PSY100-disorders11
... Somatization Disorder A. History of many physical complaints beginning before age 30 that result in treatment being sought or significant impairment B. Each of the following criteria must have been met: 1. Four pain symptoms 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms 3. One sexual or reproductive symptom 4. ...
... Somatization Disorder A. History of many physical complaints beginning before age 30 that result in treatment being sought or significant impairment B. Each of the following criteria must have been met: 1. Four pain symptoms 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms 3. One sexual or reproductive symptom 4. ...
Mood Spectrum Disorders
... Some individuals noticed that their mood and/or energy levels shift drastically from time to time ______ . These individuals notice that, at times, their moody and/or energy level is very low , and at other times, and very high______. During their " low" phases, these individuals often feel a lack o ...
... Some individuals noticed that their mood and/or energy levels shift drastically from time to time ______ . These individuals notice that, at times, their moody and/or energy level is very low , and at other times, and very high______. During their " low" phases, these individuals often feel a lack o ...
Functional illness in elderly
... familial loading and have more secondary mania than bipolar disorder. ...
... familial loading and have more secondary mania than bipolar disorder. ...
Psychiatry Turkey Book
... Treatment of OCD Usually treated with medications: clomipramine, sertraline, paroxetine, fluoxetine, citalopram, escitalopram, fluvoxamine. Behavior therapy can also be used. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder ...
... Treatment of OCD Usually treated with medications: clomipramine, sertraline, paroxetine, fluoxetine, citalopram, escitalopram, fluvoxamine. Behavior therapy can also be used. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder ...
Somatoform Disorders and Mood Disorders - kyle
... 3. Irrational Depressing thoughts • People who are depressed are more likely to explain failures based on things that they feel helpless to change. If you have no hope, you get depressed. • “There’s nothing I can do” • “I’m no good” • “I’m not smart enough to pass this class” • “I can’t imagine eve ...
... 3. Irrational Depressing thoughts • People who are depressed are more likely to explain failures based on things that they feel helpless to change. If you have no hope, you get depressed. • “There’s nothing I can do” • “I’m no good” • “I’m not smart enough to pass this class” • “I can’t imagine eve ...
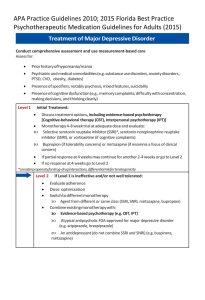
Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder with Psychosis
... Conduct comprehensive assessment and use measurement-based care Mixed features are subsyndromal hypomanic features defined according to the DSM-5. Assess for: ...
... Conduct comprehensive assessment and use measurement-based care Mixed features are subsyndromal hypomanic features defined according to the DSM-5. Assess for: ...
Depression - Psychiatric Times
... energy, decreased need for sleep, grandiosity, racing thoughts, hyper-talkativeness (pressured speech), hyperactivity, and increased sexual desires. Irritability, aggression, and impulsive activities may also accompany the manic episodes. When major depressive episodes alternate with manic episodes, ...
... energy, decreased need for sleep, grandiosity, racing thoughts, hyper-talkativeness (pressured speech), hyperactivity, and increased sexual desires. Irritability, aggression, and impulsive activities may also accompany the manic episodes. When major depressive episodes alternate with manic episodes, ...
1 - Psychology
... C) be given in higher doses to women than to men. D) need to be taken even after symptoms have been alleviated.* 34. If one could use only one treatment for schizophrenia and wanted the most effective treatment, one should choose: A) antipsychotic drugs.* B) psychodynamic therapy. C) milieu therapy. ...
... C) be given in higher doses to women than to men. D) need to be taken even after symptoms have been alleviated.* 34. If one could use only one treatment for schizophrenia and wanted the most effective treatment, one should choose: A) antipsychotic drugs.* B) psychodynamic therapy. C) milieu therapy. ...
Psychotic Disorder
... Psychotic disorder are mental health problems that cause a person to lose some touch with reality They can cause severe disturbance in behavior, thinking and emotions ...
... Psychotic disorder are mental health problems that cause a person to lose some touch with reality They can cause severe disturbance in behavior, thinking and emotions ...
TEWV FT Master PowerPoint
... lasting 4 days but with no functional impairment. Bipolar II disorder has prevalence of 0.5%. Reduce criteria for hypomania to 2 days and prevalence rises to 5.5%. Softening criteria further increases the rate of bipolar diagnoses to 50% of ‘unipolar’ cases of depression ...
... lasting 4 days but with no functional impairment. Bipolar II disorder has prevalence of 0.5%. Reduce criteria for hypomania to 2 days and prevalence rises to 5.5%. Softening criteria further increases the rate of bipolar diagnoses to 50% of ‘unipolar’ cases of depression ...
Mood Disorders and Schizophrenia
... – About 1.3% of people will suffer from schizophrenia at some point in their lives – More common in developed countries – Equal occurrence for men and women – Onset is usually in the 20’s Genetics – Concordance rate is 50% – However, genes are not the only influence – A gene has not been located for ...
... – About 1.3% of people will suffer from schizophrenia at some point in their lives – More common in developed countries – Equal occurrence for men and women – Onset is usually in the 20’s Genetics – Concordance rate is 50% – However, genes are not the only influence – A gene has not been located for ...
Bulletin Title: Diagnosis of Bipolar Disorder - Dartmouth
... Like other mental illnesses, bipolar disorder cannot yet be identified physiologically-for example, through a blood test or a brain scan. Therefore, a diagnosis of bipolar disorder is made on the basis of symptoms, course of illness, and, when available, family history. The diagnostic criteria for b ...
... Like other mental illnesses, bipolar disorder cannot yet be identified physiologically-for example, through a blood test or a brain scan. Therefore, a diagnosis of bipolar disorder is made on the basis of symptoms, course of illness, and, when available, family history. The diagnostic criteria for b ...
Mood Disorders - Davaar Consultancy
... depression. This diet is high in vegetables, fruits and nuts, cereals, legumes and fish, has a high monounsaturated to saturated fatty acids ratio and includes moderate amounts of alcohol. The Mediterranean diet is thought to reduce inflammatory and metabolic processes that may be involved in depres ...
... depression. This diet is high in vegetables, fruits and nuts, cereals, legumes and fish, has a high monounsaturated to saturated fatty acids ratio and includes moderate amounts of alcohol. The Mediterranean diet is thought to reduce inflammatory and metabolic processes that may be involved in depres ...
DSM5 Diagnostic Criteria Oppositional Defiant Disorder
... otherwise noted (Criterion A8). While these frequency criteria provide guidance on a minimal level of frequency to define symptoms, other factors should also be considered, such as whether the frequency and intensity of the behaviors are outside a range that is normative for the individual’s develop ...
... otherwise noted (Criterion A8). While these frequency criteria provide guidance on a minimal level of frequency to define symptoms, other factors should also be considered, such as whether the frequency and intensity of the behaviors are outside a range that is normative for the individual’s develop ...
Mood Disorders
... recurrent depressive episodes. Both biological and social factors play a part in these patterns. For example, women who experience severe premenstrual mood changes are more vulnerable to other mood disorders including postpartum depression. For bipolar disorder, men and woman are equally represented ...
... recurrent depressive episodes. Both biological and social factors play a part in these patterns. For example, women who experience severe premenstrual mood changes are more vulnerable to other mood disorders including postpartum depression. For bipolar disorder, men and woman are equally represented ...
Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders
... studies, and she’s on the verge of failing all her courses. This suggests that she may suffer from a (1) generalized anxiety disorder, which may lead to (2) physical problems, such as ulcers and high blood pressure. Because Carol cannot identify the cause of her tension, it would be described by Sig ...
... studies, and she’s on the verge of failing all her courses. This suggests that she may suffer from a (1) generalized anxiety disorder, which may lead to (2) physical problems, such as ulcers and high blood pressure. Because Carol cannot identify the cause of her tension, it would be described by Sig ...
Psychiatric History Taking
... can be put out of mind • Obsessional thoughts are ideas, images, impulses that repeatedly enter mind in stereotyped form, seen as senseless, distressing, recognised as own thought even if repugnant. • Compulsions are obsessional motor acts, often resulting from obsession, may be attempt to “neutrali ...
... can be put out of mind • Obsessional thoughts are ideas, images, impulses that repeatedly enter mind in stereotyped form, seen as senseless, distressing, recognised as own thought even if repugnant. • Compulsions are obsessional motor acts, often resulting from obsession, may be attempt to “neutrali ...
CH79 Page 1-6
... altered thyroid tests. Carbamazepine also has numerous drug interactions with other hepatically metabolized drugs. Most importantly, it is a CYP3A4 inducer and in fact initially induces its own metabolism potentially requiring a dosage adjustment after 1–2 weeks of treatment. • Other atypical antip ...
... altered thyroid tests. Carbamazepine also has numerous drug interactions with other hepatically metabolized drugs. Most importantly, it is a CYP3A4 inducer and in fact initially induces its own metabolism potentially requiring a dosage adjustment after 1–2 weeks of treatment. • Other atypical antip ...
PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS - Eleanor L. Ronquillo MD October 13
... Not associated with a mood disorder, a substance-related disorder, or a psychotic disorder caused by a general medical condition Schizophreniform Disorder 1-6 months Return to their baseline level of functioning Cause - not known; stressor? Lacks a long prodromal phase Functional impairm ...
... Not associated with a mood disorder, a substance-related disorder, or a psychotic disorder caused by a general medical condition Schizophreniform Disorder 1-6 months Return to their baseline level of functioning Cause - not known; stressor? Lacks a long prodromal phase Functional impairm ...
Psychological processes in bipolar affective disorder
... candidate endophenotypes or by providing targets for neuroimaging studies. Some studies have identified depression-related psychological abnormalities in people with bipolar disorder, for example low1 or unstable self-esteem,2 rumination,3 dysfunctional attitudes to self-evaluation4 and a pessimisti ...
... candidate endophenotypes or by providing targets for neuroimaging studies. Some studies have identified depression-related psychological abnormalities in people with bipolar disorder, for example low1 or unstable self-esteem,2 rumination,3 dysfunctional attitudes to self-evaluation4 and a pessimisti ...
Depression and Newer Antidepressants
... • Depression increases the risks for developing HIV, coronary artery disease, and asthma. • Depression is frequently under-diagnosed. • Depression is often under-treated. ...
... • Depression increases the risks for developing HIV, coronary artery disease, and asthma. • Depression is frequently under-diagnosed. • Depression is often under-treated. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... • Avoiding social situations where food is there • Distorted body image • Preoccupied with exercise ...
... • Avoiding social situations where food is there • Distorted body image • Preoccupied with exercise ...
Bipolar Mood Disorder Article
... world” and not realise that your feelings are behaviour is not normal. Your thoughts are racing and you speak very quickly, often jumping from one topic to the next, making it difficult for others to understand you. You are full of enthusiasm for everything, have an inflated self-esteem and may take ...
... world” and not realise that your feelings are behaviour is not normal. Your thoughts are racing and you speak very quickly, often jumping from one topic to the next, making it difficult for others to understand you. You are full of enthusiasm for everything, have an inflated self-esteem and may take ...