I. Innate vs. Learned Behavior
... B. Learned Behavior – also called acquired behavior; behavior that changes as a result of experience. Develop over time. 4 major types: habituation, classical conditioning, operant conditioning, insight learning 1. Habituation – process by which an animal decreases or stops its response to a repetit ...
... B. Learned Behavior – also called acquired behavior; behavior that changes as a result of experience. Develop over time. 4 major types: habituation, classical conditioning, operant conditioning, insight learning 1. Habituation – process by which an animal decreases or stops its response to a repetit ...
PSY 402
... Bolles taught a rat 4 responses (right/left, up/down levers), then punished one of them. ...
... Bolles taught a rat 4 responses (right/left, up/down levers), then punished one of them. ...
Chapter 5 - Behavior Therapy
... Primary motivation for humans is survival Behavior enables humans to get things that facilitate survival ...
... Primary motivation for humans is survival Behavior enables humans to get things that facilitate survival ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... 2) Imprinting = behavior that is learned during a specific developmental time-frame (called the Critical Period) Ex. Ducklings follow the first moving object they see after birth (Konrad Lorenz) Ex. Birds learn how to perform species-specific mating signals 3) Associative Learning = a change in ...
... 2) Imprinting = behavior that is learned during a specific developmental time-frame (called the Critical Period) Ex. Ducklings follow the first moving object they see after birth (Konrad Lorenz) Ex. Birds learn how to perform species-specific mating signals 3) Associative Learning = a change in ...
Document
... sequence of four stages can be identified. The stages are: Sensori-motor stage (birth - 18mths) Developing operations (18mths – 7yrs) Concrete operations (7 – 12yrs) Formal operations (12 – adulthood) Vygotsky believed that children benefit from play because it allows them to engage in activ ...
... sequence of four stages can be identified. The stages are: Sensori-motor stage (birth - 18mths) Developing operations (18mths – 7yrs) Concrete operations (7 – 12yrs) Formal operations (12 – adulthood) Vygotsky believed that children benefit from play because it allows them to engage in activ ...
ch 51 notes
... cranes as a means to teach the birds a migration route. A pilot wearing a crane suit in an ultra light plane acts as a surrogate parent. Crane handlers wear special suits to prevent the cranes from imprinting on humans ...
... cranes as a means to teach the birds a migration route. A pilot wearing a crane suit in an ultra light plane acts as a surrogate parent. Crane handlers wear special suits to prevent the cranes from imprinting on humans ...
Theoretical Perspectives
... Studies children’s cognitive development. Studies how we attend, perceive, think, remember, solve problems and arrive at beliefs. ...
... Studies children’s cognitive development. Studies how we attend, perceive, think, remember, solve problems and arrive at beliefs. ...
Ch. 3 Power point
... gender, ready to mate and even that other is not a threat 2. Ex. Peacock males feather display 3. Result of natural selection refining courtship rituals to improve reprod. ...
... gender, ready to mate and even that other is not a threat 2. Ex. Peacock males feather display 3. Result of natural selection refining courtship rituals to improve reprod. ...
Learning and Memory PP
... Encoding: the conversion of incoming information into a form that can be stored in memory. Storage: maintaining information in memory over a period of time. Retrieval: the process of searching for stored information and bringing it to mind. ...
... Encoding: the conversion of incoming information into a form that can be stored in memory. Storage: maintaining information in memory over a period of time. Retrieval: the process of searching for stored information and bringing it to mind. ...
Document
... - Sought to understand how animals learn to act - Built “conditioning chamber” – identified principal of reinforcement - Advised the society incentivise healthy living and good will using this principal ...
... - Sought to understand how animals learn to act - Built “conditioning chamber” – identified principal of reinforcement - Advised the society incentivise healthy living and good will using this principal ...
What is Development
... What implications do these theories have for your teaching your future students? How does the information processing theory help you to understand the learning process in which students engage during class? ...
... What implications do these theories have for your teaching your future students? How does the information processing theory help you to understand the learning process in which students engage during class? ...
Animal Behavior
... • Different species have heightened senses which are used for communication. – Visual – Auditory – Tactile ...
... • Different species have heightened senses which are used for communication. – Visual – Auditory – Tactile ...
The Process of Science: Studying Animal Behavior
... c. Operant conditioning (trial and error learning) = animal learns to associate a positive or negative effect with one of its own acts 1.)will purposely repeat for reward/ purposely avoid for punishment 2.) Ex. Coyote and porcupine 3.) Often reinforces behaviors for survival 4.) Common in predator-p ...
... c. Operant conditioning (trial and error learning) = animal learns to associate a positive or negative effect with one of its own acts 1.)will purposely repeat for reward/ purposely avoid for punishment 2.) Ex. Coyote and porcupine 3.) Often reinforces behaviors for survival 4.) Common in predator-p ...
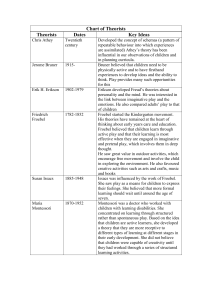
Educational theorists
... However, Freud found that some events and desires were often too frightening or painful for his patients to acknowledge. Freud believed such information was locked away in a region he called the unconscious mind. This happens through the process of repression. Sigmund Freud emphasized the importance ...
... However, Freud found that some events and desires were often too frightening or painful for his patients to acknowledge. Freud believed such information was locked away in a region he called the unconscious mind. This happens through the process of repression. Sigmund Freud emphasized the importance ...
Chapter 1
... attractive babies are held, cuddled, and kissed more Attractive Children have more friends are seen by teachers as being smarter are disciplined less often Adolescence attractive teens have more dates Attractive Adults receive higher interview scores receive higher performance appraisa ...
... attractive babies are held, cuddled, and kissed more Attractive Children have more friends are seen by teachers as being smarter are disciplined less often Adolescence attractive teens have more dates Attractive Adults receive higher interview scores receive higher performance appraisa ...
File
... Instinctual Behavior: an inborn patter of behavior in a specific species in response to an environmental stimulus; reflex Innate Behavior: something instinctual but that doesn’t need experience to perfect Habituation: decrease in response to a stimuli after having experienced it numerous times Opera ...
... Instinctual Behavior: an inborn patter of behavior in a specific species in response to an environmental stimulus; reflex Innate Behavior: something instinctual but that doesn’t need experience to perfect Habituation: decrease in response to a stimuli after having experienced it numerous times Opera ...
Animal Behavior 09
... 2) Classical conditioning - making a mental connection between a stimulus & reward or punishment – Pavlov’s dog ...
... 2) Classical conditioning - making a mental connection between a stimulus & reward or punishment – Pavlov’s dog ...
Psychology Review Sheet
... Ch 7 and Ch 14: Learning and Personality Mr. Inderbitzin Chapter 7 Conditioning Classical Conditioning Pavlov and his wondrous dogs UCS UCR CS CR Neutral Know the steps it takes to get classical conditioning Emotional Conditioning John Watson Little Albert Stimulus Generalization Stimulus Extinction ...
... Ch 7 and Ch 14: Learning and Personality Mr. Inderbitzin Chapter 7 Conditioning Classical Conditioning Pavlov and his wondrous dogs UCS UCR CS CR Neutral Know the steps it takes to get classical conditioning Emotional Conditioning John Watson Little Albert Stimulus Generalization Stimulus Extinction ...
Behavior handout
... Animal Behavior • Action or re-action to stimuli • Happens in the brain (non-motor) and can be manifested through muscular response, but often involves both • There can be a temporal component to the actual behavior (learning) • Short-term trigger for behavior, or effect on the organism • Long-term ...
... Animal Behavior • Action or re-action to stimuli • Happens in the brain (non-motor) and can be manifested through muscular response, but often involves both • There can be a temporal component to the actual behavior (learning) • Short-term trigger for behavior, or effect on the organism • Long-term ...
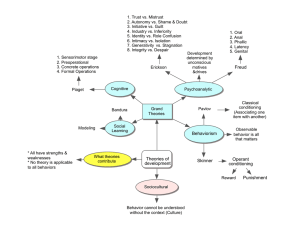
02Theories of development
... 1. Trust vs. Mistrust 2. Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt 3. Initiative vs. Guilt 4. Industry vs. Inferiority 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation 8. Integrity vs. Despair 1. Sensorimotor stage 2. Preoperational 3. Concrete operations 4. Formal Operations ...
... 1. Trust vs. Mistrust 2. Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt 3. Initiative vs. Guilt 4. Industry vs. Inferiority 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation 8. Integrity vs. Despair 1. Sensorimotor stage 2. Preoperational 3. Concrete operations 4. Formal Operations ...
Introduction to Behaviorism Introduction Basic Assumptions of
... Learning is documented by observable behavior change. ...
... Learning is documented by observable behavior change. ...
Observational learning

Observational learning is learning that occurs through observing the behavior of others. It is a form of social learning which takes various forms, based on various processes. In humans, this form of learning seems not need reinforcement to occur, but instead, requires a social model such as a parent, sibling, friend, or teacher. Particularly in childhood, a model is someone of authority or higher status. In animals, observational learning is often based on classical conditioning, in which an instinctive behavior is elicited by observing the behavior of another (e.g. mobbing in birds), but other processes may be involved as well.