Preview the test
... d) All of the above e) B and C 82) DSM-5 defines a Substance Use Disorder as a maladaptive pattern leading to clinically significant impairment or distress for at least: a) 3 months b) 6 months c) 9 months d) 12 months 83) Which symptom has been added to the new Substance Use Disorder diagnosis (whi ...
... d) All of the above e) B and C 82) DSM-5 defines a Substance Use Disorder as a maladaptive pattern leading to clinically significant impairment or distress for at least: a) 3 months b) 6 months c) 9 months d) 12 months 83) Which symptom has been added to the new Substance Use Disorder diagnosis (whi ...
No Slide Title
... A. depressed patients with atypical features have shortened REM period latency. B. those who look least like patients with melancholia are those who experienced an early onset of their depressive illness and subsequently did not experience well-being. C. those who look least like patients with melan ...
... A. depressed patients with atypical features have shortened REM period latency. B. those who look least like patients with melancholia are those who experienced an early onset of their depressive illness and subsequently did not experience well-being. C. those who look least like patients with melan ...
The influence of emotional factors on the report of somatic symptoms
... concept of neuroticism), which can be defined as a general dimension of emotional distress and a predisposition to experience negative emotions (disgust, anxiety, sadness, hostility-anger, guilt, fear, depression, dissatisfaction with oneself, being more self-critical and having a negative bias in t ...
... concept of neuroticism), which can be defined as a general dimension of emotional distress and a predisposition to experience negative emotions (disgust, anxiety, sadness, hostility-anger, guilt, fear, depression, dissatisfaction with oneself, being more self-critical and having a negative bias in t ...
Binge eating disorder
... important to maintain a distinction between this symptom and the disorder itself. ...
... important to maintain a distinction between this symptom and the disorder itself. ...
Association Between Symptom Dimensions and Categorical
... the dimensional approach remain unresolved. First, there is no consensus regarding the structure of the dimensional model of psychosis; it is unclear whether symptom dimensions are related to one other and whether they assume a hierarchical form. To date, 1 study has shown that psychopathology in ch ...
... the dimensional approach remain unresolved. First, there is no consensus regarding the structure of the dimensional model of psychosis; it is unclear whether symptom dimensions are related to one other and whether they assume a hierarchical form. To date, 1 study has shown that psychopathology in ch ...
Information on body dysmorphic disorder
... dermatologist) for reassurance about how they look. Studies from psychiatric settings have found that nearly all patients experience social interference as a result of their concern, thinking they are too ugly and feeling too embarrassed and self conscious to be around other people.12–17 Academic an ...
... dermatologist) for reassurance about how they look. Studies from psychiatric settings have found that nearly all patients experience social interference as a result of their concern, thinking they are too ugly and feeling too embarrassed and self conscious to be around other people.12–17 Academic an ...
persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)
... psychiatric problem are less likely to have remissions or respond to treatment. Other factors that influence the course of major depressive disorder are the severity of symptoms; the duration of symptoms; young age; multiple episodes of depression, and; the length of time after symptom onset that t ...
... psychiatric problem are less likely to have remissions or respond to treatment. Other factors that influence the course of major depressive disorder are the severity of symptoms; the duration of symptoms; young age; multiple episodes of depression, and; the length of time after symptom onset that t ...
Depressive disorders include disruptive mood
... psychiatric problem are less likely to have remissions or respond to treatment. Other factors that influence the course of major depressive disorder are the severity of symptoms; the duration of symptoms; young age; multiple episodes of depression, and; the length of time after symptom onset that t ...
... psychiatric problem are less likely to have remissions or respond to treatment. Other factors that influence the course of major depressive disorder are the severity of symptoms; the duration of symptoms; young age; multiple episodes of depression, and; the length of time after symptom onset that t ...
A hoarding syndrome, Syllogomania, disposophobia
... actual cruelty, neglect, brutality by the parents of many years’ duration are factors found in these patients. These factors operate more or less constantly over many years from earliest childhood” (Bradly, Conklin, Westen in O’Donohue, Fowler and Lilienfeld, 2007:176-177). He obviously did not get ...
... actual cruelty, neglect, brutality by the parents of many years’ duration are factors found in these patients. These factors operate more or less constantly over many years from earliest childhood” (Bradly, Conklin, Westen in O’Donohue, Fowler and Lilienfeld, 2007:176-177). He obviously did not get ...
A BPD Brief - National Education Alliance for Borderline Personality
... About 70% of people with BPD report a history of physical and/or sexual abuse. Childhood traumas may contribute to symptoms such as alienation, the desperate search for protective relationships, and the eruption of intense feeling that characterize BPD. Still, since relatively few people who are phy ...
... About 70% of people with BPD report a history of physical and/or sexual abuse. Childhood traumas may contribute to symptoms such as alienation, the desperate search for protective relationships, and the eruption of intense feeling that characterize BPD. Still, since relatively few people who are phy ...
Antecedents of Personality Disorders in Young
... perceiving oneself and relating to the environment that result in psychosocial impairment or subjective distress. The enduring nature of the behaviors, their impact on social functioning, the lack of clear boundaries between normality and illness, and the patient's perception of the symptoms as not ...
... perceiving oneself and relating to the environment that result in psychosocial impairment or subjective distress. The enduring nature of the behaviors, their impact on social functioning, the lack of clear boundaries between normality and illness, and the patient's perception of the symptoms as not ...
From DSM-IV-TR to DSM-5
... dimensions for reporters (or the patient himself), and about symptom severity (Likert-type scale from 0-4) (APA, 2013a) (other scales may be found in the official APA website). A separate mention should be made of the scale directed at the patient or informant, since of the two questions about psycho ...
... dimensions for reporters (or the patient himself), and about symptom severity (Likert-type scale from 0-4) (APA, 2013a) (other scales may be found in the official APA website). A separate mention should be made of the scale directed at the patient or informant, since of the two questions about psycho ...
Practice Parameter for the Prevention and Management of
... tics causing severe impairment in quality of life or when medication responsive psychiatric comorbidities are present that target both tic symptoms and comorbid conditions. ...
... tics causing severe impairment in quality of life or when medication responsive psychiatric comorbidities are present that target both tic symptoms and comorbid conditions. ...
The Physician`s Role in Managing Acute Stress Disorder
... Features include anxiety, intense fear or helplessness, dissociative symptoms, reexperiencing the event, and avoidance behaviors. Persons with this disorder are at increased risk of developing posttraumatic stress disorder. Other risk factors for posttraumatic stress disorder include current or fami ...
... Features include anxiety, intense fear or helplessness, dissociative symptoms, reexperiencing the event, and avoidance behaviors. Persons with this disorder are at increased risk of developing posttraumatic stress disorder. Other risk factors for posttraumatic stress disorder include current or fami ...
Copyright 2006, the FSU CPEIP and Robert J
... Indicate any coexisting physical (including medical and neurological) and/or developmental diagnoses made using other diagnostic and classification systems ...
... Indicate any coexisting physical (including medical and neurological) and/or developmental diagnoses made using other diagnostic and classification systems ...
- Journal of Affective Disorders
... Psychiatric Association, 1968) described a few syndrome-like chronic depressive conditions such as depressive reaction disorder, depressive neurosis, or cyclothymic personality. The formal Dysthymic Disorder diagnosis was introduced with DSM-III (American Psychiatric Association, 1980), though not w ...
... Psychiatric Association, 1968) described a few syndrome-like chronic depressive conditions such as depressive reaction disorder, depressive neurosis, or cyclothymic personality. The formal Dysthymic Disorder diagnosis was introduced with DSM-III (American Psychiatric Association, 1980), though not w ...
PowerPoint 12
... Childhood schizophrenia can be mistaken for brief psychotic episode in context of mood or disruptive behavior disorder Delusions need to be distinguished from imaginary friends, magical thinking, or hypnagogic experiences Disorganized speech is common in many healthy children younger than age ...
... Childhood schizophrenia can be mistaken for brief psychotic episode in context of mood or disruptive behavior disorder Delusions need to be distinguished from imaginary friends, magical thinking, or hypnagogic experiences Disorganized speech is common in many healthy children younger than age ...
11 symptoms
... Recurrent substance use resulting in a failure to fulfill major role obligations at work, school, or home. ...
... Recurrent substance use resulting in a failure to fulfill major role obligations at work, school, or home. ...
University of Pittsburgh School of Social Work MH 2065 Fall term 2005
... reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning. Mental disorders are usually associated with significant distress or disability in social, occupational, or other important activities. An expectable or culturally approved response to ...
... reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning. Mental disorders are usually associated with significant distress or disability in social, occupational, or other important activities. An expectable or culturally approved response to ...
Towards Developing an Annotation Scheme for Depressive
... sleeping too much, NOS E.g. “I could sleep my life away; I’m a depressed sleeping beauty” • Psychomotor agitation or retardation: feeling slowed down, feeling restless or fidgety, NOS E.g. “I just feel like I’m talking and moving in slow motion” • Fatigue or loss of energy: feeling tired, insufficie ...
... sleeping too much, NOS E.g. “I could sleep my life away; I’m a depressed sleeping beauty” • Psychomotor agitation or retardation: feeling slowed down, feeling restless or fidgety, NOS E.g. “I just feel like I’m talking and moving in slow motion” • Fatigue or loss of energy: feeling tired, insufficie ...
The Depressed Patient And Suicidal Patient In The Emergency
... There are approximately 12 million emergency department (ED) visits related to mental health/substance abuse annually. Approximately 650,000 patients are evaluated annually for suicide attempts. Evidence to guide the management and treatment of depression and suicidal ideation in the ED is limited. ...
... There are approximately 12 million emergency department (ED) visits related to mental health/substance abuse annually. Approximately 650,000 patients are evaluated annually for suicide attempts. Evidence to guide the management and treatment of depression and suicidal ideation in the ED is limited. ...
Personality Disorders
... been shown to be effective in symptom control in double-blind studies, though they may not help deeper problems with personal relations. The benefits of these drugs must be balanced against the risk of tardive dyskinesia. Antidepressants are commonly used, usually for treatment of concomitant mood a ...
... been shown to be effective in symptom control in double-blind studies, though they may not help deeper problems with personal relations. The benefits of these drugs must be balanced against the risk of tardive dyskinesia. Antidepressants are commonly used, usually for treatment of concomitant mood a ...
Comorbidity With ADHD Decreases Response to Pharmacotherapy
... To be significant for the metaanalysis, trials had to report treatment response in samples of children and adolescents with BD where comorbidity with ADHD was systematically addressed. Clinical-outcome data had to be available on treatment response according to ADHD comorbidity. When detailed outcom ...
... To be significant for the metaanalysis, trials had to report treatment response in samples of children and adolescents with BD where comorbidity with ADHD was systematically addressed. Clinical-outcome data had to be available on treatment response according to ADHD comorbidity. When detailed outcom ...
69/2009 - Repatriation Medical Authority
... The panic attacks are not better accounted for by another mental disorder, such as social phobia (e.g., occurring on exposure to feared social situations), specific phobia (e.g., on exposure to a specific phobic situation), obsessivecompulsive disorder (e.g., on exposure to dirt in someone with an o ...
... The panic attacks are not better accounted for by another mental disorder, such as social phobia (e.g., occurring on exposure to feared social situations), specific phobia (e.g., on exposure to a specific phobic situation), obsessivecompulsive disorder (e.g., on exposure to dirt in someone with an o ...
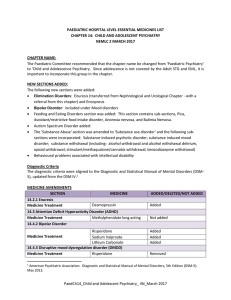
PaedCh 14_Psychiatry RN_4C_ March 2017
... Lithium: Added An antipsychotic agent is usually the first line therapy for patients presenting with psychosis or behavioural disturbances, and will have a more rapid response rate than mood stabilisers such as lithium. Treatment can then be augmented with a mood stabiliser in partial responders. 2 ...
... Lithium: Added An antipsychotic agent is usually the first line therapy for patients presenting with psychosis or behavioural disturbances, and will have a more rapid response rate than mood stabilisers such as lithium. Treatment can then be augmented with a mood stabiliser in partial responders. 2 ...