering the lost person), interpersonal role dispute (ways of resolving them), interpersonal role transition (develop social support and skills t ...
Schizophrenia
... Neurochemical abnormalities central Models have been hypothesised using drug induced psychotic models Dopamine hypothesis: hyperdopaminergia is main protagonist Drugs that reduce firing of mesolimbic dopamine neurons have antipsychotic effect Drugs that stimulate dopamine increase psychosis ...
... Neurochemical abnormalities central Models have been hypothesised using drug induced psychotic models Dopamine hypothesis: hyperdopaminergia is main protagonist Drugs that reduce firing of mesolimbic dopamine neurons have antipsychotic effect Drugs that stimulate dopamine increase psychosis ...
130K PPT
... After your intervention, the pt agrees to remain on her Rxs and continues to do well for the next wk. Sometime later, you receive a call from her husband who reports that the pt has been up all night every night for about 3 or 4 nights in-a-row, making consecutive (and very uncharacteristic) $500-1, ...
... After your intervention, the pt agrees to remain on her Rxs and continues to do well for the next wk. Sometime later, you receive a call from her husband who reports that the pt has been up all night every night for about 3 or 4 nights in-a-row, making consecutive (and very uncharacteristic) $500-1, ...
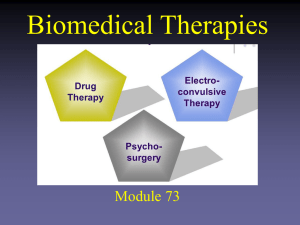
Module 73 - Biomedical Therapies
... • Used to treat bipolar disorder (manic-depression) • Used to interrupt acute manic attacks and prevent relapse – 7 in 10 people with Bipolar Disorder benefit from taking Lithium ...
... • Used to treat bipolar disorder (manic-depression) • Used to interrupt acute manic attacks and prevent relapse – 7 in 10 people with Bipolar Disorder benefit from taking Lithium ...
Bipolar Disorder - Psychiatry Lectures
... A. A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary). B. During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritabl ...
... A. A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary). B. During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritabl ...
Kids and Teens with Mood Disorders
... I cannot imagine leading a normal life without both taking lithium and having had the benefits of psychotherapy…ineffably, psychotherapy heals. It makes some sense of the confusion, reigns in the terrifying thoughts and feelings, returns some control and hope and possibility of learning from it all ...
... I cannot imagine leading a normal life without both taking lithium and having had the benefits of psychotherapy…ineffably, psychotherapy heals. It makes some sense of the confusion, reigns in the terrifying thoughts and feelings, returns some control and hope and possibility of learning from it all ...
Unit 6
... Bipolar disorder rates are the same for both genders. Married women are more often depressed than single women. The more children a woman has the more likely she is to become depressed. Learned helplessness: a condition is which a person has accepted the generalized idea that she can do nothing to h ...
... Bipolar disorder rates are the same for both genders. Married women are more often depressed than single women. The more children a woman has the more likely she is to become depressed. Learned helplessness: a condition is which a person has accepted the generalized idea that she can do nothing to h ...
Psychosis - Santa Barbara Therapist
... • Promodal- symptoms prior to acute episode • Residual- symptoms following the episode • During both patients seem flat and burnt out • Early on: active symptoms and hospitalizations. Later, less psychotic symptoms, but more apathy, low energy, social withdrawal, and low tolerence for stress ...
... • Promodal- symptoms prior to acute episode • Residual- symptoms following the episode • During both patients seem flat and burnt out • Early on: active symptoms and hospitalizations. Later, less psychotic symptoms, but more apathy, low energy, social withdrawal, and low tolerence for stress ...
as presented by Emiliano Valles, MD
... Diagnosing Mania Mania: 3 • Criteria A: One week of elevated, expansive, irritable mood AND increased energy ... • Plus 3 of the following from B Criteria: • Distractibility • Indiscretion or Irresponsibility • Grandiosity • Flight of ideas • Activity (increased goal-directed activity) • Sleep (de ...
... Diagnosing Mania Mania: 3 • Criteria A: One week of elevated, expansive, irritable mood AND increased energy ... • Plus 3 of the following from B Criteria: • Distractibility • Indiscretion or Irresponsibility • Grandiosity • Flight of ideas • Activity (increased goal-directed activity) • Sleep (de ...
Document
... Rapid-cycling bipolar disorder is characterized by four or more mood episodes that occur within a 12-month period. Some people experience multiple episodes within a single week, or even within a single day. Rapid cycling tends to develop later in the course of illness. Women are more likely than m ...
... Rapid-cycling bipolar disorder is characterized by four or more mood episodes that occur within a 12-month period. Some people experience multiple episodes within a single week, or even within a single day. Rapid cycling tends to develop later in the course of illness. Women are more likely than m ...