Chapter 3 Practice Test with Answers
... Operant conditioning is a form of conditioning also called trial-and-error learning. Insight is the ability to respond appropriately to a new situation without previous experience. Imprinting is learning that is limited to a specific time period in an animal’s life and that is usually irreversible _ ...
... Operant conditioning is a form of conditioning also called trial-and-error learning. Insight is the ability to respond appropriately to a new situation without previous experience. Imprinting is learning that is limited to a specific time period in an animal’s life and that is usually irreversible _ ...
Personality Theories Trait Theory
... Describe individual differences and explain why they are important in understanding organizational behavior. ...
... Describe individual differences and explain why they are important in understanding organizational behavior. ...
Behavior can be learned
... The following questions are considered when analyzing animal behavior: • What is the stimulus that elicits the behavior and what is the physiological mechanism of the response? (proximate cause) • How do animal’s experiences influence the response? (proximate cause) • How does the behavior aid survi ...
... The following questions are considered when analyzing animal behavior: • What is the stimulus that elicits the behavior and what is the physiological mechanism of the response? (proximate cause) • How do animal’s experiences influence the response? (proximate cause) • How does the behavior aid survi ...
Chapter 35: Animal Behavior
... • Many instinctive behaviors consist of actions that always continue in a certain order once they have begun ...
... • Many instinctive behaviors consist of actions that always continue in a certain order once they have begun ...
Animal Behavior
... Cognition: the ability of an animals nervous system to perceive, store, process, and use information gathered by sensory receptors. Cognitive maps: internal representation of the spatial relationship of object in their surroundings Cognitive maps have been studied in animals that migrate. The three ...
... Cognition: the ability of an animals nervous system to perceive, store, process, and use information gathered by sensory receptors. Cognitive maps: internal representation of the spatial relationship of object in their surroundings Cognitive maps have been studied in animals that migrate. The three ...
(Personality and Learning)
... They are: Repression- pushing thoughts out of conscious awareness. Denial- not accepting the truth. (Biff waits at the locker for Muffy) Displacement- redirecting feelings toward another person/object. (Ex. Father yells at kids after a bad day at work). Projection- believing thoughts you have about ...
... They are: Repression- pushing thoughts out of conscious awareness. Denial- not accepting the truth. (Biff waits at the locker for Muffy) Displacement- redirecting feelings toward another person/object. (Ex. Father yells at kids after a bad day at work). Projection- believing thoughts you have about ...
Behavioral Biology: Ethology
... provide the only feature in which there is no continuum between humans and other animals. • No other species comes close to matching the social learning and cultural transmission that occurs ...
... provide the only feature in which there is no continuum between humans and other animals. • No other species comes close to matching the social learning and cultural transmission that occurs ...
Adult Learning Theory
... Orientation to learning aspects: this provided me with the understating that adults can be utilized in the production of learning experiences by integration them into resources for learning. Often times, people do not utilize this reservoir of experiences and talents. At the same time, relating lear ...
... Orientation to learning aspects: this provided me with the understating that adults can be utilized in the production of learning experiences by integration them into resources for learning. Often times, people do not utilize this reservoir of experiences and talents. At the same time, relating lear ...
Behavior - Roslyn School
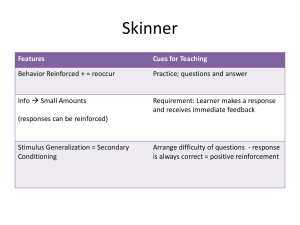
... behavioral pattern that the experimenter would like to see repeated, the animal is rewarded which results in the organisms repeating this behavior more often – how dogs are trained – can teach rats in cages to depress a lever to release food discovered by B.F. Skinner ...
... behavioral pattern that the experimenter would like to see repeated, the animal is rewarded which results in the organisms repeating this behavior more often – how dogs are trained – can teach rats in cages to depress a lever to release food discovered by B.F. Skinner ...
CABIG-ppt
... • Expose learner to variety of stimulus (e.g. Something they feared of or unsolicited exercise). • Let them do an observation. • Then, accompany them with pleasing words. ...
... • Expose learner to variety of stimulus (e.g. Something they feared of or unsolicited exercise). • Let them do an observation. • Then, accompany them with pleasing words. ...
Chapter 29
... produce a particular RESPONSE, usually through an association with a POSITIVE or NEGATIVE experience. ...
... produce a particular RESPONSE, usually through an association with a POSITIVE or NEGATIVE experience. ...
LEARNER CENTERED APPROACH
... Principle 7: Motivational and emotional influences on learning What and how much is learned is influenced by the learner's motivation. Motivation to learn, in turn, is influenced by the individual's emotional states, beliefs, interests and goals, and habits of thinking. Principle 8: Intrinsic motiva ...
... Principle 7: Motivational and emotional influences on learning What and how much is learned is influenced by the learner's motivation. Motivation to learn, in turn, is influenced by the individual's emotional states, beliefs, interests and goals, and habits of thinking. Principle 8: Intrinsic motiva ...
Inherited and Learned Behaviors
... Learned and Inherited • Some behaviors animals have are a combination of learned and inherited traits. • Examples: Young cheetahs have the instinct to hunt, but at first do not know how to sneak up on their prey. They learn how to do that by watching their mother when she hunts. Wolves have the ins ...
... Learned and Inherited • Some behaviors animals have are a combination of learned and inherited traits. • Examples: Young cheetahs have the instinct to hunt, but at first do not know how to sneak up on their prey. They learn how to do that by watching their mother when she hunts. Wolves have the ins ...
Animal Behavior
... genes. Therefore, helping a relative survive increases the chance that the genes an individual shares with that relative will be passed along to offspring. ...
... genes. Therefore, helping a relative survive increases the chance that the genes an individual shares with that relative will be passed along to offspring. ...
Motivation - Studies
... believe you can accomplish something you will work harder to accomplish it) • Causes: – Enactive mastery experience (past performance) – Vicarious experience (modeling) – Persuasion (feedback) ...
... believe you can accomplish something you will work harder to accomplish it) • Causes: – Enactive mastery experience (past performance) – Vicarious experience (modeling) – Persuasion (feedback) ...
Animal Behavior
... • If a bird goes deaf after he makes a song memory but before he is mature enough to sing…he is out of luck ...
... • If a bird goes deaf after he makes a song memory but before he is mature enough to sing…he is out of luck ...
Behavior - Cloudfront.net
... 5. Describe the examples of behavioral ecology (songbirds, foraging behavior). • Behavioral ecology a field of study that assumes animals increase fitness through optimal behavior • Optimal behavior a behavior that maximizes individual fitness (natural ...
... 5. Describe the examples of behavioral ecology (songbirds, foraging behavior). • Behavioral ecology a field of study that assumes animals increase fitness through optimal behavior • Optimal behavior a behavior that maximizes individual fitness (natural ...
Psy 120 Human Development
... • http://www.youtube.com/watch?feat ure=endscreen&v=ikTxfIDYx6Q&N R=1 • Not exactly, but cute. • This is more like it. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8 ZXOp5PopIA&feature=related ...
... • http://www.youtube.com/watch?feat ure=endscreen&v=ikTxfIDYx6Q&N R=1 • Not exactly, but cute. • This is more like it. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8 ZXOp5PopIA&feature=related ...
ppt - Language Log
... Examples: size, symmetry, ornamentation • may be environmentally adaptive or not • “runaway sexual selection” ...
... Examples: size, symmetry, ornamentation • may be environmentally adaptive or not • “runaway sexual selection” ...
Chapter 03
... reasoning a more complex form of cognitive learning where conclusions are reached by connected thought reference group a group of people that influences an individual’s attitude or behaviour rote learning the learning of two or more concepts without conditioning ...
... reasoning a more complex form of cognitive learning where conclusions are reached by connected thought reference group a group of people that influences an individual’s attitude or behaviour rote learning the learning of two or more concepts without conditioning ...
CD ch1-2 - Fairfield Public Schools
... because of positive and negative reinforcement (reward and punishment) ...
... because of positive and negative reinforcement (reward and punishment) ...
Observational learning

Observational learning is learning that occurs through observing the behavior of others. It is a form of social learning which takes various forms, based on various processes. In humans, this form of learning seems not need reinforcement to occur, but instead, requires a social model such as a parent, sibling, friend, or teacher. Particularly in childhood, a model is someone of authority or higher status. In animals, observational learning is often based on classical conditioning, in which an instinctive behavior is elicited by observing the behavior of another (e.g. mobbing in birds), but other processes may be involved as well.