manic depression - Geisel School of Medicine
... With manic depression, periods of normal mood usually occur between the periods of extreme highs and lows.The lengths of episodes vary from person to person and can change over time. If you or someone you know has experienced cycles of the following behaviors, professional help should be considered: ...
... With manic depression, periods of normal mood usually occur between the periods of extreme highs and lows.The lengths of episodes vary from person to person and can change over time. If you or someone you know has experienced cycles of the following behaviors, professional help should be considered: ...
Organic Mental Disorders as Hypothetical Pathogenetic Processes
... terms of its usual symptoms. This property also belongs to a concept such as myocardial infarction, which alongside its symptomatic criteria has a strict definition in terms of pathology; cf (8) p 36. In contrast, von Economo’s disease does not have, and never had, any such strict definition; all th ...
... terms of its usual symptoms. This property also belongs to a concept such as myocardial infarction, which alongside its symptomatic criteria has a strict definition in terms of pathology; cf (8) p 36. In contrast, von Economo’s disease does not have, and never had, any such strict definition; all th ...
IBP Distance Learning - Institute for Brain Potential
... of this provider are accepted by the AGD for Fellowship/Mastership and membership maintenance credit. Approval does not imply acceptance by a state or provincial board of dentistry or AGD endorsement. The current term of approval extends from 12/01/14 – 11/30/18. Provider ID# 312413. This program pr ...
... of this provider are accepted by the AGD for Fellowship/Mastership and membership maintenance credit. Approval does not imply acceptance by a state or provincial board of dentistry or AGD endorsement. The current term of approval extends from 12/01/14 – 11/30/18. Provider ID# 312413. This program pr ...
Panic Disorder
... also has depressive disorder. An associated depression increases risk of suicide. ...
... also has depressive disorder. An associated depression increases risk of suicide. ...
Signs and Symptoms of Mental Illness
... substance/medication related disorder is accompanied by a non-substancerelated diagnosis such as major depression since both may have contributed equally to the need for admission or treatment. Principal diagnosis is listed first and the term "Principal diagnosis" follows the diagnosis name Rema ...
... substance/medication related disorder is accompanied by a non-substancerelated diagnosis such as major depression since both may have contributed equally to the need for admission or treatment. Principal diagnosis is listed first and the term "Principal diagnosis" follows the diagnosis name Rema ...
Other Personality Disorders
... substance/medication related disorder is accompanied by a non-substancerelated diagnosis such as major depression since both may have contributed equally to the need for admission or treatment. Principal diagnosis is listed first and the term "Principal diagnosis" follows the diagnosis name Rema ...
... substance/medication related disorder is accompanied by a non-substancerelated diagnosis such as major depression since both may have contributed equally to the need for admission or treatment. Principal diagnosis is listed first and the term "Principal diagnosis" follows the diagnosis name Rema ...
Chapter 15: Psychological Disorders
... infections and toxins as well as psychosocial traumas—might be the key to unlocking the secrets of psychiatric genetics. Although the short gene variant appears to predict who will become depressed following life stress about as well as a test for bone mineral density predicts who will get a fractu ...
... infections and toxins as well as psychosocial traumas—might be the key to unlocking the secrets of psychiatric genetics. Although the short gene variant appears to predict who will become depressed following life stress about as well as a test for bone mineral density predicts who will get a fractu ...
Approach to Suicide Risk and Assessment in the ER Resident
... impulse control disorders 40% alcohol dependence likely higher levels of aggression greater levels of panic disorder, phobic disorders and GAD ...
... impulse control disorders 40% alcohol dependence likely higher levels of aggression greater levels of panic disorder, phobic disorders and GAD ...
DSM-5: Implications for Social Work Practice Latino Social Work Organization October 16, 2014
... Social (Pragmatic) Communication Disorder • There are no repetitive patterns or restricted interests (i.e. criteria for ASD would not be met). • Language impairment is a common associated feature as is ADHD, behavior problems and specific learning disorders. Family history of ASD, LD or communicatio ...
... Social (Pragmatic) Communication Disorder • There are no repetitive patterns or restricted interests (i.e. criteria for ASD would not be met). • Language impairment is a common associated feature as is ADHD, behavior problems and specific learning disorders. Family history of ASD, LD or communicatio ...
Anxiety Disorders
... worries, concerns regarding danger (doesn’t include psychotic symptoms, and if suicidal ideation present, look for comorbid depression) ...
... worries, concerns regarding danger (doesn’t include psychotic symptoms, and if suicidal ideation present, look for comorbid depression) ...
Mental Illness in the Legal Profession
... different from the normal ups and downs that everyone goes through from time to time. Bipolar disorder symptoms can result in damaged relationships, poor job or school performance, and even suicide. But bipolar disorder can be treated, and people with this illness can lead full and productive lives. ...
... different from the normal ups and downs that everyone goes through from time to time. Bipolar disorder symptoms can result in damaged relationships, poor job or school performance, and even suicide. But bipolar disorder can be treated, and people with this illness can lead full and productive lives. ...
PSYCHIATRY MADE RIDICULOUSLY SIMPLE by William V. Good
... biopsychosocial perspective to adequately evaluate the patient. The patient's personal and family history of illnesses as well as life traumas are particularly relevant. The initial diagnostic impression will lead to a treatment plan addressing the need for psychotropic medication (bio), psychothera ...
... biopsychosocial perspective to adequately evaluate the patient. The patient's personal and family history of illnesses as well as life traumas are particularly relevant. The initial diagnostic impression will lead to a treatment plan addressing the need for psychotropic medication (bio), psychothera ...
Delusional Paralysis: An Unusual Variant of Cotard`s Syndrome
... nihilistic and hypochondriacal type (she thought that parts of her body did not function well, feared to be buried alive, and was at times not sure whether she was still living or not), accompanied by ideas of guilt and agitated depression. Characteristically, the syndrome had been of sudden onset, ...
... nihilistic and hypochondriacal type (she thought that parts of her body did not function well, feared to be buried alive, and was at times not sure whether she was still living or not), accompanied by ideas of guilt and agitated depression. Characteristically, the syndrome had been of sudden onset, ...
The DSM5: Classification and criteria changes
... consideration of possible evidence of racial, ethnic, or gender bias in diagnostic criteria; the emergence of new data about gender or cultural differences, like discrepancies in prevalence or symptom presentations; and the presence of gaps in the literature signaling the need for field trial testin ...
... consideration of possible evidence of racial, ethnic, or gender bias in diagnostic criteria; the emergence of new data about gender or cultural differences, like discrepancies in prevalence or symptom presentations; and the presence of gaps in the literature signaling the need for field trial testin ...
Guideline Document - Medicaidmentalhealth.org
... It is reported that one in five children has a diagnosable mental health problem, and that nearly two-thirds get little help or treatment. The consequences of children not receiving timely mental health care are far-reaching and include school failure, involvement in the criminal justice system, and ...
... It is reported that one in five children has a diagnosable mental health problem, and that nearly two-thirds get little help or treatment. The consequences of children not receiving timely mental health care are far-reaching and include school failure, involvement in the criminal justice system, and ...
Quality-of-Life Impairment in Depressive and Anxiety Disorders
... and major depressive disorder (11). No studies have assessed quality of life across a broad range of mood and anxiety disorders with the same standardized instrument. What factors are associated with relatively better or worse quality of life for people suffering from mood and anxiety disorders? For ...
... and major depressive disorder (11). No studies have assessed quality of life across a broad range of mood and anxiety disorders with the same standardized instrument. What factors are associated with relatively better or worse quality of life for people suffering from mood and anxiety disorders? For ...
Somatoform disorders in general practice Prevalence, functional
... fatigue, headache or gastrointestinal symptoms) that cause clinically significant distress or impairment for at least 6 months. The prevalence of current anxiety disorders was 5.5% and of current depressive disorders was 4.1%. When the new DSM–IV criterion of moderate to severe clinical impairment w ...
... fatigue, headache or gastrointestinal symptoms) that cause clinically significant distress or impairment for at least 6 months. The prevalence of current anxiety disorders was 5.5% and of current depressive disorders was 4.1%. When the new DSM–IV criterion of moderate to severe clinical impairment w ...
Emotional Disorders
... • Ten million U.S. citizens suffer from depression each year. • 5 of every 100 teenagers suffer its most severe form. DEPRESSION can be difficult to diagnose. ...
... • Ten million U.S. citizens suffer from depression each year. • 5 of every 100 teenagers suffer its most severe form. DEPRESSION can be difficult to diagnose. ...
Management of panic disorder in primary care
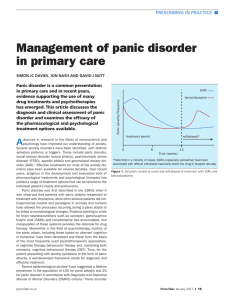
... Risk factors and clinical course Patients frequently have a family history of panic disorder or other anxiety and mood disorders. Epidemiological studies suggest a significant genetic contribution,8 although the specific genes implicated have not yet been identified. It is more common in females tha ...
... Risk factors and clinical course Patients frequently have a family history of panic disorder or other anxiety and mood disorders. Epidemiological studies suggest a significant genetic contribution,8 although the specific genes implicated have not yet been identified. It is more common in females tha ...
Conversion Disorder in Childhood
... rarely in childhood (Robins and O’Neal, 1953). Approximately one percent of females have this disorder; it occurs rarely in men. Family members of patients may have antisocial personality disorder as well as somatization disorder (Brasic, 1978; Goodwin and Guze, 1996). Somatization disorder in women ...
... rarely in childhood (Robins and O’Neal, 1953). Approximately one percent of females have this disorder; it occurs rarely in men. Family members of patients may have antisocial personality disorder as well as somatization disorder (Brasic, 1978; Goodwin and Guze, 1996). Somatization disorder in women ...
At Issue: Hierarchical Diagnosis in Chronic
... these phenomena that we are aware of. Several studies of psychosis with comorbid anxiety disorders included schizophrenia spectrum patients in their samples and so are included in table 1 (Garvey et al. 1991; Strakowski et al. 1993; Cassano et al. 1998). However, these studies defined the schizophre ...
... these phenomena that we are aware of. Several studies of psychosis with comorbid anxiety disorders included schizophrenia spectrum patients in their samples and so are included in table 1 (Garvey et al. 1991; Strakowski et al. 1993; Cassano et al. 1998). However, these studies defined the schizophre ...
Neuropsychological Assessment of Effort and Motivation
... symptoms represent a “final common endpoint” of many overlapping diagnoses and disorders Poor understanding of mechanisms of brain processing, injury, and recovery Poor understanding of base rates of symptoms among “normal” individuals ...
... symptoms represent a “final common endpoint” of many overlapping diagnoses and disorders Poor understanding of mechanisms of brain processing, injury, and recovery Poor understanding of base rates of symptoms among “normal” individuals ...
rajiv gandhi university of health sciences
... Is unusual reluctant to take personal risk or to engage in any new activities because they may prove embarrassing. ...
... Is unusual reluctant to take personal risk or to engage in any new activities because they may prove embarrassing. ...
Definitions and Diagnosis of Schizophrenia
... • D: Schizoaffective and depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features have been ruled out because either: 1. No major depressive or manic episodes have occurred concurrently with the active-phase symptoms 2. If mood episodes have occurred during active-phase symptoms, they have been presen ...
... • D: Schizoaffective and depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features have been ruled out because either: 1. No major depressive or manic episodes have occurred concurrently with the active-phase symptoms 2. If mood episodes have occurred during active-phase symptoms, they have been presen ...
Intellectual Disability and Psychiatric Disorders
... Finally, assessments must also assume that limitations in individuals often coexist with strengths, and that a person’s level of life functioning will improve if appropriate personalized supports are provided over a sustained period. Psychiatric (Mental) Disorder Definition (Diagnostic and Statisti ...
... Finally, assessments must also assume that limitations in individuals often coexist with strengths, and that a person’s level of life functioning will improve if appropriate personalized supports are provided over a sustained period. Psychiatric (Mental) Disorder Definition (Diagnostic and Statisti ...