Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Juvenile Mood
... Untreated MDD may affect social, emotional, cognitive, and interpersonal skills and the attachment bond between parent and child Juveniles with MDD are at higher risk for substance abuse, physical illness, poor academic functioning Protracted, chronic course in ~10% of cases. ...
... Untreated MDD may affect social, emotional, cognitive, and interpersonal skills and the attachment bond between parent and child Juveniles with MDD are at higher risk for substance abuse, physical illness, poor academic functioning Protracted, chronic course in ~10% of cases. ...
melatonin Mood disorders
... Mood Disorders • Major Depressive Disorder: severe form of lowered mood in which a person experiences feelings of worthlessness and diminished pleasure or interest in many activities. -spend at least two weeks feeling sad, anxious, fatigued, and agitated. -cannot be attributed to loss of a loved ...
... Mood Disorders • Major Depressive Disorder: severe form of lowered mood in which a person experiences feelings of worthlessness and diminished pleasure or interest in many activities. -spend at least two weeks feeling sad, anxious, fatigued, and agitated. -cannot be attributed to loss of a loved ...
Mood Disorders - Texas Christian University
... No manic or hypomanic episode ( hypomanic episode is an episode of increased energy that are not sufficiently severe to classify as full blown mania) Major Depressive Disorder most often follows a course of repeated episodes through life ...
... No manic or hypomanic episode ( hypomanic episode is an episode of increased energy that are not sufficiently severe to classify as full blown mania) Major Depressive Disorder most often follows a course of repeated episodes through life ...
The Practical Management of Depression
... Weygandt “Uber die Mischzustande des manisch-depressiven Irreseins” (Munchen, 1899) ...
... Weygandt “Uber die Mischzustande des manisch-depressiven Irreseins” (Munchen, 1899) ...
Depression - Faculty of Homeopathy
... Can be useful in grief . Lack of concentration , thinking of lost person May escape into alcohol or drugs . Keynote - lack of interest in the present . ...
... Can be useful in grief . Lack of concentration , thinking of lost person May escape into alcohol or drugs . Keynote - lack of interest in the present . ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... Major Depressive Disorder Depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). ...
... Major Depressive Disorder Depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). ...
2._Mood_Disorders
... causes should be done including full blood count, drug screening , hormonal essays including thyroid function tests, EEG, CT scan and if necessary other neuroimaging techniques. ...
... causes should be done including full blood count, drug screening , hormonal essays including thyroid function tests, EEG, CT scan and if necessary other neuroimaging techniques. ...
An Update On Depressive Disorders
... state with concurrent additional symptoms (i.e. a diagnosable syndrome) 2. distinguish whether there is a diagnosis that is either subsyndromal or syndromal in duration and intensity ...
... state with concurrent additional symptoms (i.e. a diagnosable syndrome) 2. distinguish whether there is a diagnosis that is either subsyndromal or syndromal in duration and intensity ...
Anxiety and Mood Disorders
... Symptoms include: sadness feelings of worthlessness changes in sleep changes in eating anhedonia suicidal behavior ...
... Symptoms include: sadness feelings of worthlessness changes in sleep changes in eating anhedonia suicidal behavior ...
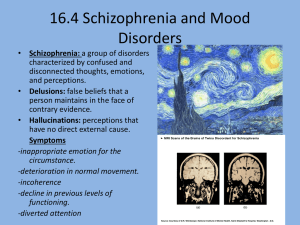
Mood Disorders
... depressed they are (Evans et al., 2005). Cognitive triad- depressed recall more negative events than positive ones, select pessimistic statements, rate their behaviour in labs as poor (Ridout et al., 2003). Errors in logic: female subjects asked to read and interpret paragraphs about women in di ...
... depressed they are (Evans et al., 2005). Cognitive triad- depressed recall more negative events than positive ones, select pessimistic statements, rate their behaviour in labs as poor (Ridout et al., 2003). Errors in logic: female subjects asked to read and interpret paragraphs about women in di ...
People with Mental Illness in Disaster Shelters
... Disorganized Behavior Abnormal Emotions Social Withdrawal Cognitive Problems: Concentration, Attention, Problem Solving, Abstraction, Motivation ...
... Disorganized Behavior Abnormal Emotions Social Withdrawal Cognitive Problems: Concentration, Attention, Problem Solving, Abstraction, Motivation ...
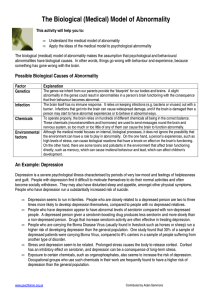
The Biological (Medical) Model of Abnormality
... high levels of stress, can cause biological reactions that have a knock-on effect on the brain’s functioning. On the other hand, there are some toxins and pollutants in the environment that affect brain functioning directly, such as mercury, which can cause irrational behaviour and lead, which can a ...
... high levels of stress, can cause biological reactions that have a knock-on effect on the brain’s functioning. On the other hand, there are some toxins and pollutants in the environment that affect brain functioning directly, such as mercury, which can cause irrational behaviour and lead, which can a ...
Mental illness in the public eye
... believes he has a voodoo spell on him( Someone from Haiti believing the same may not be deluded) 3 Organic The symptoms are due to a degenerative brain disorder (Dementias, Huntingdon’s disease) or a ‘Medical’ condition (eg urinary infection causing delirium)- confusion /amnesia 4 Personality Disord ...
... believes he has a voodoo spell on him( Someone from Haiti believing the same may not be deluded) 3 Organic The symptoms are due to a degenerative brain disorder (Dementias, Huntingdon’s disease) or a ‘Medical’ condition (eg urinary infection causing delirium)- confusion /amnesia 4 Personality Disord ...
Mood Disorders
... Also known as “Affective Disorders” It affects a person's everyday emotional state. Nearly one in ten people aged 18 and older have/have had a mood disorder ...
... Also known as “Affective Disorders” It affects a person's everyday emotional state. Nearly one in ten people aged 18 and older have/have had a mood disorder ...
Chapter 7 Mood Disorders
... • 2 Fundamental states: Depression & Mania • Depression: “The Low” – Major Depressive Episode ...
... • 2 Fundamental states: Depression & Mania • Depression: “The Low” – Major Depressive Episode ...
Mood Disorders
... • Emotional—sadness, hopelessness, guilt, turning away from others • Behavioral—tearfulness, dejected facial expression, loss of interest in normal activities, slowed movements and gestures, withdrawal from social activities • Cognitive—difficulty thinking and concentrating, global negativity, preoc ...
... • Emotional—sadness, hopelessness, guilt, turning away from others • Behavioral—tearfulness, dejected facial expression, loss of interest in normal activities, slowed movements and gestures, withdrawal from social activities • Cognitive—difficulty thinking and concentrating, global negativity, preoc ...
Depression Fact Sheet
... The main symptom of depression is a sad, despairing mood that: • is present most days and lasts most of the day • lasts for more than two weeks • impairs the person’s performance at work, at school or in social relationships. Other symptoms of depression may include: • changes in appetite and weight ...
... The main symptom of depression is a sad, despairing mood that: • is present most days and lasts most of the day • lasts for more than two weeks • impairs the person’s performance at work, at school or in social relationships. Other symptoms of depression may include: • changes in appetite and weight ...
Evidence-Based Psychiatry: An Introduction
... “The conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients…involving the integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values.1 Emphasis on patient preferences and values 1Sackett, DL (2000): Often kn ...
... “The conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients…involving the integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values.1 Emphasis on patient preferences and values 1Sackett, DL (2000): Often kn ...
Cognitive Behavior Therapy for Depression and Anxiety
... • Major Depressive Disorder is a clinical diagnosis • No diagnostic blood test or brain scan • Insight needed for optimal self-report • Optimal assessment involves skilled clinical assessment and information from an outside informant ...
... • Major Depressive Disorder is a clinical diagnosis • No diagnostic blood test or brain scan • Insight needed for optimal self-report • Optimal assessment involves skilled clinical assessment and information from an outside informant ...
Mental Health Issues
... Anxiety becomes a problem when it interferes with life in the absence of a real threat or after danger has passed. Anxiety disorders affect about 40 million (18%) American adults age 18 years and older in a given year. ◦ Women are 60% more likely than men to experience an anxiety disorder over their ...
... Anxiety becomes a problem when it interferes with life in the absence of a real threat or after danger has passed. Anxiety disorders affect about 40 million (18%) American adults age 18 years and older in a given year. ◦ Women are 60% more likely than men to experience an anxiety disorder over their ...
Mood Disorders/ Reflection Paper - Jay
... time. Happy or sad is a good example of a person’s mood, though in a clinical setting a mental health professional will use the term mood in a different way. The term mood is used to describe a continuous emotional state of mind that will affect how a person looks and the world and how that person c ...
... time. Happy or sad is a good example of a person’s mood, though in a clinical setting a mental health professional will use the term mood in a different way. The term mood is used to describe a continuous emotional state of mind that will affect how a person looks and the world and how that person c ...
Alternatives to Antidepressants
... more ineffective, giving the illusion of improved drug efficacy. • Most antidepressant trials rarely last more than 8 weeks, long term efficacy and safety have never been established. ...
... more ineffective, giving the illusion of improved drug efficacy. • Most antidepressant trials rarely last more than 8 weeks, long term efficacy and safety have never been established. ...
Anxiety Fact Sheet
... breakdown or financial difficulties. In other situations, the person may have an inherent tendency towards depression. Genetic factors can be key in the case of bipolar disorder, another type of mood disorder which involves periods of depression as well as periods of elation, where the mood is signific ...
... breakdown or financial difficulties. In other situations, the person may have an inherent tendency towards depression. Genetic factors can be key in the case of bipolar disorder, another type of mood disorder which involves periods of depression as well as periods of elation, where the mood is signific ...
Major depressive disorder

Major depressive disorder (MDD) (also known as clinical depression, major depression, unipolar depression, or unipolar disorder; or as recurrent depression in the case of repeated episodes) is a mental disorder characterized by a pervasive and persistent low mood that is accompanied by low self-esteem and by a loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. The term ""depression"" is used in a number of different ways. It is often used to mean this syndrome but may refer to other mood disorders or simply to a low mood. Major depressive disorder is a disabling condition that adversely affects a person's family, work or school life, sleeping and eating habits, and general health. In the United States, around 3.4% of people with major depression commit suicide, and up to 60% of people who commit suicide had depression or another mood disorder.The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the patient's self-reported experiences, behavior reported by relatives or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for major depression, although physicians generally request tests for physical conditions that may cause similar symptoms. The most common time of onset is between the ages of 20 and 30 years, with a later peak between 30 and 40 years.Typically, people are treated with antidepressant medication and, in many cases, also receive counseling, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). Medication appears to be effective, but the effect may only be significant in the most severely depressed. Hospitalization may be necessary in cases with associated self-neglect or a significant risk of harm to self or others. A minority are treated with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). The course of the disorder varies widely, from one episode lasting weeks to a lifelong disorder with recurrent major depressive episodes. Depressed individuals have shorter life expectancies than those without depression, in part because of greater susceptibility to medical illnesses and suicide. It is unclear whether medications affect the risk of suicide. Current and former patients may be stigmatized.The understanding of the nature and causes of depression has evolved over the centuries, though this understanding is incomplete and has left many aspects of depression as the subject of discussion and research. Proposed causes include psychological, psycho-social, hereditary, evolutionary and biological factors. Long-term substance abuse may cause or worsen depressive symptoms. Psychological treatments are based on theories of personality, interpersonal communication, and learning. Most biological theories focus on the monoamine chemicals serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine, which are naturally present in the brain and assist communication between nerve cells. This cluster of symptoms (syndrome) was named, described and classified as one of the mood disorders in the 1980 edition of the American Psychiatric Association's diagnostic manual.